Defence Exam > Defence Questions > Goods and Services Tax likely to be levied in...
Start Learning for Free
Goods and Services Tax likely to be levied in India is not a
- a)Gross value tax
- b)Value-added tax
- c)Consumption tax
- d)Destination-based tax
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Goods and Services Tax likely to be levied in India is not aa)Gross va...
Most Upvoted Answer
Goods and Services Tax likely to be levied in India is not aa)Gross va...
Introduction:
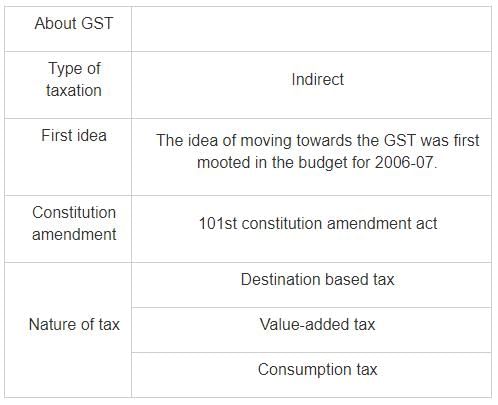
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a comprehensive indirect tax levied on the supply of goods and services in India. It is a destination-based tax system that aims to replace multiple indirect taxes levied by the central and state governments. GST has been implemented to simplify the tax structure, increase tax compliance, and promote ease of doing business in the country.
Gross Value Tax:
A gross value tax is a tax levied on the total value of a product or service without considering any deductions or exemptions. In this type of tax, the tax liability is calculated based on the gross value of the product or service, regardless of whether any value has been added to it during the production or distribution process.
Value-Added Tax (VAT):
Value-added tax (VAT) is a tax levied on the value added at each stage of the production and distribution process. It is based on the principle that tax should be levied only on the value added by each economic entity in the supply chain. VAT allows for the deduction of taxes paid on inputs and raw materials, thereby avoiding tax cascading or double taxation.
Consumption Tax:
A consumption tax is a tax levied on the consumption of goods and services. It is imposed at the point of sale or at the time of consumption. Consumption taxes are typically regressive, as they tend to impose a higher burden on low-income individuals who spend a larger proportion of their income on consumption.
Destination-Based Tax:
A destination-based tax is a tax system where the tax liability is determined based on the destination or place of consumption of goods and services. In this system, the tax is levied in the jurisdiction where the final consumer resides or where the goods or services are consumed. This ensures that the tax revenue is collected by the government of the consumer's jurisdiction.
Explanation:
The correct answer to the question is option 'A' - Gross value tax. GST in India is not a gross value tax because it does not impose tax on the total value of a product or service without considering any deductions or exemptions. Instead, GST follows the value-added tax (VAT) principle, where tax is levied only on the value added at each stage of the supply chain.
GST is a destination-based tax system, which means that the tax revenue is collected by the government of the consumer's jurisdiction. It is a consumption tax as it is levied on the consumption of goods and services. GST allows for the input tax credit, where businesses can claim credit for the taxes paid on inputs and raw materials, thereby avoiding tax cascading.
In conclusion, GST in India is a value-added tax (VAT) and a destination-based tax, but it is not a gross value tax or a consumption tax. It has been implemented to streamline the indirect tax structure and promote a simplified and unified tax system in the country.
The Goods and Services Tax (GST) is a comprehensive indirect tax levied on the supply of goods and services in India. It is a destination-based tax system that aims to replace multiple indirect taxes levied by the central and state governments. GST has been implemented to simplify the tax structure, increase tax compliance, and promote ease of doing business in the country.
Gross Value Tax:
A gross value tax is a tax levied on the total value of a product or service without considering any deductions or exemptions. In this type of tax, the tax liability is calculated based on the gross value of the product or service, regardless of whether any value has been added to it during the production or distribution process.
Value-Added Tax (VAT):
Value-added tax (VAT) is a tax levied on the value added at each stage of the production and distribution process. It is based on the principle that tax should be levied only on the value added by each economic entity in the supply chain. VAT allows for the deduction of taxes paid on inputs and raw materials, thereby avoiding tax cascading or double taxation.
Consumption Tax:
A consumption tax is a tax levied on the consumption of goods and services. It is imposed at the point of sale or at the time of consumption. Consumption taxes are typically regressive, as they tend to impose a higher burden on low-income individuals who spend a larger proportion of their income on consumption.
Destination-Based Tax:
A destination-based tax is a tax system where the tax liability is determined based on the destination or place of consumption of goods and services. In this system, the tax is levied in the jurisdiction where the final consumer resides or where the goods or services are consumed. This ensures that the tax revenue is collected by the government of the consumer's jurisdiction.
Explanation:
The correct answer to the question is option 'A' - Gross value tax. GST in India is not a gross value tax because it does not impose tax on the total value of a product or service without considering any deductions or exemptions. Instead, GST follows the value-added tax (VAT) principle, where tax is levied only on the value added at each stage of the supply chain.
GST is a destination-based tax system, which means that the tax revenue is collected by the government of the consumer's jurisdiction. It is a consumption tax as it is levied on the consumption of goods and services. GST allows for the input tax credit, where businesses can claim credit for the taxes paid on inputs and raw materials, thereby avoiding tax cascading.
In conclusion, GST in India is a value-added tax (VAT) and a destination-based tax, but it is not a gross value tax or a consumption tax. It has been implemented to streamline the indirect tax structure and promote a simplified and unified tax system in the country.

|
Explore Courses for Defence exam
|

|
Similar Defence Doubts
Goods and Services Tax likely to be levied in India is not aa)Gross value taxb)Value-added taxc)Consumption taxd)Destination-based taxCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Goods and Services Tax likely to be levied in India is not aa)Gross value taxb)Value-added taxc)Consumption taxd)Destination-based taxCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Defence 2024 is part of Defence preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Defence exam syllabus. Information about Goods and Services Tax likely to be levied in India is not aa)Gross value taxb)Value-added taxc)Consumption taxd)Destination-based taxCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Defence 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Goods and Services Tax likely to be levied in India is not aa)Gross value taxb)Value-added taxc)Consumption taxd)Destination-based taxCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Goods and Services Tax likely to be levied in India is not aa)Gross value taxb)Value-added taxc)Consumption taxd)Destination-based taxCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Defence 2024 is part of Defence preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Defence exam syllabus. Information about Goods and Services Tax likely to be levied in India is not aa)Gross value taxb)Value-added taxc)Consumption taxd)Destination-based taxCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Defence 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Goods and Services Tax likely to be levied in India is not aa)Gross value taxb)Value-added taxc)Consumption taxd)Destination-based taxCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Goods and Services Tax likely to be levied in India is not aa)Gross value taxb)Value-added taxc)Consumption taxd)Destination-based taxCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Defence.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Defence Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Goods and Services Tax likely to be levied in India is not aa)Gross value taxb)Value-added taxc)Consumption taxd)Destination-based taxCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Goods and Services Tax likely to be levied in India is not aa)Gross value taxb)Value-added taxc)Consumption taxd)Destination-based taxCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Goods and Services Tax likely to be levied in India is not aa)Gross value taxb)Value-added taxc)Consumption taxd)Destination-based taxCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Goods and Services Tax likely to be levied in India is not aa)Gross value taxb)Value-added taxc)Consumption taxd)Destination-based taxCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Goods and Services Tax likely to be levied in India is not aa)Gross value taxb)Value-added taxc)Consumption taxd)Destination-based taxCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Defence tests.

|
Explore Courses for Defence exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















