Physics Exam > Physics Questions > Which of the following has bcc structure?a)Mg...
Start Learning for Free
Which of the following has bcc structure?
- a)MgO
- b)CsCI
- c)MnO
- d)NaCI
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
Which of the following has bcc structure?a)MgOb)CsCIc)MnOd)NaCICorrect...
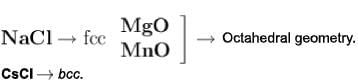
CsCl shows a body centred cubic lattice with a coordination number 8 for each ion.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Which of the following has bcc structure?a)MgOb)CsCIc)MnOd)NaCICorrect...
Explanation:
BCC structure:
The body-centered cubic (BCC) structure is a type of crystal structure in which the lattice points are located at the corners and at the center of the cube. In this structure, each atom or ion is surrounded by eight nearest neighboring atoms or ions.
Identification of BCC Structures:
To identify whether a compound has a BCC structure, we need to analyze the arrangement of atoms or ions in its crystal lattice.
Analysis of the Given Options:
a) MgO:
MgO does not have a BCC structure. It has a rock salt (NaCl) structure, which is a type of face-centered cubic (FCC) structure. In an FCC structure, the lattice points are located at the corners and at the center of each face of the cube.
b) CsCl:
CsCl (Cesium Chloride) has a BCC crystal structure. In the CsCl structure, the cesium ions are located at the corners of the cube, while the chloride ions are located at the center of the cube. This arrangement follows the body-centered cubic structure.
c) MnO:
MnO does not have a BCC structure. It has a rock salt (NaCl) structure, similar to MgO. The manganese ions are located at the corners of the cube, and the oxygen ions are located at the center of each face of the cube.
d) NaCl:
NaCl (Sodium Chloride) does not have a BCC structure. It also has a rock salt (NaCl) structure, where the sodium ions are located at the corners of the cube, and the chloride ions are located at the center of each face of the cube.
Conclusion:
Among the given options, CsCl is the only compound that has a BCC crystal structure. The other compounds (MgO, MnO, and NaCl) have different crystal structures.
BCC structure:
The body-centered cubic (BCC) structure is a type of crystal structure in which the lattice points are located at the corners and at the center of the cube. In this structure, each atom or ion is surrounded by eight nearest neighboring atoms or ions.
Identification of BCC Structures:
To identify whether a compound has a BCC structure, we need to analyze the arrangement of atoms or ions in its crystal lattice.
Analysis of the Given Options:
a) MgO:
MgO does not have a BCC structure. It has a rock salt (NaCl) structure, which is a type of face-centered cubic (FCC) structure. In an FCC structure, the lattice points are located at the corners and at the center of each face of the cube.
b) CsCl:
CsCl (Cesium Chloride) has a BCC crystal structure. In the CsCl structure, the cesium ions are located at the corners of the cube, while the chloride ions are located at the center of the cube. This arrangement follows the body-centered cubic structure.
c) MnO:
MnO does not have a BCC structure. It has a rock salt (NaCl) structure, similar to MgO. The manganese ions are located at the corners of the cube, and the oxygen ions are located at the center of each face of the cube.
d) NaCl:
NaCl (Sodium Chloride) does not have a BCC structure. It also has a rock salt (NaCl) structure, where the sodium ions are located at the corners of the cube, and the chloride ions are located at the center of each face of the cube.
Conclusion:
Among the given options, CsCl is the only compound that has a BCC crystal structure. The other compounds (MgO, MnO, and NaCl) have different crystal structures.

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Question Description
Which of the following has bcc structure?a)MgOb)CsCIc)MnOd)NaCICorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2025 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following has bcc structure?a)MgOb)CsCIc)MnOd)NaCICorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following has bcc structure?a)MgOb)CsCIc)MnOd)NaCICorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Which of the following has bcc structure?a)MgOb)CsCIc)MnOd)NaCICorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Physics 2025 is part of Physics preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Physics exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following has bcc structure?a)MgOb)CsCIc)MnOd)NaCICorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Physics 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following has bcc structure?a)MgOb)CsCIc)MnOd)NaCICorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Which of the following has bcc structure?a)MgOb)CsCIc)MnOd)NaCICorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Physics.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Physics Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Which of the following has bcc structure?a)MgOb)CsCIc)MnOd)NaCICorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Which of the following has bcc structure?a)MgOb)CsCIc)MnOd)NaCICorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Which of the following has bcc structure?a)MgOb)CsCIc)MnOd)NaCICorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Which of the following has bcc structure?a)MgOb)CsCIc)MnOd)NaCICorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Which of the following has bcc structure?a)MgOb)CsCIc)MnOd)NaCICorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Physics tests.

|
Explore Courses for Physics exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



















