Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > The Muskingum method of flood routing gives Q...
Start Learning for Free
The Muskingum method of flood routing gives Q2 = C0I2 + C1I1 + C2Q1. The coefficients in this equation will have values such that
- a)C0 + C1 = C2
- b)C0 - C1 - C2 =1
- c)C0 + C1 + C2 = 0
- d)C0 + C1 + C2 = 1
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
The Muskingum method of flood routing gives Q2 = C0I2 + C1I1 + C2Q1. T...
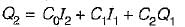
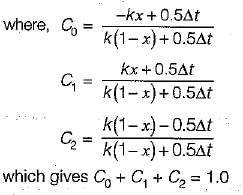
Most Upvoted Answer
The Muskingum method of flood routing gives Q2 = C0I2 + C1I1 + C2Q1. T...
Muskingum Method for Flood Routing
The Muskingum method is a hydrological technique used for flood routing in rivers and streams. It is a linear reservoir model that predicts the outflow hydrograph from an upstream river reach to a downstream river reach. The method is based on the principle of conservation of mass and the assumption that the flow in a river can be represented by a single channel with uniform characteristics.
Equation for Flood Routing
The Muskingum method of flood routing gives the following equation:
Q2 = C0I2 + C1I1 + C2Q1
where Q2 is the outflow at the downstream reach, Q1 is the inflow at the upstream reach, I1 and I2 are the inflows at the current and previous time steps, and C0, C1, and C2 are the coefficients that determine the routing characteristics.
Coefficients in the Equation
The coefficients in the Muskingum equation are determined by the channel characteristics and the routing parameters. The values of the coefficients depend on the channel geometry, roughness, and slope, as well as the time step and the length of the reach.
The coefficients have the following properties:
- C0 + C1 + C2 = 1, which ensures that the outflow is a linear combination of the inflows.
- C0, C1, and C2 are all positive and less than or equal to 0.5, which ensures stability and accuracy of the method.
- The values of the coefficients depend on the ratio of the time step to the reach length, which affects the storage and attenuation characteristics of the reach.
Conclusion
In summary, the Muskingum method is a widely used technique for flood routing in rivers and streams. The method is based on a linear reservoir model and uses the Muskingum equation to predict the outflow hydrograph at the downstream reach. The coefficients in the equation are determined by the channel characteristics and the routing parameters, and have specific properties that ensure stability and accuracy of the method.
The Muskingum method is a hydrological technique used for flood routing in rivers and streams. It is a linear reservoir model that predicts the outflow hydrograph from an upstream river reach to a downstream river reach. The method is based on the principle of conservation of mass and the assumption that the flow in a river can be represented by a single channel with uniform characteristics.
Equation for Flood Routing
The Muskingum method of flood routing gives the following equation:
Q2 = C0I2 + C1I1 + C2Q1
where Q2 is the outflow at the downstream reach, Q1 is the inflow at the upstream reach, I1 and I2 are the inflows at the current and previous time steps, and C0, C1, and C2 are the coefficients that determine the routing characteristics.
Coefficients in the Equation
The coefficients in the Muskingum equation are determined by the channel characteristics and the routing parameters. The values of the coefficients depend on the channel geometry, roughness, and slope, as well as the time step and the length of the reach.
The coefficients have the following properties:
- C0 + C1 + C2 = 1, which ensures that the outflow is a linear combination of the inflows.
- C0, C1, and C2 are all positive and less than or equal to 0.5, which ensures stability and accuracy of the method.
- The values of the coefficients depend on the ratio of the time step to the reach length, which affects the storage and attenuation characteristics of the reach.
Conclusion
In summary, the Muskingum method is a widely used technique for flood routing in rivers and streams. The method is based on a linear reservoir model and uses the Muskingum equation to predict the outflow hydrograph at the downstream reach. The coefficients in the equation are determined by the channel characteristics and the routing parameters, and have specific properties that ensure stability and accuracy of the method.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
The Muskingum method of flood routing gives Q2 = C0I2 + C1I1 + C2Q1. The coefficients in this equation will have values such thata)C0 + C1 = C2b)C0- C1 - C2 =1c)C0 + C1 + C2 = 0d)C0 + C1 + C2 = 1Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The Muskingum method of flood routing gives Q2 = C0I2 + C1I1 + C2Q1. The coefficients in this equation will have values such thata)C0 + C1 = C2b)C0- C1 - C2 =1c)C0 + C1 + C2 = 0d)C0 + C1 + C2 = 1Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about The Muskingum method of flood routing gives Q2 = C0I2 + C1I1 + C2Q1. The coefficients in this equation will have values such thata)C0 + C1 = C2b)C0- C1 - C2 =1c)C0 + C1 + C2 = 0d)C0 + C1 + C2 = 1Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The Muskingum method of flood routing gives Q2 = C0I2 + C1I1 + C2Q1. The coefficients in this equation will have values such thata)C0 + C1 = C2b)C0- C1 - C2 =1c)C0 + C1 + C2 = 0d)C0 + C1 + C2 = 1Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
The Muskingum method of flood routing gives Q2 = C0I2 + C1I1 + C2Q1. The coefficients in this equation will have values such thata)C0 + C1 = C2b)C0- C1 - C2 =1c)C0 + C1 + C2 = 0d)C0 + C1 + C2 = 1Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about The Muskingum method of flood routing gives Q2 = C0I2 + C1I1 + C2Q1. The coefficients in this equation will have values such thata)C0 + C1 = C2b)C0- C1 - C2 =1c)C0 + C1 + C2 = 0d)C0 + C1 + C2 = 1Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The Muskingum method of flood routing gives Q2 = C0I2 + C1I1 + C2Q1. The coefficients in this equation will have values such thata)C0 + C1 = C2b)C0- C1 - C2 =1c)C0 + C1 + C2 = 0d)C0 + C1 + C2 = 1Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The Muskingum method of flood routing gives Q2 = C0I2 + C1I1 + C2Q1. The coefficients in this equation will have values such thata)C0 + C1 = C2b)C0- C1 - C2 =1c)C0 + C1 + C2 = 0d)C0 + C1 + C2 = 1Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The Muskingum method of flood routing gives Q2 = C0I2 + C1I1 + C2Q1. The coefficients in this equation will have values such thata)C0 + C1 = C2b)C0- C1 - C2 =1c)C0 + C1 + C2 = 0d)C0 + C1 + C2 = 1Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The Muskingum method of flood routing gives Q2 = C0I2 + C1I1 + C2Q1. The coefficients in this equation will have values such thata)C0 + C1 = C2b)C0- C1 - C2 =1c)C0 + C1 + C2 = 0d)C0 + C1 + C2 = 1Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The Muskingum method of flood routing gives Q2 = C0I2 + C1I1 + C2Q1. The coefficients in this equation will have values such thata)C0 + C1 = C2b)C0- C1 - C2 =1c)C0 + C1 + C2 = 0d)C0 + C1 + C2 = 1Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The Muskingum method of flood routing gives Q2 = C0I2 + C1I1 + C2Q1. The coefficients in this equation will have values such thata)C0 + C1 = C2b)C0- C1 - C2 =1c)C0 + C1 + C2 = 0d)C0 + C1 + C2 = 1Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The Muskingum method of flood routing gives Q2 = C0I2 + C1I1 + C2Q1. The coefficients in this equation will have values such thata)C0 + C1 = C2b)C0- C1 - C2 =1c)C0 + C1 + C2 = 0d)C0 + C1 + C2 = 1Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























