Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Questions > Image formation by a convex lens: when object...
Start Learning for Free
Image formation by a convex lens: when object is at 2F?
Most Upvoted Answer
Image formation by a convex lens: when object is at 2F?
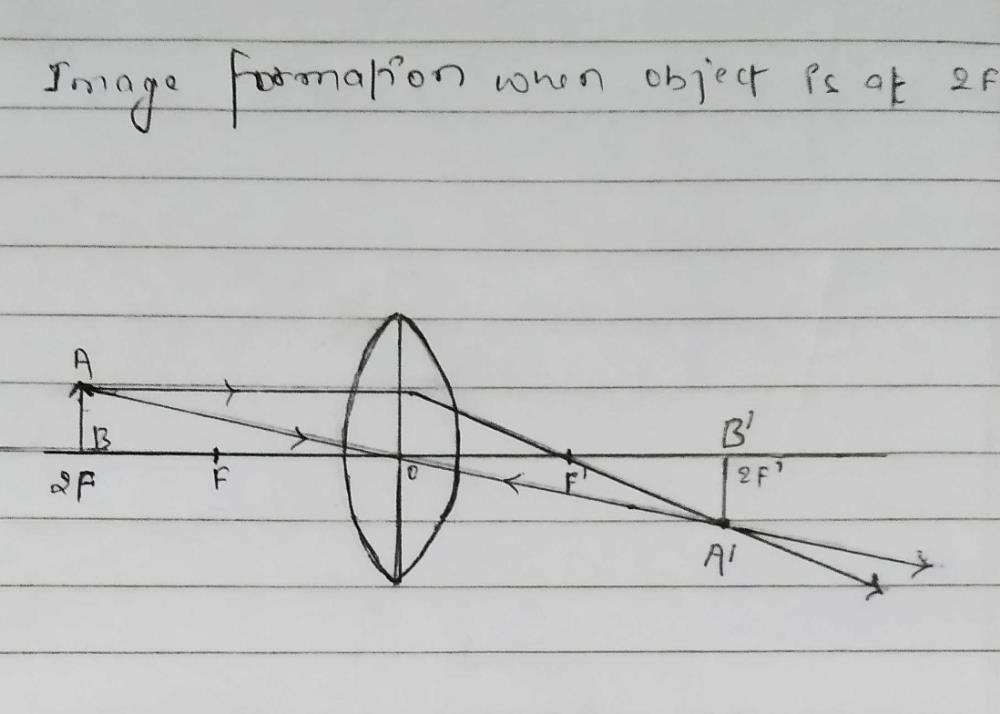
Community Answer
Image formation by a convex lens: when object is at 2F?
Image Formation by a Convex Lens when Object is at 2F
When an object is placed at twice the focal length (2F) of a convex lens, the image formed is real, inverted, and the same size as the object. This is a special case known as the "2F rule".
- Formation of Image:
- In this scenario, the light rays from the object are refracted by the convex lens and converge at a point on the opposite side of the lens.
- The image is formed beyond the 2F point on the side of the lens where the object is placed.
- Real Image:
- The image formed is real because the light rays actually converge at a point where the image is formed.
- This means that the image can be projected onto a screen and is visible.
- Inverted Image:
- The image formed is inverted, which means that the top of the object corresponds to the bottom of the image and vice versa.
- This is a characteristic of images formed by convex lenses.
- Same Size Image:
- The size of the image formed is the same as the size of the object.
- This is because the object is placed at 2F, resulting in an image that is not magnified or diminished.
In conclusion, when an object is placed at twice the focal length of a convex lens, a real, inverted, and same-sized image is formed. This rule is important in understanding the behavior of convex lenses and image formation.

|
Explore Courses for Class 8 exam
|

|
Question Description
Image formation by a convex lens: when object is at 2F? for Class 8 2025 is part of Class 8 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 8 exam syllabus. Information about Image formation by a convex lens: when object is at 2F? covers all topics & solutions for Class 8 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Image formation by a convex lens: when object is at 2F?.
Image formation by a convex lens: when object is at 2F? for Class 8 2025 is part of Class 8 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 8 exam syllabus. Information about Image formation by a convex lens: when object is at 2F? covers all topics & solutions for Class 8 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Image formation by a convex lens: when object is at 2F?.
Solutions for Image formation by a convex lens: when object is at 2F? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 8.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 8 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Image formation by a convex lens: when object is at 2F? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Image formation by a convex lens: when object is at 2F?, a detailed solution for Image formation by a convex lens: when object is at 2F? has been provided alongside types of Image formation by a convex lens: when object is at 2F? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Image formation by a convex lens: when object is at 2F? tests, examples and also practice Class 8 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 8 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























