Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > The single-phase half-bridge inverter has a r...
Start Learning for Free
The single-phase half-bridge inverter has a resistive load of 10Ω and the centre-tap dc input voltage is 96 V. The fundamental power consumed by the load is
- a)628.6 Watt
- b)525.0Watt'
- c)746.5 Watt
- d)824.4 Watt
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
The single-phase half-bridge inverter has a resistive load of 10&Omega...
The nth harmonic-component of output voltage is
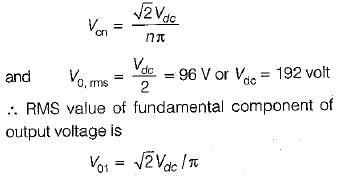
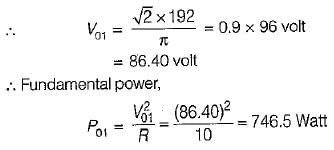
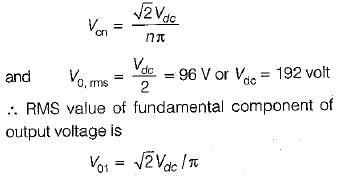
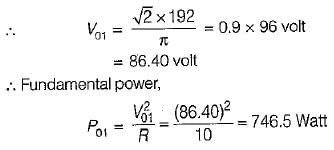
Most Upvoted Answer
The single-phase half-bridge inverter has a resistive load of 10&Omega...
A single phase half bridge inverter has a resistive load of R =10 and the dc input voltage vdc = 80v determine
rms value of output voltage
output power
average peak current of each thyristor
rms value of output voltage
output power
average peak current of each thyristor
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The single-phase half-bridge inverter has a resistive load of 10&Omega...
The single-phase half-bridge inverter with a resistive load of 10 ohms operates by switching two power electronic devices, typically transistors, to alternate the direction of current flow through the load. This creates an AC output voltage waveform.
The operation of the half-bridge inverter can be divided into two modes: the positive half-cycle and the negative half-cycle.
During the positive half-cycle, one of the transistors is turned on, allowing current to flow from the DC input source through the load in one direction. The other transistor is turned off to prevent current flow in the opposite direction. This creates a positive half-cycle of the AC output voltage.
During the negative half-cycle, the state of the transistors is reversed. The previously turned-on transistor is turned off, while the previously turned-off transistor is turned on. This allows current to flow through the load in the opposite direction, creating a negative half-cycle of the AC output voltage.
By switching between these two modes at a high frequency, typically in the range of tens or hundreds of kilohertz, the half-bridge inverter can effectively generate an AC output voltage waveform.
The resistive load of 10 ohms determines the amount of current flowing through the load and thus the power dissipated. Using Ohm's Law (V = I * R), with a known load resistance of 10 ohms, the current flowing through the load can be calculated for a given output voltage.
For example, if the AC output voltage is 100 volts, the current flowing through the load would be 100 volts / 10 ohms = 10 amps. The power dissipated in the load can then be calculated using the formula P = I^2 * R, which would be 10 amps^2 * 10 ohms = 1000 watts or 1 kilowatt.
The operation of the half-bridge inverter can be divided into two modes: the positive half-cycle and the negative half-cycle.
During the positive half-cycle, one of the transistors is turned on, allowing current to flow from the DC input source through the load in one direction. The other transistor is turned off to prevent current flow in the opposite direction. This creates a positive half-cycle of the AC output voltage.
During the negative half-cycle, the state of the transistors is reversed. The previously turned-on transistor is turned off, while the previously turned-off transistor is turned on. This allows current to flow through the load in the opposite direction, creating a negative half-cycle of the AC output voltage.
By switching between these two modes at a high frequency, typically in the range of tens or hundreds of kilohertz, the half-bridge inverter can effectively generate an AC output voltage waveform.
The resistive load of 10 ohms determines the amount of current flowing through the load and thus the power dissipated. Using Ohm's Law (V = I * R), with a known load resistance of 10 ohms, the current flowing through the load can be calculated for a given output voltage.
For example, if the AC output voltage is 100 volts, the current flowing through the load would be 100 volts / 10 ohms = 10 amps. The power dissipated in the load can then be calculated using the formula P = I^2 * R, which would be 10 amps^2 * 10 ohms = 1000 watts or 1 kilowatt.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Question Description
The single-phase half-bridge inverter has a resistive load of 10Ω and the centre-tap dc input voltage is 96 V. The fundamental power consumed by the load isa)628.6 Wattb)525.0Watt'c)746.5 Wattd)824.4 WattCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about The single-phase half-bridge inverter has a resistive load of 10Ω and the centre-tap dc input voltage is 96 V. The fundamental power consumed by the load isa)628.6 Wattb)525.0Watt'c)746.5 Wattd)824.4 WattCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The single-phase half-bridge inverter has a resistive load of 10Ω and the centre-tap dc input voltage is 96 V. The fundamental power consumed by the load isa)628.6 Wattb)525.0Watt'c)746.5 Wattd)824.4 WattCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
The single-phase half-bridge inverter has a resistive load of 10Ω and the centre-tap dc input voltage is 96 V. The fundamental power consumed by the load isa)628.6 Wattb)525.0Watt'c)746.5 Wattd)824.4 WattCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about The single-phase half-bridge inverter has a resistive load of 10Ω and the centre-tap dc input voltage is 96 V. The fundamental power consumed by the load isa)628.6 Wattb)525.0Watt'c)746.5 Wattd)824.4 WattCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The single-phase half-bridge inverter has a resistive load of 10Ω and the centre-tap dc input voltage is 96 V. The fundamental power consumed by the load isa)628.6 Wattb)525.0Watt'c)746.5 Wattd)824.4 WattCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The single-phase half-bridge inverter has a resistive load of 10Ω and the centre-tap dc input voltage is 96 V. The fundamental power consumed by the load isa)628.6 Wattb)525.0Watt'c)746.5 Wattd)824.4 WattCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The single-phase half-bridge inverter has a resistive load of 10Ω and the centre-tap dc input voltage is 96 V. The fundamental power consumed by the load isa)628.6 Wattb)525.0Watt'c)746.5 Wattd)824.4 WattCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The single-phase half-bridge inverter has a resistive load of 10Ω and the centre-tap dc input voltage is 96 V. The fundamental power consumed by the load isa)628.6 Wattb)525.0Watt'c)746.5 Wattd)824.4 WattCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The single-phase half-bridge inverter has a resistive load of 10Ω and the centre-tap dc input voltage is 96 V. The fundamental power consumed by the load isa)628.6 Wattb)525.0Watt'c)746.5 Wattd)824.4 WattCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The single-phase half-bridge inverter has a resistive load of 10Ω and the centre-tap dc input voltage is 96 V. The fundamental power consumed by the load isa)628.6 Wattb)525.0Watt'c)746.5 Wattd)824.4 WattCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The single-phase half-bridge inverter has a resistive load of 10Ω and the centre-tap dc input voltage is 96 V. The fundamental power consumed by the load isa)628.6 Wattb)525.0Watt'c)746.5 Wattd)824.4 WattCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















