Class 7 Exam > Class 7 Questions > what is Wegener's theory of continental drif...
Start Learning for Free
what is Wegener's theory of continental drift
? Related: Major landforms of the Earth
Most Upvoted Answer
what is Wegener's theory of continental drift Related: Major landfor...
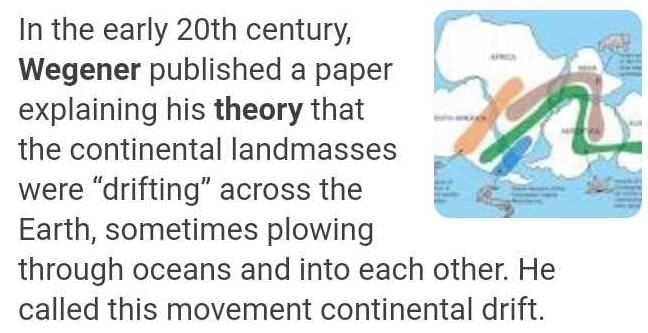
Community Answer
what is Wegener's theory of continental drift Related: Major landfor...
Wegener's Theory of Continental Drift was proposed by German meteorologist and geophysicist Alfred Wegener in the early 20th century. This theory revolutionized our understanding of the Earth's landforms and provided a key foundation for the development of plate tectonics.
The Theory
According to Wegener's theory, all the continents were once part of a single supercontinent called Pangaea, which existed about 300 million years ago. Over time, Pangaea began to break apart, and the continents drifted to their current positions.
Evidence for Continental Drift
Wegener supported his theory with several lines of evidence:
1. Puzzle-Like Fit: The coastlines of South America and Africa appear to fit together like puzzle pieces, suggesting that they were once joined.
2. Fossil Evidence: Similar fossils of plants and animals are found on different continents that are now far apart. For example, the same fossilized reptile species were discovered in South America and Africa, which implies that these continents were once connected.
3. Rock Types and Structures: Mountain ranges and geological formations on different continents align when the continents are reconstructed into Pangaea. For instance, the Appalachian Mountains in the eastern United States align with the Caledonian Mountains in Europe.
4. Gondwana: The geological history of the southern continents, including South America, Africa, India, Australia, and Antarctica, can be better explained if they were once part of a larger landmass called Gondwana.
Major Landforms and Plate Tectonics
Wegener's theory of continental drift provided crucial insights into the formation of major landforms on Earth. These landforms are closely related to the movement of tectonic plates, which are large pieces of the Earth's crust that float on the semi-fluid asthenosphere below. Some of the major landforms influenced by plate tectonics include:
1. Mountains: The collision of tectonic plates can lead to the formation of mountains. For example, the Himalayas were formed when the Indian subcontinent collided with the Eurasian Plate.
2. Volcanoes: Volcanoes are often associated with plate boundaries, where magma from the mantle rises to the surface. The Pacific Ring of Fire, a major area of volcanic activity, is located at the boundaries of several tectonic plates.
3. Earthquakes: Earthquakes occur when tectonic plates move and release built-up energy. The majority of earthquakes happen along plate boundaries.
4. Rift Valleys: Rift valleys form when tectonic plates move apart, creating a depression in the Earth's crust. The East African Rift Valley is an example of a rift valley formed due to the separation of the African Plate.
In conclusion, Wegener's Theory of Continental Drift proposed that the continents were once connected and have since moved to their present positions. This theory provided the foundation for our understanding of plate tectonics and helped explain the formation of major landforms on Earth.
The Theory
According to Wegener's theory, all the continents were once part of a single supercontinent called Pangaea, which existed about 300 million years ago. Over time, Pangaea began to break apart, and the continents drifted to their current positions.
Evidence for Continental Drift
Wegener supported his theory with several lines of evidence:
1. Puzzle-Like Fit: The coastlines of South America and Africa appear to fit together like puzzle pieces, suggesting that they were once joined.
2. Fossil Evidence: Similar fossils of plants and animals are found on different continents that are now far apart. For example, the same fossilized reptile species were discovered in South America and Africa, which implies that these continents were once connected.
3. Rock Types and Structures: Mountain ranges and geological formations on different continents align when the continents are reconstructed into Pangaea. For instance, the Appalachian Mountains in the eastern United States align with the Caledonian Mountains in Europe.
4. Gondwana: The geological history of the southern continents, including South America, Africa, India, Australia, and Antarctica, can be better explained if they were once part of a larger landmass called Gondwana.
Major Landforms and Plate Tectonics
Wegener's theory of continental drift provided crucial insights into the formation of major landforms on Earth. These landforms are closely related to the movement of tectonic plates, which are large pieces of the Earth's crust that float on the semi-fluid asthenosphere below. Some of the major landforms influenced by plate tectonics include:
1. Mountains: The collision of tectonic plates can lead to the formation of mountains. For example, the Himalayas were formed when the Indian subcontinent collided with the Eurasian Plate.
2. Volcanoes: Volcanoes are often associated with plate boundaries, where magma from the mantle rises to the surface. The Pacific Ring of Fire, a major area of volcanic activity, is located at the boundaries of several tectonic plates.
3. Earthquakes: Earthquakes occur when tectonic plates move and release built-up energy. The majority of earthquakes happen along plate boundaries.
4. Rift Valleys: Rift valleys form when tectonic plates move apart, creating a depression in the Earth's crust. The East African Rift Valley is an example of a rift valley formed due to the separation of the African Plate.
In conclusion, Wegener's Theory of Continental Drift proposed that the continents were once connected and have since moved to their present positions. This theory provided the foundation for our understanding of plate tectonics and helped explain the formation of major landforms on Earth.
Attention Class 7 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 7 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 7.

|
Explore Courses for Class 7 exam
|

|
Similar Class 7 Doubts
what is Wegener's theory of continental drift Related: Major landforms of the Earth?
Question Description
what is Wegener's theory of continental drift Related: Major landforms of the Earth? for Class 7 2024 is part of Class 7 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 7 exam syllabus. Information about what is Wegener's theory of continental drift Related: Major landforms of the Earth? covers all topics & solutions for Class 7 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for what is Wegener's theory of continental drift Related: Major landforms of the Earth?.
what is Wegener's theory of continental drift Related: Major landforms of the Earth? for Class 7 2024 is part of Class 7 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 7 exam syllabus. Information about what is Wegener's theory of continental drift Related: Major landforms of the Earth? covers all topics & solutions for Class 7 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for what is Wegener's theory of continental drift Related: Major landforms of the Earth?.
Solutions for what is Wegener's theory of continental drift Related: Major landforms of the Earth? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 7.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 7 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of what is Wegener's theory of continental drift Related: Major landforms of the Earth? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
what is Wegener's theory of continental drift Related: Major landforms of the Earth?, a detailed solution for what is Wegener's theory of continental drift Related: Major landforms of the Earth? has been provided alongside types of what is Wegener's theory of continental drift Related: Major landforms of the Earth? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice what is Wegener's theory of continental drift Related: Major landforms of the Earth? tests, examples and also practice Class 7 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 7 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























