Mechanical Engineering Exam > Mechanical Engineering Questions > Eutectic product in Fe-C system is calleda)pe...
Start Learning for Free
Eutectic product in Fe-C system is called
- a)pearlite
- b)bainite
- c)ledeburite
- d)spheroidite
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Eutectic product in Fe-C system is calleda)pearliteb)bainitec)ledeburi...
A eutectic reaction occurs at 1146°C
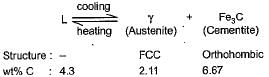
On cooling through the eutectic temperature, the lowest melting liquid of the system decomposes to solid phases, austenite and cementite. This eutectic mixture is knonw as ledeburite.

On cooling through the eutectic temperature, the lowest melting liquid of the system decomposes to solid phases, austenite and cementite. This eutectic mixture is knonw as ledeburite.
Most Upvoted Answer
Eutectic product in Fe-C system is calleda)pearliteb)bainitec)ledeburi...
Eutectic product in Fe-C system is called Ledeburite.
Ledeburite is a eutectic mixture of austenite and cementite formed in the Fe-C system. It is a two-phase structure formed at a eutectic composition of 4.3% carbon and 1400°C. The structure consists of alternating layers of austenite and cementite that form a lamellar pattern.
Formation of Ledeburite:
When the Fe-C alloy is heated to a temperature above its eutectic point, the liquid phase begins to solidify. The first solid to form is primarily austenite, which has a carbon content of 2.11%. As cooling continues, the austenite becomes richer in carbon and eventually reaches the eutectic composition of 4.3% carbon. At this point, the remaining liquid solidifies into a mixture of austenite and cementite, known as ledeburite.
Properties of Ledeburite:
- It is a two-phase structure consisting of alternating layers of austenite and cementite.
- It has a lamellar pattern.
- It is brittle and has poor mechanical properties.
- It is not useful for most engineering applications.
Applications of Ledeburite:
Ledeburite is not useful for most engineering applications due to its poor mechanical properties. However, it is an important structure in the study of iron-carbon alloys and is used to understand the formation of other microstructures such as pearlite, bainite, and martensite.
Ledeburite is a eutectic mixture of austenite and cementite formed in the Fe-C system. It is a two-phase structure formed at a eutectic composition of 4.3% carbon and 1400°C. The structure consists of alternating layers of austenite and cementite that form a lamellar pattern.
Formation of Ledeburite:
When the Fe-C alloy is heated to a temperature above its eutectic point, the liquid phase begins to solidify. The first solid to form is primarily austenite, which has a carbon content of 2.11%. As cooling continues, the austenite becomes richer in carbon and eventually reaches the eutectic composition of 4.3% carbon. At this point, the remaining liquid solidifies into a mixture of austenite and cementite, known as ledeburite.
Properties of Ledeburite:
- It is a two-phase structure consisting of alternating layers of austenite and cementite.
- It has a lamellar pattern.
- It is brittle and has poor mechanical properties.
- It is not useful for most engineering applications.
Applications of Ledeburite:
Ledeburite is not useful for most engineering applications due to its poor mechanical properties. However, it is an important structure in the study of iron-carbon alloys and is used to understand the formation of other microstructures such as pearlite, bainite, and martensite.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Question Description
Eutectic product in Fe-C system is calleda)pearliteb)bainitec)ledeburited)spheroiditeCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about Eutectic product in Fe-C system is calleda)pearliteb)bainitec)ledeburited)spheroiditeCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Eutectic product in Fe-C system is calleda)pearliteb)bainitec)ledeburited)spheroiditeCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Eutectic product in Fe-C system is calleda)pearliteb)bainitec)ledeburited)spheroiditeCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about Eutectic product in Fe-C system is calleda)pearliteb)bainitec)ledeburited)spheroiditeCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Eutectic product in Fe-C system is calleda)pearliteb)bainitec)ledeburited)spheroiditeCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Eutectic product in Fe-C system is calleda)pearliteb)bainitec)ledeburited)spheroiditeCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Mechanical Engineering.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Eutectic product in Fe-C system is calleda)pearliteb)bainitec)ledeburited)spheroiditeCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Eutectic product in Fe-C system is calleda)pearliteb)bainitec)ledeburited)spheroiditeCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Eutectic product in Fe-C system is calleda)pearliteb)bainitec)ledeburited)spheroiditeCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Eutectic product in Fe-C system is calleda)pearliteb)bainitec)ledeburited)spheroiditeCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Eutectic product in Fe-C system is calleda)pearliteb)bainitec)ledeburited)spheroiditeCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Mechanical Engineering tests.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















