Class 11 Exam > Class 11 Questions > Machanical properties of fluids (quick revisi...
Start Learning for Free
Machanical properties of fluids (quick revision formula)?
Most Upvoted Answer
Machanical properties of fluids (quick revision formula)?
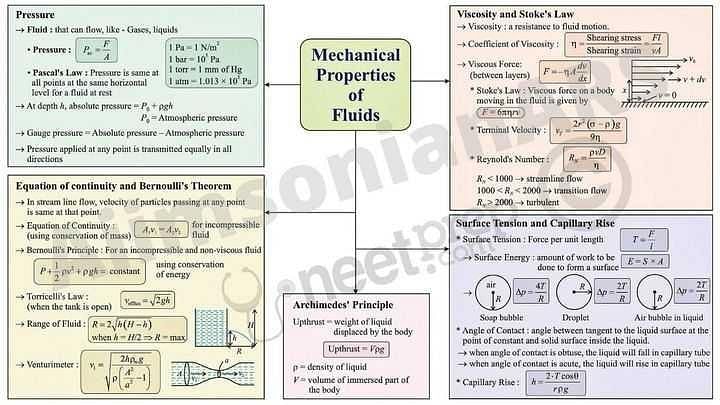
Community Answer
Machanical properties of fluids (quick revision formula)?
Introduction:
Mechanical properties of fluids refer to the physical characteristics that define the behavior of fluids under the influence of mechanical forces. These properties are crucial in understanding the flow and deformation of fluids and are used in various engineering applications, such as designing hydraulic systems, calculating fluid velocities, and predicting pressure drops.
Key Mechanical Properties:
There are several key mechanical properties of fluids that are important to understand. These properties include:
1. Density: Density is the measure of mass per unit volume of a fluid. It determines how heavy a fluid is and is usually denoted by the symbol "ρ" (rho). The density of a fluid is typically expressed in kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³) or grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³).
2. Viscosity: Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's resistance to flow. It describes the internal friction between fluid layers as they move past each other. Fluids with high viscosity are thick and flow slowly, while fluids with low viscosity are thin and flow easily. Viscosity is represented by the symbol "η" (eta) and is measured in units of pascal-seconds (Pa·s) or poise (P).
3. Surface Tension: Surface tension is the force exerted by the surface of a liquid that tends to minimize its surface area. It is responsible for phenomena such as capillary action and meniscus formation. Surface tension is denoted by the symbol "γ" (gamma) and is measured in units of newtons per meter (N/m) or dyn/cm.
4. Compressibility: Compressibility refers to the change in volume of a fluid when subjected to changes in pressure. It is a property that is more pronounced in gases compared to liquids. Compressibility is quantified by the bulk modulus of elasticity, which is represented by the symbol "K" and is measured in units of pascals (Pa).
5. Elasticity: Elasticity is the ability of a fluid to return to its original shape after being deformed by an external force. It is characterized by the fluid's modulus of elasticity, which measures its resistance to deformation. Elasticity is denoted by the symbol "E" and is measured in units of pascals (Pa).
Conclusion:
Understanding the mechanical properties of fluids is essential in various engineering applications. Density, viscosity, surface tension, compressibility, and elasticity are some of the key properties that define the behavior of fluids under mechanical forces. By considering these properties, engineers can accurately predict and analyze the flow, deformation, and other characteristics of fluids in different systems and processes.
Mechanical properties of fluids refer to the physical characteristics that define the behavior of fluids under the influence of mechanical forces. These properties are crucial in understanding the flow and deformation of fluids and are used in various engineering applications, such as designing hydraulic systems, calculating fluid velocities, and predicting pressure drops.
Key Mechanical Properties:
There are several key mechanical properties of fluids that are important to understand. These properties include:
1. Density: Density is the measure of mass per unit volume of a fluid. It determines how heavy a fluid is and is usually denoted by the symbol "ρ" (rho). The density of a fluid is typically expressed in kilograms per cubic meter (kg/m³) or grams per cubic centimeter (g/cm³).
2. Viscosity: Viscosity is a measure of a fluid's resistance to flow. It describes the internal friction between fluid layers as they move past each other. Fluids with high viscosity are thick and flow slowly, while fluids with low viscosity are thin and flow easily. Viscosity is represented by the symbol "η" (eta) and is measured in units of pascal-seconds (Pa·s) or poise (P).
3. Surface Tension: Surface tension is the force exerted by the surface of a liquid that tends to minimize its surface area. It is responsible for phenomena such as capillary action and meniscus formation. Surface tension is denoted by the symbol "γ" (gamma) and is measured in units of newtons per meter (N/m) or dyn/cm.
4. Compressibility: Compressibility refers to the change in volume of a fluid when subjected to changes in pressure. It is a property that is more pronounced in gases compared to liquids. Compressibility is quantified by the bulk modulus of elasticity, which is represented by the symbol "K" and is measured in units of pascals (Pa).
5. Elasticity: Elasticity is the ability of a fluid to return to its original shape after being deformed by an external force. It is characterized by the fluid's modulus of elasticity, which measures its resistance to deformation. Elasticity is denoted by the symbol "E" and is measured in units of pascals (Pa).
Conclusion:
Understanding the mechanical properties of fluids is essential in various engineering applications. Density, viscosity, surface tension, compressibility, and elasticity are some of the key properties that define the behavior of fluids under mechanical forces. By considering these properties, engineers can accurately predict and analyze the flow, deformation, and other characteristics of fluids in different systems and processes.
Attention Class 11 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 11 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 11.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Similar Class 11 Doubts
Machanical properties of fluids (quick revision formula)?
Question Description
Machanical properties of fluids (quick revision formula)? for Class 11 2024 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Machanical properties of fluids (quick revision formula)? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Machanical properties of fluids (quick revision formula)?.
Machanical properties of fluids (quick revision formula)? for Class 11 2024 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Machanical properties of fluids (quick revision formula)? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Machanical properties of fluids (quick revision formula)?.
Solutions for Machanical properties of fluids (quick revision formula)? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 11.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 11 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Machanical properties of fluids (quick revision formula)? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Machanical properties of fluids (quick revision formula)?, a detailed solution for Machanical properties of fluids (quick revision formula)? has been provided alongside types of Machanical properties of fluids (quick revision formula)? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Machanical properties of fluids (quick revision formula)? tests, examples and also practice Class 11 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























