Class 6 Exam > Class 6 Questions > parts of flower Related: NCERT Solution - Wh...
Start Learning for Free
parts of flower
?Verified Answer
parts of flower Related: NCERT Solution - Where does it Come from??
Flowers have many different shapes and sizes, and there are many variations in colour, number of flower parts and the arrangements of these parts. Though there is a great diversity of flower types, all flowers have some common structural elements.
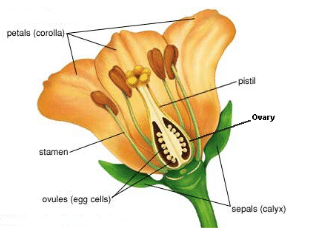
Parts of a Flower
A typical flower can be grouped into four sets based on appearance and function: sepals, petals, stamens, and pistils.
The sepals and petals are lowermost on the shoot, toward the sides of the flower. The stamens and pistils are at the tip of the shoot at the inside. While sepals and petals are easy to see, stamens and pistils are often visible only when the flower is closely examined.
Sepals
Of the four main parts, the sepals which are the outer most part of a flower are generally small leaf-like structures seen at the base of the flowers and hold the petals together. It protects the immature flower during the bud stage. Sepals are usually green. In some flowers however, they are as colourful as the petals and increase the flower's attractiveness to insects.
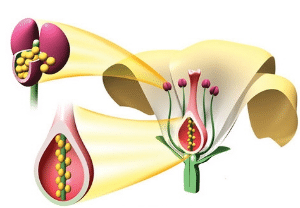
Petals

Petals
Above the sepals are the petals. Although flattened like the sepal, each petal is usually soft and coloured. Usually, the number of petals in a flower will be the same as the number of sepals. If the sepals of a flower are joined together, then its petals are separate and not joined.
Stamen
The stamens, located inside the petals, are composed of a small anther and a threadlike filament connecting the anther to the rest of the flower.
Pistil
The pistils form the final set of the parts. Each pistil is often shaped like a vase, although the shape varies. The ovary which is the base of the pistil, is swollen and hollow. The inner parts of the ovary have small bead like structures called ovules. Even If the petals of a flower are joined together, the pistil need not necessarily be joined to the petal.
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 6 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 6 courses
Most Upvoted Answer
parts of flower Related: NCERT Solution - Where does it Come from??
Parts of a Flower:
- Reproductive Parts:
- Stamen: The male reproductive part of the flower consisting of the anther and filament.
- Pistil: The female reproductive part of the flower consisting of the stigma, style, and ovary.
- Non-Reproductive Parts:
- Petal: Often colorful and fragrant, attracting pollinators to the flower.
- Sepal: Protects the flower in bud stage and supports the petals when in bloom.
- Receptacle: The tip of the stem where the flower parts are attached.
NCERT Solution - Where does it Come from??
Plants are the primary producers in the food chain, manufacturing their food through the process of photosynthesis. They require sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce glucose and oxygen. The process takes place in the chloroplasts of plant cells, specifically in the green pigment called chlorophyll.
The roots of the plant absorb water and minerals from the soil, which are then transported to the leaves through the stem. The leaves have tiny openings called stomata through which carbon dioxide enters and oxygen exits. The sunlight is absorbed by the chlorophyll, which converts it into chemical energy to produce glucose.
The glucose produced is used by the plant as a source of energy for growth and development. It is stored in different parts of the plant, such as roots, stems, leaves, and fruits. The excess glucose is converted into starch for long-term storage.
In conclusion, plants get their food through the process of photosynthesis, where they use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce glucose and oxygen. This glucose serves as a source of energy for the plant's growth and development, stored in various parts of the plant for future use.
- Reproductive Parts:
- Stamen: The male reproductive part of the flower consisting of the anther and filament.
- Pistil: The female reproductive part of the flower consisting of the stigma, style, and ovary.
- Non-Reproductive Parts:
- Petal: Often colorful and fragrant, attracting pollinators to the flower.
- Sepal: Protects the flower in bud stage and supports the petals when in bloom.
- Receptacle: The tip of the stem where the flower parts are attached.
NCERT Solution - Where does it Come from??
Plants are the primary producers in the food chain, manufacturing their food through the process of photosynthesis. They require sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce glucose and oxygen. The process takes place in the chloroplasts of plant cells, specifically in the green pigment called chlorophyll.
The roots of the plant absorb water and minerals from the soil, which are then transported to the leaves through the stem. The leaves have tiny openings called stomata through which carbon dioxide enters and oxygen exits. The sunlight is absorbed by the chlorophyll, which converts it into chemical energy to produce glucose.
The glucose produced is used by the plant as a source of energy for growth and development. It is stored in different parts of the plant, such as roots, stems, leaves, and fruits. The excess glucose is converted into starch for long-term storage.
In conclusion, plants get their food through the process of photosynthesis, where they use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to produce glucose and oxygen. This glucose serves as a source of energy for the plant's growth and development, stored in various parts of the plant for future use.
Attention Class 6 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 6 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 6.

|
Explore Courses for Class 6 exam
|

|
Similar Class 6 Doubts
parts of flower Related: NCERT Solution - Where does it Come from??
Question Description
parts of flower Related: NCERT Solution - Where does it Come from?? for Class 6 2024 is part of Class 6 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 6 exam syllabus. Information about parts of flower Related: NCERT Solution - Where does it Come from?? covers all topics & solutions for Class 6 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for parts of flower Related: NCERT Solution - Where does it Come from??.
parts of flower Related: NCERT Solution - Where does it Come from?? for Class 6 2024 is part of Class 6 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 6 exam syllabus. Information about parts of flower Related: NCERT Solution - Where does it Come from?? covers all topics & solutions for Class 6 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for parts of flower Related: NCERT Solution - Where does it Come from??.
Solutions for parts of flower Related: NCERT Solution - Where does it Come from?? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 6.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 6 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of parts of flower Related: NCERT Solution - Where does it Come from?? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
parts of flower Related: NCERT Solution - Where does it Come from??, a detailed solution for parts of flower Related: NCERT Solution - Where does it Come from?? has been provided alongside types of parts of flower Related: NCERT Solution - Where does it Come from?? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice parts of flower Related: NCERT Solution - Where does it Come from?? tests, examples and also practice Class 6 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 6 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























