Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > Liver when chronically exposed to chloroform ...
Start Learning for Free
Liver when chronically exposed to chloroform gets damaged because
- a)chloroform gets converted to carbonyl chloride which is poison
- b)chloroform is not metabolised in the liver
- c)chloroform is metabolised to phosgene in the liver
- d)Both B and D
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Liver when chronically exposed to chloroform gets damaged becausea)chl...
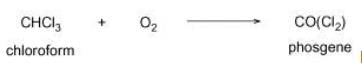
Phosgene is also called carbonyl chloride.
Both A and C are correct
Most Upvoted Answer
Liver when chronically exposed to chloroform gets damaged becausea)chl...
The correct answer is option 'A,C'.
Explanation:
Chloroform (CHCl3) is a volatile organic compound that was historically used as an anesthetic. However, it is now known to be toxic and potentially harmful to the liver. When chronically exposed to chloroform, the liver can get damaged due to the following reasons:
a) Chloroform gets converted to carbonyl chloride which is poison:
Chloroform can be metabolized by cytochrome P450 enzymes in the liver. One of the metabolic products of chloroform metabolism is phosgene (carbonyl chloride), which is a highly toxic gas. Phosgene can react with proteins and cellular components, leading to cell damage and liver toxicity. It can disrupt cellular processes and cause oxidative stress, leading to liver injury.
c) Chloroform is metabolized to phosgene in the liver:
Another metabolic product of chloroform metabolism in the liver is phosgene. Phosgene is a highly reactive compound that can react with cellular components, including proteins and DNA. This can lead to cellular damage and disruption of normal cellular functions, ultimately resulting in liver damage.
The liver plays a crucial role in metabolizing and detoxifying various compounds in the body. However, the metabolic breakdown of chloroform can generate toxic intermediates, such as phosgene, which can cause liver damage.
It is important to note that chloroform is not efficiently metabolized in the liver (option B). While there is some metabolism of chloroform in the liver, it is not the primary reason for liver damage. The primary mechanism of liver damage from chronic exposure to chloroform is the formation of toxic metabolites like phosgene.
In conclusion, chronic exposure to chloroform can lead to liver damage due to the conversion of chloroform to carbonyl chloride (phosgene) in the liver. This toxic metabolite can cause cellular damage and disrupt normal liver function. Therefore, options A and C are the correct answers.
Explanation:
Chloroform (CHCl3) is a volatile organic compound that was historically used as an anesthetic. However, it is now known to be toxic and potentially harmful to the liver. When chronically exposed to chloroform, the liver can get damaged due to the following reasons:
a) Chloroform gets converted to carbonyl chloride which is poison:
Chloroform can be metabolized by cytochrome P450 enzymes in the liver. One of the metabolic products of chloroform metabolism is phosgene (carbonyl chloride), which is a highly toxic gas. Phosgene can react with proteins and cellular components, leading to cell damage and liver toxicity. It can disrupt cellular processes and cause oxidative stress, leading to liver injury.
c) Chloroform is metabolized to phosgene in the liver:
Another metabolic product of chloroform metabolism in the liver is phosgene. Phosgene is a highly reactive compound that can react with cellular components, including proteins and DNA. This can lead to cellular damage and disruption of normal cellular functions, ultimately resulting in liver damage.
The liver plays a crucial role in metabolizing and detoxifying various compounds in the body. However, the metabolic breakdown of chloroform can generate toxic intermediates, such as phosgene, which can cause liver damage.
It is important to note that chloroform is not efficiently metabolized in the liver (option B). While there is some metabolism of chloroform in the liver, it is not the primary reason for liver damage. The primary mechanism of liver damage from chronic exposure to chloroform is the formation of toxic metabolites like phosgene.
In conclusion, chronic exposure to chloroform can lead to liver damage due to the conversion of chloroform to carbonyl chloride (phosgene) in the liver. This toxic metabolite can cause cellular damage and disrupt normal liver function. Therefore, options A and C are the correct answers.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Liver when chronically exposed to chloroform gets damaged becausea)chloroform gets converted to carbonyl chloride which is poisonb)chloroform is not metabolised in the liverc)chloroform is metabolised to phosgene in the liverd)Both B and DCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Liver when chronically exposed to chloroform gets damaged becausea)chloroform gets converted to carbonyl chloride which is poisonb)chloroform is not metabolised in the liverc)chloroform is metabolised to phosgene in the liverd)Both B and DCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Liver when chronically exposed to chloroform gets damaged becausea)chloroform gets converted to carbonyl chloride which is poisonb)chloroform is not metabolised in the liverc)chloroform is metabolised to phosgene in the liverd)Both B and DCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Liver when chronically exposed to chloroform gets damaged becausea)chloroform gets converted to carbonyl chloride which is poisonb)chloroform is not metabolised in the liverc)chloroform is metabolised to phosgene in the liverd)Both B and DCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Liver when chronically exposed to chloroform gets damaged becausea)chloroform gets converted to carbonyl chloride which is poisonb)chloroform is not metabolised in the liverc)chloroform is metabolised to phosgene in the liverd)Both B and DCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Liver when chronically exposed to chloroform gets damaged becausea)chloroform gets converted to carbonyl chloride which is poisonb)chloroform is not metabolised in the liverc)chloroform is metabolised to phosgene in the liverd)Both B and DCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Liver when chronically exposed to chloroform gets damaged becausea)chloroform gets converted to carbonyl chloride which is poisonb)chloroform is not metabolised in the liverc)chloroform is metabolised to phosgene in the liverd)Both B and DCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Liver when chronically exposed to chloroform gets damaged becausea)chloroform gets converted to carbonyl chloride which is poisonb)chloroform is not metabolised in the liverc)chloroform is metabolised to phosgene in the liverd)Both B and DCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Liver when chronically exposed to chloroform gets damaged becausea)chloroform gets converted to carbonyl chloride which is poisonb)chloroform is not metabolised in the liverc)chloroform is metabolised to phosgene in the liverd)Both B and DCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Liver when chronically exposed to chloroform gets damaged becausea)chloroform gets converted to carbonyl chloride which is poisonb)chloroform is not metabolised in the liverc)chloroform is metabolised to phosgene in the liverd)Both B and DCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Liver when chronically exposed to chloroform gets damaged becausea)chloroform gets converted to carbonyl chloride which is poisonb)chloroform is not metabolised in the liverc)chloroform is metabolised to phosgene in the liverd)Both B and DCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Liver when chronically exposed to chloroform gets damaged becausea)chloroform gets converted to carbonyl chloride which is poisonb)chloroform is not metabolised in the liverc)chloroform is metabolised to phosgene in the liverd)Both B and DCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Liver when chronically exposed to chloroform gets damaged becausea)chloroform gets converted to carbonyl chloride which is poisonb)chloroform is not metabolised in the liverc)chloroform is metabolised to phosgene in the liverd)Both B and DCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
















