Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > Wheatstone bridge is used to measurea)potenti...
Start Learning for Free
Wheatstone bridge is used to measure
- a)potential
- b)emf
- c)current
- d)resistance
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
Wheatstone bridge is used to measurea)potentialb)emfc)currentd)resista...
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Wheatstone bridge is used to measurea)potentialb)emfc)currentd)resista...
Introduction to Wheatstone Bridge
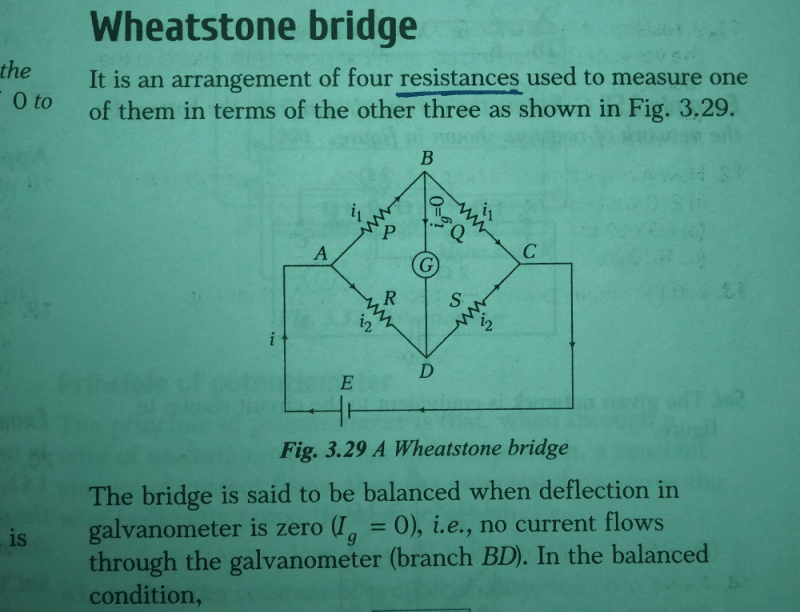
The Wheatstone bridge is a fundamental circuit used for measuring electrical resistance. It is particularly effective for determining unknown resistances by balancing two legs of a bridge circuit.
How Does the Wheatstone Bridge Work?
- The bridge consists of four resistors arranged in a diamond shape.
- Two resistors (R1 and R2) are in one leg, and two (R3 and the unknown resistor Rx) are in the other leg.
- A galvanometer is connected between the two junctions of the resistors.
Balancing the Bridge
- The bridge is balanced when no current flows through the galvanometer. This occurs when the ratio of the resistors is equal:
R1/R2 = Rx/R3
- At this point, the voltage across the galvanometer is zero, indicating that the potential difference is equal on both sides.
Calculating Resistance
- To find the value of the unknown resistor (Rx), the equation can be rearranged:
Rx = (R3 * R1) / R2
- This formula allows for precise measurement of resistance, making the Wheatstone bridge a valuable tool in laboratories and various applications.
Applications of Wheatstone Bridge
- Used in calibration of measuring instruments.
- Employed in strain gauges for measuring deformation.
- Utilized in temperature sensors.
Conclusion
In summary, the Wheatstone bridge is primarily used to measure resistance, making option 'D' the correct answer. Its design and principle of operation allow for accurate resistance measurements, which is crucial in various scientific and engineering fields.
The Wheatstone bridge is a fundamental circuit used for measuring electrical resistance. It is particularly effective for determining unknown resistances by balancing two legs of a bridge circuit.
How Does the Wheatstone Bridge Work?
- The bridge consists of four resistors arranged in a diamond shape.
- Two resistors (R1 and R2) are in one leg, and two (R3 and the unknown resistor Rx) are in the other leg.
- A galvanometer is connected between the two junctions of the resistors.
Balancing the Bridge
- The bridge is balanced when no current flows through the galvanometer. This occurs when the ratio of the resistors is equal:
R1/R2 = Rx/R3
- At this point, the voltage across the galvanometer is zero, indicating that the potential difference is equal on both sides.
Calculating Resistance
- To find the value of the unknown resistor (Rx), the equation can be rearranged:
Rx = (R3 * R1) / R2
- This formula allows for precise measurement of resistance, making the Wheatstone bridge a valuable tool in laboratories and various applications.
Applications of Wheatstone Bridge
- Used in calibration of measuring instruments.
- Employed in strain gauges for measuring deformation.
- Utilized in temperature sensors.
Conclusion
In summary, the Wheatstone bridge is primarily used to measure resistance, making option 'D' the correct answer. Its design and principle of operation allow for accurate resistance measurements, which is crucial in various scientific and engineering fields.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Question Description
Wheatstone bridge is used to measurea)potentialb)emfc)currentd)resistanceCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Wheatstone bridge is used to measurea)potentialb)emfc)currentd)resistanceCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Wheatstone bridge is used to measurea)potentialb)emfc)currentd)resistanceCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Wheatstone bridge is used to measurea)potentialb)emfc)currentd)resistanceCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Wheatstone bridge is used to measurea)potentialb)emfc)currentd)resistanceCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Wheatstone bridge is used to measurea)potentialb)emfc)currentd)resistanceCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Wheatstone bridge is used to measurea)potentialb)emfc)currentd)resistanceCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Wheatstone bridge is used to measurea)potentialb)emfc)currentd)resistanceCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Wheatstone bridge is used to measurea)potentialb)emfc)currentd)resistanceCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Wheatstone bridge is used to measurea)potentialb)emfc)currentd)resistanceCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Wheatstone bridge is used to measurea)potentialb)emfc)currentd)resistanceCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Wheatstone bridge is used to measurea)potentialb)emfc)currentd)resistanceCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



















