IIT JAM Exam > IIT JAM Questions > Which of the following is true about the suga...
Start Learning for Free
Which of the following is true about the sugar puckering in B DNA
- a)C-2 endo
- b)C-3 endo
- c)C-2 exo
- d)C-3 exo
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Which of the following is true about the sugar puckering in B DNAa)C-2...
Endo puckering is the displacement of a specific carbon atom towards the oxygen atom, while exo puckering is displacement away from oxygen atom. In case of B-DNA (naturally occurring form), it is C-2 endo puckering.
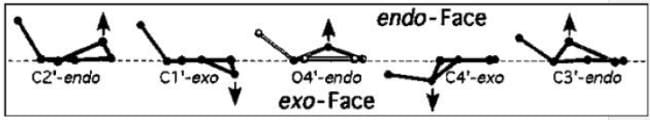
In an endo form, sugars have carbon atoms puckered above the plane (on the side as the base) while in an exo form, the carbon atoms are puckered below this plane (on opposite side of base). C3’ endo pucker is prevalent in RNA and A-form DNA, whereas the C2’ endo pucker is characteristic of B-form DNA (C2’ endo pucker has the C2’ carbon pointed up and towards the base and in C3’ endo pucker, C3’-carbon pointed up and towards the base). The two conformations affects the overall conformation of DNA in the way that they specify different phosphate-phosphate distances along each strand (~7 Å for C2’-endo and ~6 Å for C3’-endo).
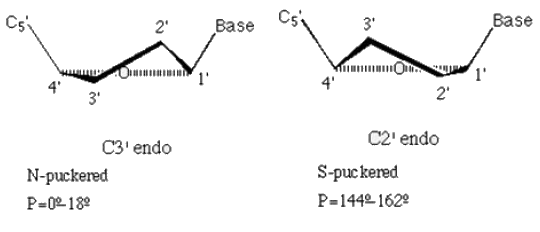

In an endo form, sugars have carbon atoms puckered above the plane (on the side as the base) while in an exo form, the carbon atoms are puckered below this plane (on opposite side of base). C3’ endo pucker is prevalent in RNA and A-form DNA, whereas the C2’ endo pucker is characteristic of B-form DNA (C2’ endo pucker has the C2’ carbon pointed up and towards the base and in C3’ endo pucker, C3’-carbon pointed up and towards the base). The two conformations affects the overall conformation of DNA in the way that they specify different phosphate-phosphate distances along each strand (~7 Å for C2’-endo and ~6 Å for C3’-endo).

Most Upvoted Answer
Which of the following is true about the sugar puckering in B DNAa)C-2...
Sugar Puckering in B DNA
The sugar puckering in B DNA refers to the conformational changes that occur in the deoxyribose sugar molecule of the DNA backbone. The term "puckering" describes the distortion of the sugar ring from its ideal planar conformation. In B DNA, the sugar puckering occurs primarily at the C2' carbon atom.
Explanation:
The sugar puckering in B DNA is a result of the presence of a deoxyribose sugar molecule in the DNA backbone. The deoxyribose sugar has five carbon atoms, labeled C1' to C5', with the nitrogenous base attached to the C1' carbon atom.
In B DNA, the sugar puckering predominantly occurs at the C2' carbon atom. The sugar ring can adopt two different conformations at the C2' carbon:
1. C2' endo: In the C2' endo conformation, the C2' carbon atom is displaced towards the nitrogenous base. This conformation results in the sugar ring being slightly folded towards the nitrogenous base.
2. C2' exo: In the C2' exo conformation, the C2' carbon atom is displaced away from the nitrogenous base. This conformation results in the sugar ring being slightly unfolded away from the nitrogenous base.
Correct Answer:
The correct answer to the question is option 'A' - C-2 endo. This means that in B DNA, the sugar puckering occurs at the C2' carbon atom and the conformation of the sugar ring is C2' endo, where the C2' carbon is displaced towards the nitrogenous base.
Conclusion:
In B DNA, the sugar puckering primarily occurs at the C2' carbon atom, and the conformation of the sugar ring is C2' endo. This conformation is significant as it affects the overall structure and stability of the DNA molecule. Understanding the sugar puckering in DNA is crucial in studying DNA structure and its interactions with other molecules.
The sugar puckering in B DNA refers to the conformational changes that occur in the deoxyribose sugar molecule of the DNA backbone. The term "puckering" describes the distortion of the sugar ring from its ideal planar conformation. In B DNA, the sugar puckering occurs primarily at the C2' carbon atom.
Explanation:
The sugar puckering in B DNA is a result of the presence of a deoxyribose sugar molecule in the DNA backbone. The deoxyribose sugar has five carbon atoms, labeled C1' to C5', with the nitrogenous base attached to the C1' carbon atom.
In B DNA, the sugar puckering predominantly occurs at the C2' carbon atom. The sugar ring can adopt two different conformations at the C2' carbon:
1. C2' endo: In the C2' endo conformation, the C2' carbon atom is displaced towards the nitrogenous base. This conformation results in the sugar ring being slightly folded towards the nitrogenous base.
2. C2' exo: In the C2' exo conformation, the C2' carbon atom is displaced away from the nitrogenous base. This conformation results in the sugar ring being slightly unfolded away from the nitrogenous base.
Correct Answer:
The correct answer to the question is option 'A' - C-2 endo. This means that in B DNA, the sugar puckering occurs at the C2' carbon atom and the conformation of the sugar ring is C2' endo, where the C2' carbon is displaced towards the nitrogenous base.
Conclusion:
In B DNA, the sugar puckering primarily occurs at the C2' carbon atom, and the conformation of the sugar ring is C2' endo. This conformation is significant as it affects the overall structure and stability of the DNA molecule. Understanding the sugar puckering in DNA is crucial in studying DNA structure and its interactions with other molecules.

|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Similar IIT JAM Doubts
Which of the following is true about the sugar puckering in B DNAa)C-2 endob)C-3 endoc)C-2 exod)C-3 exoCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Which of the following is true about the sugar puckering in B DNAa)C-2 endob)C-3 endoc)C-2 exod)C-3 exoCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for IIT JAM 2024 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following is true about the sugar puckering in B DNAa)C-2 endob)C-3 endoc)C-2 exod)C-3 exoCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following is true about the sugar puckering in B DNAa)C-2 endob)C-3 endoc)C-2 exod)C-3 exoCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Which of the following is true about the sugar puckering in B DNAa)C-2 endob)C-3 endoc)C-2 exod)C-3 exoCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for IIT JAM 2024 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following is true about the sugar puckering in B DNAa)C-2 endob)C-3 endoc)C-2 exod)C-3 exoCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following is true about the sugar puckering in B DNAa)C-2 endob)C-3 endoc)C-2 exod)C-3 exoCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Which of the following is true about the sugar puckering in B DNAa)C-2 endob)C-3 endoc)C-2 exod)C-3 exoCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for IIT JAM.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for IIT JAM Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Which of the following is true about the sugar puckering in B DNAa)C-2 endob)C-3 endoc)C-2 exod)C-3 exoCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Which of the following is true about the sugar puckering in B DNAa)C-2 endob)C-3 endoc)C-2 exod)C-3 exoCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Which of the following is true about the sugar puckering in B DNAa)C-2 endob)C-3 endoc)C-2 exod)C-3 exoCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Which of the following is true about the sugar puckering in B DNAa)C-2 endob)C-3 endoc)C-2 exod)C-3 exoCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Which of the following is true about the sugar puckering in B DNAa)C-2 endob)C-3 endoc)C-2 exod)C-3 exoCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice IIT JAM tests.

|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















