Mechanical Engineering Exam > Mechanical Engineering Questions > Which one of the following is extensive prope...
Start Learning for Free
Which one of the following is extensive property of a thermodynamics system
- a)Volume
- b)Pressure
- c)Temperature
- d)Density
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Which one of the following is extensive property of a thermodynamics s...
Intensive Property: These are the properties of system which are independent of mass under consideration. For e.g. Pressure, Temperature, density
Extensive Properties: The properties which depend on the mass of system under consideration.
For e.g Internal Energy, Enthalpy, Volume, Entropy
Note: All specific properties are intensive properties. For e.g. specific volume, specific entropy etc.
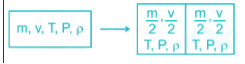
Since volume depends on mass hence it is extensive property.
Most Upvoted Answer
Which one of the following is extensive property of a thermodynamics s...
Intensive Property: These are the properties of system which are independent of mass under consideration. For e.g. Pressure, Temperature, density
Extensive Properties: The properties which depend on the mass of system under consideration.
For e.g Internal Energy, Enthalpy, Volume, Entropy
Note: All specific properties are intensive properties. For e.g. specific volume, specific entropy etc.
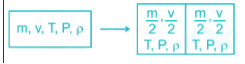
Since volume depends on mass hence it is extensive property.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Which one of the following is extensive property of a thermodynamics s...
Extensive Property of a Thermodynamics System: Volume
Introduction:
In thermodynamics, properties of a system can be categorized as intensive or extensive. Intensive properties are independent of the system size or mass, while extensive properties depend on the size or mass of the system. In this context, we will discuss the extensive property of volume.
Definition and Explanation of Volume:
Volume is defined as the amount of space occupied by a substance or system. It is a measure of the three-dimensional extent of a system. In thermodynamics, volume is denoted by the symbol "V" and is commonly measured in cubic meters (m³) or liters (L).
Why Volume is an Extensive Property:
Volume is considered an extensive property because it depends on the size or mass of the system. If we take two identical systems and combine them, the total volume of the combined system will be the sum of the volumes of the individual systems. This additive property of volume makes it extensive.
Example:
Let's consider two identical containers, each filled with 1 liter of water. If we combine these two containers, the total volume of the combined system will be 2 liters. This example illustrates the additive nature of volume, and how it depends on the size or mass of the system.
Mathematical Representation:
Mathematically, if we have a system with mass "m" and volume "V", the volume of the combined system can be represented as:
V_total = V_1 + V_2 + ... + V_n
where V_total is the total volume and V_1, V_2, ..., V_n are the volumes of the individual components.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, volume is an extensive property of a thermodynamics system. It depends on the size or mass of the system and exhibits an additive behavior. This property is widely used in thermodynamic calculations and analysis.
Introduction:
In thermodynamics, properties of a system can be categorized as intensive or extensive. Intensive properties are independent of the system size or mass, while extensive properties depend on the size or mass of the system. In this context, we will discuss the extensive property of volume.
Definition and Explanation of Volume:
Volume is defined as the amount of space occupied by a substance or system. It is a measure of the three-dimensional extent of a system. In thermodynamics, volume is denoted by the symbol "V" and is commonly measured in cubic meters (m³) or liters (L).
Why Volume is an Extensive Property:
Volume is considered an extensive property because it depends on the size or mass of the system. If we take two identical systems and combine them, the total volume of the combined system will be the sum of the volumes of the individual systems. This additive property of volume makes it extensive.
Example:
Let's consider two identical containers, each filled with 1 liter of water. If we combine these two containers, the total volume of the combined system will be 2 liters. This example illustrates the additive nature of volume, and how it depends on the size or mass of the system.
Mathematical Representation:
Mathematically, if we have a system with mass "m" and volume "V", the volume of the combined system can be represented as:
V_total = V_1 + V_2 + ... + V_n
where V_total is the total volume and V_1, V_2, ..., V_n are the volumes of the individual components.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, volume is an extensive property of a thermodynamics system. It depends on the size or mass of the system and exhibits an additive behavior. This property is widely used in thermodynamic calculations and analysis.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Question Description
Which one of the following is extensive property of a thermodynamics systema)Volumeb)Pressurec)Temperatured)DensityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about Which one of the following is extensive property of a thermodynamics systema)Volumeb)Pressurec)Temperatured)DensityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which one of the following is extensive property of a thermodynamics systema)Volumeb)Pressurec)Temperatured)DensityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Which one of the following is extensive property of a thermodynamics systema)Volumeb)Pressurec)Temperatured)DensityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about Which one of the following is extensive property of a thermodynamics systema)Volumeb)Pressurec)Temperatured)DensityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which one of the following is extensive property of a thermodynamics systema)Volumeb)Pressurec)Temperatured)DensityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Which one of the following is extensive property of a thermodynamics systema)Volumeb)Pressurec)Temperatured)DensityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Mechanical Engineering.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Which one of the following is extensive property of a thermodynamics systema)Volumeb)Pressurec)Temperatured)DensityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Which one of the following is extensive property of a thermodynamics systema)Volumeb)Pressurec)Temperatured)DensityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Which one of the following is extensive property of a thermodynamics systema)Volumeb)Pressurec)Temperatured)DensityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Which one of the following is extensive property of a thermodynamics systema)Volumeb)Pressurec)Temperatured)DensityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Which one of the following is extensive property of a thermodynamics systema)Volumeb)Pressurec)Temperatured)DensityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Mechanical Engineering tests.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















