Mechanical Engineering Exam > Mechanical Engineering Questions > Value of Wahl stress factor K for springs wit...
Start Learning for Free
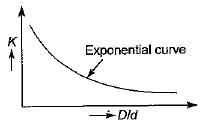
Value of Wahl stress factor K for springs with increase in value of C
- a)decrease linearly
- b)remains constant
- c)decreases exponentially
- d)increases linearly
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Value of Wahl stress factor K for springs with increase in value of Ca...
Most Upvoted Answer
Value of Wahl stress factor K for springs with increase in value of Ca...
The Wahl stress factor K is a parameter used to account for the effect of residual stress on the fatigue life of a spring. It is a dimensionless factor that is typically determined experimentally.
When the value of the Wahl stress factor K is increased, it means that the residual stress in the spring is also increased. This can occur due to factors such as the manufacturing process or the operating conditions of the spring. The effect of the Wahl stress factor K on the fatigue life of the spring depends on the specific material and design of the spring.
Explanation:
The value of the Wahl stress factor K can affect the fatigue life of a spring in different ways. The correct answer is option C, which states that the value of K decreases exponentially with an increase in the value of Ca.
1. Residual Stress and Wahl Stress Factor K:
- Residual stress refers to the stress that remains in a material after the original cause of the stress is removed.
- The Wahl stress factor K is defined as the ratio of the maximum residual stress to the yield strength of the material.
- A higher value of K indicates a higher level of residual stress in the spring.
2. Effect of Residual Stress on Fatigue Life:
- Residual stress can have a significant influence on the fatigue life of a spring.
- High levels of residual stress can lead to premature failure of the spring due to the initiation and propagation of cracks.
- The presence of residual stress can reduce the actual stress range experienced by the spring during operation, leading to a longer fatigue life.
- However, if the residual stress exceeds a certain threshold, it can have a detrimental effect on the fatigue life.
3. Relationship between Wahl Stress Factor K and Ca:
- The value of Ca represents the stress amplitude of the spring.
- As the value of Ca increases, the stress range experienced by the spring also increases.
- The Wahl stress factor K is inversely proportional to the stress range, i.e., as Ca increases, K decreases.
- This relationship can be expressed as an exponential decay function.
Conclusion:
In summary, the value of the Wahl stress factor K for springs decreases exponentially with an increase in the value of Ca. This indicates that as the stress range experienced by the spring increases, the level of residual stress decreases. Understanding the relationship between K and Ca is essential for predicting the fatigue life of springs and designing them to withstand the desired operating conditions.
When the value of the Wahl stress factor K is increased, it means that the residual stress in the spring is also increased. This can occur due to factors such as the manufacturing process or the operating conditions of the spring. The effect of the Wahl stress factor K on the fatigue life of the spring depends on the specific material and design of the spring.
Explanation:
The value of the Wahl stress factor K can affect the fatigue life of a spring in different ways. The correct answer is option C, which states that the value of K decreases exponentially with an increase in the value of Ca.
1. Residual Stress and Wahl Stress Factor K:
- Residual stress refers to the stress that remains in a material after the original cause of the stress is removed.
- The Wahl stress factor K is defined as the ratio of the maximum residual stress to the yield strength of the material.
- A higher value of K indicates a higher level of residual stress in the spring.
2. Effect of Residual Stress on Fatigue Life:
- Residual stress can have a significant influence on the fatigue life of a spring.
- High levels of residual stress can lead to premature failure of the spring due to the initiation and propagation of cracks.
- The presence of residual stress can reduce the actual stress range experienced by the spring during operation, leading to a longer fatigue life.
- However, if the residual stress exceeds a certain threshold, it can have a detrimental effect on the fatigue life.
3. Relationship between Wahl Stress Factor K and Ca:
- The value of Ca represents the stress amplitude of the spring.
- As the value of Ca increases, the stress range experienced by the spring also increases.
- The Wahl stress factor K is inversely proportional to the stress range, i.e., as Ca increases, K decreases.
- This relationship can be expressed as an exponential decay function.
Conclusion:
In summary, the value of the Wahl stress factor K for springs decreases exponentially with an increase in the value of Ca. This indicates that as the stress range experienced by the spring increases, the level of residual stress decreases. Understanding the relationship between K and Ca is essential for predicting the fatigue life of springs and designing them to withstand the desired operating conditions.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Similar Mechanical Engineering Doubts
Value of Wahl stress factor K for springs with increase in value of Ca)decrease linearlyb)remains constantc)decreases exponentiallyd)increases linearlyCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Value of Wahl stress factor K for springs with increase in value of Ca)decrease linearlyb)remains constantc)decreases exponentiallyd)increases linearlyCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about Value of Wahl stress factor K for springs with increase in value of Ca)decrease linearlyb)remains constantc)decreases exponentiallyd)increases linearlyCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Value of Wahl stress factor K for springs with increase in value of Ca)decrease linearlyb)remains constantc)decreases exponentiallyd)increases linearlyCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Value of Wahl stress factor K for springs with increase in value of Ca)decrease linearlyb)remains constantc)decreases exponentiallyd)increases linearlyCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about Value of Wahl stress factor K for springs with increase in value of Ca)decrease linearlyb)remains constantc)decreases exponentiallyd)increases linearlyCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Value of Wahl stress factor K for springs with increase in value of Ca)decrease linearlyb)remains constantc)decreases exponentiallyd)increases linearlyCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Value of Wahl stress factor K for springs with increase in value of Ca)decrease linearlyb)remains constantc)decreases exponentiallyd)increases linearlyCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Mechanical Engineering.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Value of Wahl stress factor K for springs with increase in value of Ca)decrease linearlyb)remains constantc)decreases exponentiallyd)increases linearlyCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Value of Wahl stress factor K for springs with increase in value of Ca)decrease linearlyb)remains constantc)decreases exponentiallyd)increases linearlyCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Value of Wahl stress factor K for springs with increase in value of Ca)decrease linearlyb)remains constantc)decreases exponentiallyd)increases linearlyCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Value of Wahl stress factor K for springs with increase in value of Ca)decrease linearlyb)remains constantc)decreases exponentiallyd)increases linearlyCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Value of Wahl stress factor K for springs with increase in value of Ca)decrease linearlyb)remains constantc)decreases exponentiallyd)increases linearlyCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Mechanical Engineering tests.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























