NEET Exam > NEET Questions > What is DCT of nephron?
Start Learning for Free
What is DCT of nephron?
Community Answer
What is DCT of nephron?
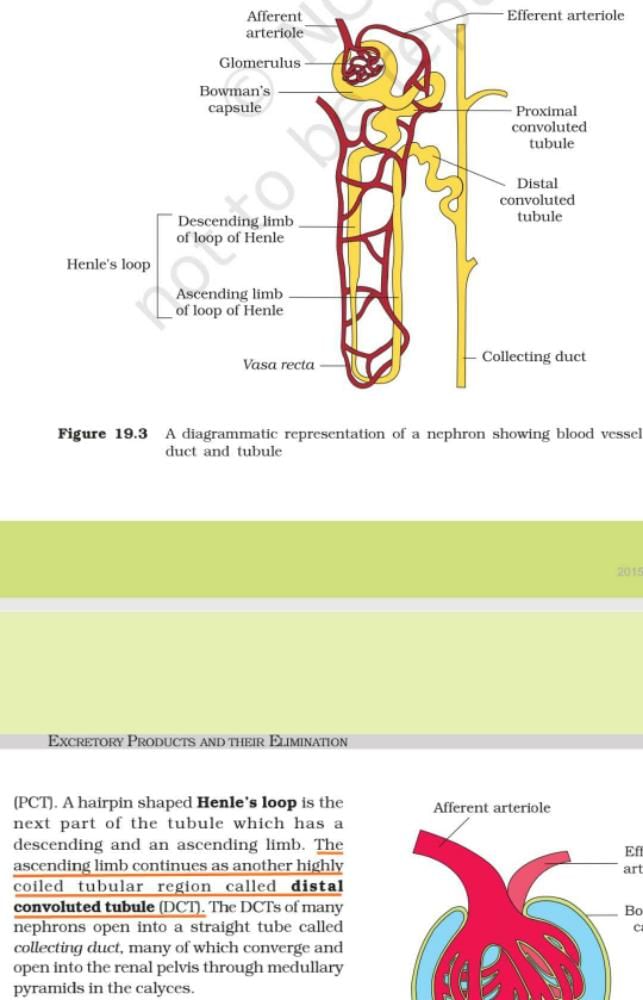
**DCT of Nephron**
The Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT) is a segment of the nephron in the kidney responsible for fine-tuning the reabsorption and secretion of substances from the filtrate. It is located in the renal cortex, between the loop of Henle and the collecting duct.
**Functions of DCT:**
1. **Reabsorption of Sodium and Chloride Ions:** The DCT actively reabsorbs sodium ions from the tubular fluid into the blood. This reabsorption is regulated by the hormone aldosterone, which increases sodium reabsorption and potassium secretion. Chloride ions are also reabsorbed along with sodium.
2. **Reabsorption of Water:** Unlike the proximal convoluted tubule, the DCT is not highly permeable to water. Therefore, only a small amount of water is reabsorbed in this segment.
3. **Reabsorption of Calcium:** The DCT plays a vital role in the reabsorption of calcium ions. Parathyroid hormone (PTH) stimulates the reabsorption of calcium by increasing the activity of calcium channels in the DCT.
4. **Secretion of Hydrogen and Potassium Ions:** The DCT secretes hydrogen ions (H+) and potassium ions (K+) into the tubular fluid. This process helps in maintaining acid-base balance and regulating potassium levels in the blood.
5. **Regulation of pH:** The DCT plays a significant role in maintaining the pH balance of the blood. It is responsible for the secretion of hydrogen ions into the tubular fluid, which helps in the excretion of excess acid from the body.
6. **Aldosterone Regulation:** The DCT is the main site of action for aldosterone, a hormone produced by the adrenal glands. Aldosterone acts on the DCT to increase the reabsorption of sodium ions and the excretion of potassium ions. This hormone also helps in regulating blood pressure and fluid balance.
**In summary, the DCT of the nephron is involved in the reabsorption of sodium, chloride, and calcium ions, as well as the secretion of hydrogen and potassium ions. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the pH balance of the blood and regulating fluid and electrolyte levels. The DCT is regulated by hormones such as aldosterone and parathyroid hormone.
The Distal Convoluted Tubule (DCT) is a segment of the nephron in the kidney responsible for fine-tuning the reabsorption and secretion of substances from the filtrate. It is located in the renal cortex, between the loop of Henle and the collecting duct.
**Functions of DCT:**
1. **Reabsorption of Sodium and Chloride Ions:** The DCT actively reabsorbs sodium ions from the tubular fluid into the blood. This reabsorption is regulated by the hormone aldosterone, which increases sodium reabsorption and potassium secretion. Chloride ions are also reabsorbed along with sodium.
2. **Reabsorption of Water:** Unlike the proximal convoluted tubule, the DCT is not highly permeable to water. Therefore, only a small amount of water is reabsorbed in this segment.
3. **Reabsorption of Calcium:** The DCT plays a vital role in the reabsorption of calcium ions. Parathyroid hormone (PTH) stimulates the reabsorption of calcium by increasing the activity of calcium channels in the DCT.
4. **Secretion of Hydrogen and Potassium Ions:** The DCT secretes hydrogen ions (H+) and potassium ions (K+) into the tubular fluid. This process helps in maintaining acid-base balance and regulating potassium levels in the blood.
5. **Regulation of pH:** The DCT plays a significant role in maintaining the pH balance of the blood. It is responsible for the secretion of hydrogen ions into the tubular fluid, which helps in the excretion of excess acid from the body.
6. **Aldosterone Regulation:** The DCT is the main site of action for aldosterone, a hormone produced by the adrenal glands. Aldosterone acts on the DCT to increase the reabsorption of sodium ions and the excretion of potassium ions. This hormone also helps in regulating blood pressure and fluid balance.
**In summary, the DCT of the nephron is involved in the reabsorption of sodium, chloride, and calcium ions, as well as the secretion of hydrogen and potassium ions. It plays a crucial role in maintaining the pH balance of the blood and regulating fluid and electrolyte levels. The DCT is regulated by hormones such as aldosterone and parathyroid hormone.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
Question Description
What is DCT of nephron? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about What is DCT of nephron? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is DCT of nephron?.
What is DCT of nephron? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about What is DCT of nephron? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is DCT of nephron?.
Solutions for What is DCT of nephron? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of What is DCT of nephron? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
What is DCT of nephron?, a detailed solution for What is DCT of nephron? has been provided alongside types of What is DCT of nephron? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice What is DCT of nephron? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup to solve all Doubts
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.