Mechanical Engineering Exam > Mechanical Engineering Questions > Heat transferred to a closed stationary syste...
Start Learning for Free
Heat transferred to a closed stationary system at constant volume is equal to
- a)increase in internal energy
- b)work transfer
- c)increase in enthalpy
- d)increase in Gibbs function
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Heat transferred to a closed stationary system at constant volume is e...
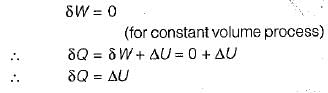
Most Upvoted Answer
Heat transferred to a closed stationary system at constant volume is e...
Heat transferred to a closed stationary system at constant volume is equal to the increase in internal energy. Let's delve into each aspect to understand why this is the correct answer.
Heat Transfer at Constant Volume:
- When heat is transferred to a system at constant volume, it means that no work is being done by the system (as it is stationary) and the volume remains constant throughout the process.
- In this scenario, the heat transferred to the system is used to increase the internal energy of the system.
Internal Energy:
- Internal energy is the sum of all the kinetic and potential energies of the molecules within a system. It includes the energy associated with the motion and interactions of the molecules.
- When heat is added to a system, the internal energy of the system increases as the molecules gain more energy and move faster.
Relationship between Heat Transfer and Internal Energy:
- The first law of thermodynamics states that the change in internal energy of a system is equal to the heat added to the system minus the work done by the system.
- In the case of a closed system at constant volume where no work is done, the heat transferred to the system is equal to the increase in internal energy.
- Therefore, when heat is transferred to a closed stationary system at constant volume, it directly leads to an increase in the internal energy of the system.
In conclusion, the heat transferred to a closed stationary system at constant volume is equal to the increase in internal energy because no work is done by the system, and the added heat is utilized to increase the internal energy of the system.
Heat Transfer at Constant Volume:
- When heat is transferred to a system at constant volume, it means that no work is being done by the system (as it is stationary) and the volume remains constant throughout the process.
- In this scenario, the heat transferred to the system is used to increase the internal energy of the system.
Internal Energy:
- Internal energy is the sum of all the kinetic and potential energies of the molecules within a system. It includes the energy associated with the motion and interactions of the molecules.
- When heat is added to a system, the internal energy of the system increases as the molecules gain more energy and move faster.
Relationship between Heat Transfer and Internal Energy:
- The first law of thermodynamics states that the change in internal energy of a system is equal to the heat added to the system minus the work done by the system.
- In the case of a closed system at constant volume where no work is done, the heat transferred to the system is equal to the increase in internal energy.
- Therefore, when heat is transferred to a closed stationary system at constant volume, it directly leads to an increase in the internal energy of the system.
In conclusion, the heat transferred to a closed stationary system at constant volume is equal to the increase in internal energy because no work is done by the system, and the added heat is utilized to increase the internal energy of the system.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Question Description
Heat transferred to a closed stationary system at constant volume is equal toa)increase in internal energyb)work transferc)increase in enthalpyd)increase in Gibbs functionCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about Heat transferred to a closed stationary system at constant volume is equal toa)increase in internal energyb)work transferc)increase in enthalpyd)increase in Gibbs functionCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Heat transferred to a closed stationary system at constant volume is equal toa)increase in internal energyb)work transferc)increase in enthalpyd)increase in Gibbs functionCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Heat transferred to a closed stationary system at constant volume is equal toa)increase in internal energyb)work transferc)increase in enthalpyd)increase in Gibbs functionCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about Heat transferred to a closed stationary system at constant volume is equal toa)increase in internal energyb)work transferc)increase in enthalpyd)increase in Gibbs functionCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Heat transferred to a closed stationary system at constant volume is equal toa)increase in internal energyb)work transferc)increase in enthalpyd)increase in Gibbs functionCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Heat transferred to a closed stationary system at constant volume is equal toa)increase in internal energyb)work transferc)increase in enthalpyd)increase in Gibbs functionCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Mechanical Engineering.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Heat transferred to a closed stationary system at constant volume is equal toa)increase in internal energyb)work transferc)increase in enthalpyd)increase in Gibbs functionCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Heat transferred to a closed stationary system at constant volume is equal toa)increase in internal energyb)work transferc)increase in enthalpyd)increase in Gibbs functionCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Heat transferred to a closed stationary system at constant volume is equal toa)increase in internal energyb)work transferc)increase in enthalpyd)increase in Gibbs functionCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Heat transferred to a closed stationary system at constant volume is equal toa)increase in internal energyb)work transferc)increase in enthalpyd)increase in Gibbs functionCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Heat transferred to a closed stationary system at constant volume is equal toa)increase in internal energyb)work transferc)increase in enthalpyd)increase in Gibbs functionCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Mechanical Engineering tests.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















