NEET Exam > NEET Questions > DNA replication is unidirectional or bidirect...
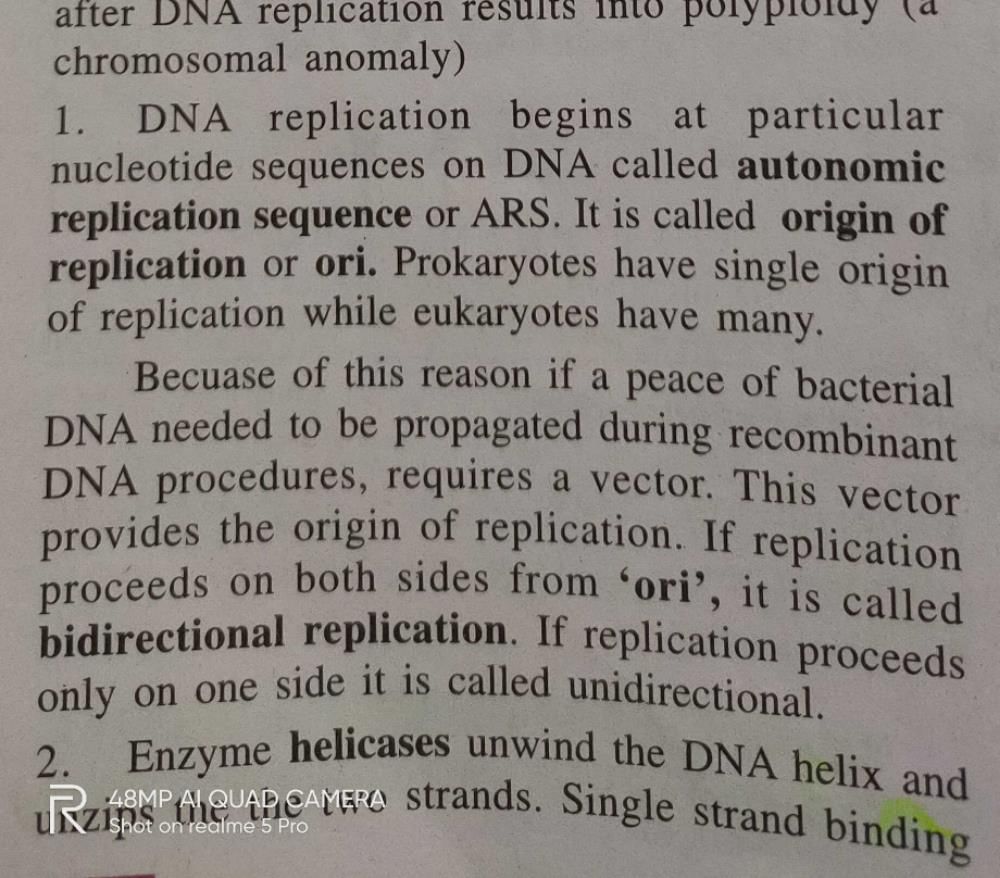
Start Learning for Free
DNA replication is unidirectional or bidirectional . If bidirectional plz give reason.?
Most Upvoted Answer
DNA replication is unidirectional or bidirectional . If bidirectional ...
Bidirectional DNA Replication
DNA replication is the process of copying genetic information from one strand of DNA to another. It is a vital process that ensures the accurate transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next. There are two types of DNA replication: unidirectional and bidirectional.
Unidirectional DNA Replication
Unidirectional DNA replication occurs when the replication fork moves in only one direction. In this process, DNA polymerase enzyme moves along the template strand of DNA in a single direction, synthesizing a new complementary strand of DNA. This type of replication is commonly observed in bacteria and viruses.
Bidirectional DNA Replication
Bidirectional DNA replication occurs when the replication fork moves in both directions. In this process, the DNA helicase enzyme unwinds the double helix structure of DNA, creating two replication forks that move in opposite directions. The DNA polymerase enzyme then moves along each template strand in the opposite direction, synthesizing new complementary strands of DNA. This type of replication is commonly observed in eukaryotic cells, including human cells.
Reasons for Bidirectional DNA Replication
There are several reasons why bidirectional DNA replication is preferred in eukaryotic cells:
1. Efficiency: Bidirectional replication is more efficient than unidirectional replication because it enables the synthesis of new DNA strands in two directions simultaneously.
2. Accuracy: Bidirectional replication ensures the accuracy of DNA replication by providing a backup mechanism in case of errors in one direction.
3. Speed: Bidirectional replication is faster than unidirectional replication because it allows for the synthesis of new DNA strands in two directions simultaneously.
4. Stability: Bidirectional replication provides more stability to the replication process by ensuring that the DNA is replicated in a consistent and uniform manner.
In conclusion, bidirectional DNA replication is preferred in eukaryotic cells because it is more efficient, accurate, fast, and stable than unidirectional replication.
DNA replication is the process of copying genetic information from one strand of DNA to another. It is a vital process that ensures the accurate transmission of genetic information from one generation to the next. There are two types of DNA replication: unidirectional and bidirectional.
Unidirectional DNA Replication
Unidirectional DNA replication occurs when the replication fork moves in only one direction. In this process, DNA polymerase enzyme moves along the template strand of DNA in a single direction, synthesizing a new complementary strand of DNA. This type of replication is commonly observed in bacteria and viruses.
Bidirectional DNA Replication
Bidirectional DNA replication occurs when the replication fork moves in both directions. In this process, the DNA helicase enzyme unwinds the double helix structure of DNA, creating two replication forks that move in opposite directions. The DNA polymerase enzyme then moves along each template strand in the opposite direction, synthesizing new complementary strands of DNA. This type of replication is commonly observed in eukaryotic cells, including human cells.
Reasons for Bidirectional DNA Replication
There are several reasons why bidirectional DNA replication is preferred in eukaryotic cells:
1. Efficiency: Bidirectional replication is more efficient than unidirectional replication because it enables the synthesis of new DNA strands in two directions simultaneously.
2. Accuracy: Bidirectional replication ensures the accuracy of DNA replication by providing a backup mechanism in case of errors in one direction.
3. Speed: Bidirectional replication is faster than unidirectional replication because it allows for the synthesis of new DNA strands in two directions simultaneously.
4. Stability: Bidirectional replication provides more stability to the replication process by ensuring that the DNA is replicated in a consistent and uniform manner.
In conclusion, bidirectional DNA replication is preferred in eukaryotic cells because it is more efficient, accurate, fast, and stable than unidirectional replication.
Community Answer
DNA replication is unidirectional or bidirectional . If bidirectional ...

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
Question Description
DNA replication is unidirectional or bidirectional . If bidirectional plz give reason.? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about DNA replication is unidirectional or bidirectional . If bidirectional plz give reason.? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for DNA replication is unidirectional or bidirectional . If bidirectional plz give reason.?.
DNA replication is unidirectional or bidirectional . If bidirectional plz give reason.? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about DNA replication is unidirectional or bidirectional . If bidirectional plz give reason.? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for DNA replication is unidirectional or bidirectional . If bidirectional plz give reason.?.
Solutions for DNA replication is unidirectional or bidirectional . If bidirectional plz give reason.? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of DNA replication is unidirectional or bidirectional . If bidirectional plz give reason.? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
DNA replication is unidirectional or bidirectional . If bidirectional plz give reason.?, a detailed solution for DNA replication is unidirectional or bidirectional . If bidirectional plz give reason.? has been provided alongside types of DNA replication is unidirectional or bidirectional . If bidirectional plz give reason.? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice DNA replication is unidirectional or bidirectional . If bidirectional plz give reason.? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup to solve all Doubts
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.





















