B Com Exam > B Com Questions > Difference between public and private sector?
Start Learning for Free
Difference between public and private sector?
Most Upvoted Answer
Difference between public and private sector?
Public Sector:
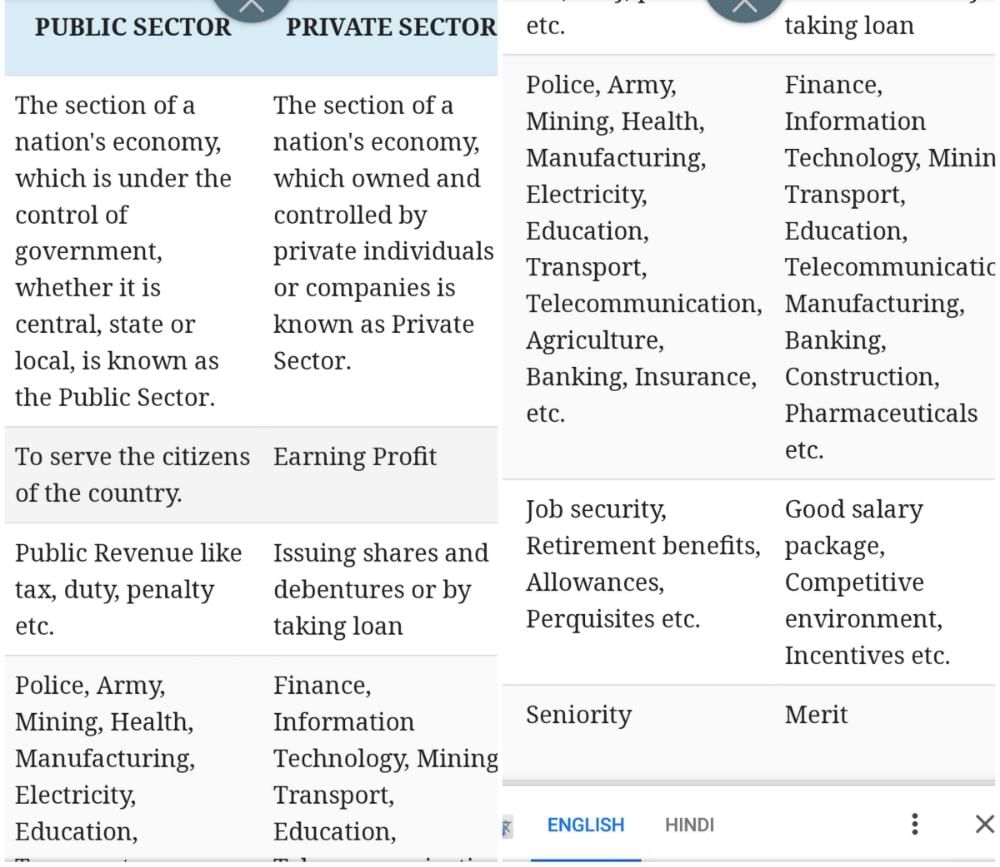
The public sector refers to the part of the economy that is owned and controlled by the government. It includes government agencies, departments, and enterprises that provide public goods and services to the citizens. Here are some key features of the public sector:
1. Ownership: The public sector is owned and controlled by the government at different levels, such as central, state, or local government bodies.
2. Objective: The primary objective of the public sector is to serve the public interest and provide essential services to the citizens, including healthcare, education, defense, infrastructure, and social welfare.
3. Funding: Public sector organizations are funded by tax revenues and government budgets. They may also generate income through user fees or charges.
4. Accountability: Public sector organizations are accountable to the government and the public. They are subject to government regulations, oversight, and scrutiny to ensure transparency and efficiency in their operations.
5. Employment: The public sector is a significant employer, offering job opportunities in various fields such as administration, healthcare, education, law enforcement, and public infrastructure.
6. Job Security: Public sector employees typically enjoy more job security compared to the private sector, as their positions are less affected by market fluctuations.
Private Sector:
The private sector refers to the part of the economy that is owned and controlled by individuals or privately-owned businesses. It operates for profit and competition in the market. Here are some key features of the private sector:
1. Ownership: The private sector is owned and controlled by individuals, partnerships, or corporations. The ownership and control of resources are in the hands of private entities.
2. Objective: The primary objective of the private sector is to generate profit and maximize shareholder wealth. Private companies operate in various industries, including manufacturing, finance, retail, technology, and services.
3. Funding: The private sector relies on private investments, loans, and capital markets for funding its operations and expansion. It may also issue shares or bonds to raise capital.
4. Accountability: Private sector organizations are accountable to their shareholders and stakeholders. They are subject to market forces, competition, and consumer demands, which influence their decision-making.
5. Employment: The private sector is a major source of employment, creating job opportunities in various sectors. Private companies hire individuals based on their skills, qualifications, and suitability for the job.
6. Job Flexibility: Private sector employees may experience more job flexibility, as private companies can adapt quickly to market changes and restructure their workforce accordingly.
In conclusion, the public sector is owned and controlled by the government, operates for the public interest, and is funded by tax revenues. On the other hand, the private sector is owned by individuals or businesses, operates for profit, and is funded by private investments. Both sectors play vital roles in the economy and society, each with its own distinct characteristics and objectives.
The public sector refers to the part of the economy that is owned and controlled by the government. It includes government agencies, departments, and enterprises that provide public goods and services to the citizens. Here are some key features of the public sector:
1. Ownership: The public sector is owned and controlled by the government at different levels, such as central, state, or local government bodies.
2. Objective: The primary objective of the public sector is to serve the public interest and provide essential services to the citizens, including healthcare, education, defense, infrastructure, and social welfare.
3. Funding: Public sector organizations are funded by tax revenues and government budgets. They may also generate income through user fees or charges.
4. Accountability: Public sector organizations are accountable to the government and the public. They are subject to government regulations, oversight, and scrutiny to ensure transparency and efficiency in their operations.
5. Employment: The public sector is a significant employer, offering job opportunities in various fields such as administration, healthcare, education, law enforcement, and public infrastructure.
6. Job Security: Public sector employees typically enjoy more job security compared to the private sector, as their positions are less affected by market fluctuations.
Private Sector:
The private sector refers to the part of the economy that is owned and controlled by individuals or privately-owned businesses. It operates for profit and competition in the market. Here are some key features of the private sector:
1. Ownership: The private sector is owned and controlled by individuals, partnerships, or corporations. The ownership and control of resources are in the hands of private entities.
2. Objective: The primary objective of the private sector is to generate profit and maximize shareholder wealth. Private companies operate in various industries, including manufacturing, finance, retail, technology, and services.
3. Funding: The private sector relies on private investments, loans, and capital markets for funding its operations and expansion. It may also issue shares or bonds to raise capital.
4. Accountability: Private sector organizations are accountable to their shareholders and stakeholders. They are subject to market forces, competition, and consumer demands, which influence their decision-making.
5. Employment: The private sector is a major source of employment, creating job opportunities in various sectors. Private companies hire individuals based on their skills, qualifications, and suitability for the job.
6. Job Flexibility: Private sector employees may experience more job flexibility, as private companies can adapt quickly to market changes and restructure their workforce accordingly.
In conclusion, the public sector is owned and controlled by the government, operates for the public interest, and is funded by tax revenues. On the other hand, the private sector is owned by individuals or businesses, operates for profit, and is funded by private investments. Both sectors play vital roles in the economy and society, each with its own distinct characteristics and objectives.
Community Answer
Difference between public and private sector?

|
Explore Courses for B Com exam
|

|
Similar B Com Doubts
Question Description
Difference between public and private sector? for B Com 2025 is part of B Com preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the B Com exam syllabus. Information about Difference between public and private sector? covers all topics & solutions for B Com 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Difference between public and private sector?.
Difference between public and private sector? for B Com 2025 is part of B Com preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the B Com exam syllabus. Information about Difference between public and private sector? covers all topics & solutions for B Com 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Difference between public and private sector?.
Solutions for Difference between public and private sector? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for B Com.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for B Com Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Difference between public and private sector? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Difference between public and private sector?, a detailed solution for Difference between public and private sector? has been provided alongside types of Difference between public and private sector? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Difference between public and private sector? tests, examples and also practice B Com tests.

|
Explore Courses for B Com exam
|

|
Signup to solve all Doubts
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.















