JEE Exam > JEE Questions > A fuel cell is a cell that is continuously su...
Start Learning for Free
A fuel cell is a cell that is continuously supplied with an oxidant and a reductant so that it can deliver a current indefinitely.
Fuel cells offer the possibility of achieving high thermodynamic efficiency in the conversion of Gibbs energy into mechanical work. Internal combustion engines at best convert only the fraction (T2 – T1)/T2 of the heat of combustion into mechanical work.
Fuel cells offer the possibility of achieving high thermodynamic efficiency in the conversion of Gibbs energy into mechanical work. Internal combustion engines at best convert only the fraction (T2 – T1)/T2 of the heat of combustion into mechanical work.
While the thermodynamic efficiency of the fuel cell is given by, 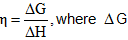 is the
is the
Gibbs energy change for the cell reaction and Δ H is the enthalpy change of the cell reaction.
A hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell may have an acidic or alkaline electrolyte.
Gibbs energy change for the cell reaction and Δ H is the enthalpy change of the cell reaction.
A hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell may have an acidic or alkaline electrolyte.
Pt|H2(g)|H+(aq.)||H2O( l )|O2(g)|Pt; 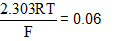
The above fuel cell is used to produce constant current supply under constant temperature & 30 atm constant total pressure condition in a cylinder. If 10 moles H2 and 5 moles of O2 were taken initially. Rate of combustion of O2 is 10 milli moles per minute. The half cell reactions are
To maximize the power per unit mass of an electrochemical cell, the electronic and electrolytic resistances of the cell must be minimized. Since fused salts have lower electrolytic resistances than aqueous solutions, high-temperature electrochemical cells are of special interest for practical applications.
Calculate e.m.f. of the given cell at t = 0. (log 2 = 0.3).
- a)1.255 V
- b)1.35 V
- c)1.3 V
- d)1.246 V
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
A fuel cell is a cell that is continuously supplied with an oxidant an...

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
A fuel cell is a cell that is continuously supplied with an oxidant and a reductant so that it can deliver a current indefinitely.Fuel cells offer the possibility of achieving high thermodynamic efficiency in the conversion of Gibbs energy into mechanical work. Internal combustion engines at best convert only the fraction (T2 T1)/T2 of the heat of combustion into mechanical work.While the thermodynamic efficiency of the fuel cell is given by, is theGibbs energy change for the cell reaction and H is the enthalpy change of the cell reaction.A hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell may have an acidic or alkaline electrolyte.Pt|H2(g)|H+(aq.)||H2O( l )|O2(g)|Pt; The above fuel cell is used to produce constant current supply under constant temperature 30 atm constant total pressure condition in a cylinder. If 10 moles H2 and 5 moles of O2 were taken initially. Rate of combustion of O2 is 10 milli moles per minute. The half cell reactions areTo maximize the power per unit mass of an electrochemical cell, the electronic and electrolytic resistances of the cell must be minimized. Since fused salts have lower electrolytic resistances than aqueous solutions, high-temperature electrochemical cells are of special interest for practical applications.Calculate e.m.f. of the given cell at t = 0. (log 2 = 0.3).a)1.255 Vb)1.35 Vc)1.3 Vd)1.246 VCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A fuel cell is a cell that is continuously supplied with an oxidant and a reductant so that it can deliver a current indefinitely.Fuel cells offer the possibility of achieving high thermodynamic efficiency in the conversion of Gibbs energy into mechanical work. Internal combustion engines at best convert only the fraction (T2 T1)/T2 of the heat of combustion into mechanical work.While the thermodynamic efficiency of the fuel cell is given by, is theGibbs energy change for the cell reaction and H is the enthalpy change of the cell reaction.A hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell may have an acidic or alkaline electrolyte.Pt|H2(g)|H+(aq.)||H2O( l )|O2(g)|Pt; The above fuel cell is used to produce constant current supply under constant temperature 30 atm constant total pressure condition in a cylinder. If 10 moles H2 and 5 moles of O2 were taken initially. Rate of combustion of O2 is 10 milli moles per minute. The half cell reactions areTo maximize the power per unit mass of an electrochemical cell, the electronic and electrolytic resistances of the cell must be minimized. Since fused salts have lower electrolytic resistances than aqueous solutions, high-temperature electrochemical cells are of special interest for practical applications.Calculate e.m.f. of the given cell at t = 0. (log 2 = 0.3).a)1.255 Vb)1.35 Vc)1.3 Vd)1.246 VCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about A fuel cell is a cell that is continuously supplied with an oxidant and a reductant so that it can deliver a current indefinitely.Fuel cells offer the possibility of achieving high thermodynamic efficiency in the conversion of Gibbs energy into mechanical work. Internal combustion engines at best convert only the fraction (T2 T1)/T2 of the heat of combustion into mechanical work.While the thermodynamic efficiency of the fuel cell is given by, is theGibbs energy change for the cell reaction and H is the enthalpy change of the cell reaction.A hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell may have an acidic or alkaline electrolyte.Pt|H2(g)|H+(aq.)||H2O( l )|O2(g)|Pt; The above fuel cell is used to produce constant current supply under constant temperature 30 atm constant total pressure condition in a cylinder. If 10 moles H2 and 5 moles of O2 were taken initially. Rate of combustion of O2 is 10 milli moles per minute. The half cell reactions areTo maximize the power per unit mass of an electrochemical cell, the electronic and electrolytic resistances of the cell must be minimized. Since fused salts have lower electrolytic resistances than aqueous solutions, high-temperature electrochemical cells are of special interest for practical applications.Calculate e.m.f. of the given cell at t = 0. (log 2 = 0.3).a)1.255 Vb)1.35 Vc)1.3 Vd)1.246 VCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A fuel cell is a cell that is continuously supplied with an oxidant and a reductant so that it can deliver a current indefinitely.Fuel cells offer the possibility of achieving high thermodynamic efficiency in the conversion of Gibbs energy into mechanical work. Internal combustion engines at best convert only the fraction (T2 T1)/T2 of the heat of combustion into mechanical work.While the thermodynamic efficiency of the fuel cell is given by, is theGibbs energy change for the cell reaction and H is the enthalpy change of the cell reaction.A hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell may have an acidic or alkaline electrolyte.Pt|H2(g)|H+(aq.)||H2O( l )|O2(g)|Pt; The above fuel cell is used to produce constant current supply under constant temperature 30 atm constant total pressure condition in a cylinder. If 10 moles H2 and 5 moles of O2 were taken initially. Rate of combustion of O2 is 10 milli moles per minute. The half cell reactions areTo maximize the power per unit mass of an electrochemical cell, the electronic and electrolytic resistances of the cell must be minimized. Since fused salts have lower electrolytic resistances than aqueous solutions, high-temperature electrochemical cells are of special interest for practical applications.Calculate e.m.f. of the given cell at t = 0. (log 2 = 0.3).a)1.255 Vb)1.35 Vc)1.3 Vd)1.246 VCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
A fuel cell is a cell that is continuously supplied with an oxidant and a reductant so that it can deliver a current indefinitely.Fuel cells offer the possibility of achieving high thermodynamic efficiency in the conversion of Gibbs energy into mechanical work. Internal combustion engines at best convert only the fraction (T2 T1)/T2 of the heat of combustion into mechanical work.While the thermodynamic efficiency of the fuel cell is given by, is theGibbs energy change for the cell reaction and H is the enthalpy change of the cell reaction.A hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell may have an acidic or alkaline electrolyte.Pt|H2(g)|H+(aq.)||H2O( l )|O2(g)|Pt; The above fuel cell is used to produce constant current supply under constant temperature 30 atm constant total pressure condition in a cylinder. If 10 moles H2 and 5 moles of O2 were taken initially. Rate of combustion of O2 is 10 milli moles per minute. The half cell reactions areTo maximize the power per unit mass of an electrochemical cell, the electronic and electrolytic resistances of the cell must be minimized. Since fused salts have lower electrolytic resistances than aqueous solutions, high-temperature electrochemical cells are of special interest for practical applications.Calculate e.m.f. of the given cell at t = 0. (log 2 = 0.3).a)1.255 Vb)1.35 Vc)1.3 Vd)1.246 VCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about A fuel cell is a cell that is continuously supplied with an oxidant and a reductant so that it can deliver a current indefinitely.Fuel cells offer the possibility of achieving high thermodynamic efficiency in the conversion of Gibbs energy into mechanical work. Internal combustion engines at best convert only the fraction (T2 T1)/T2 of the heat of combustion into mechanical work.While the thermodynamic efficiency of the fuel cell is given by, is theGibbs energy change for the cell reaction and H is the enthalpy change of the cell reaction.A hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell may have an acidic or alkaline electrolyte.Pt|H2(g)|H+(aq.)||H2O( l )|O2(g)|Pt; The above fuel cell is used to produce constant current supply under constant temperature 30 atm constant total pressure condition in a cylinder. If 10 moles H2 and 5 moles of O2 were taken initially. Rate of combustion of O2 is 10 milli moles per minute. The half cell reactions areTo maximize the power per unit mass of an electrochemical cell, the electronic and electrolytic resistances of the cell must be minimized. Since fused salts have lower electrolytic resistances than aqueous solutions, high-temperature electrochemical cells are of special interest for practical applications.Calculate e.m.f. of the given cell at t = 0. (log 2 = 0.3).a)1.255 Vb)1.35 Vc)1.3 Vd)1.246 VCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A fuel cell is a cell that is continuously supplied with an oxidant and a reductant so that it can deliver a current indefinitely.Fuel cells offer the possibility of achieving high thermodynamic efficiency in the conversion of Gibbs energy into mechanical work. Internal combustion engines at best convert only the fraction (T2 T1)/T2 of the heat of combustion into mechanical work.While the thermodynamic efficiency of the fuel cell is given by, is theGibbs energy change for the cell reaction and H is the enthalpy change of the cell reaction.A hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell may have an acidic or alkaline electrolyte.Pt|H2(g)|H+(aq.)||H2O( l )|O2(g)|Pt; The above fuel cell is used to produce constant current supply under constant temperature 30 atm constant total pressure condition in a cylinder. If 10 moles H2 and 5 moles of O2 were taken initially. Rate of combustion of O2 is 10 milli moles per minute. The half cell reactions areTo maximize the power per unit mass of an electrochemical cell, the electronic and electrolytic resistances of the cell must be minimized. Since fused salts have lower electrolytic resistances than aqueous solutions, high-temperature electrochemical cells are of special interest for practical applications.Calculate e.m.f. of the given cell at t = 0. (log 2 = 0.3).a)1.255 Vb)1.35 Vc)1.3 Vd)1.246 VCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A fuel cell is a cell that is continuously supplied with an oxidant and a reductant so that it can deliver a current indefinitely.Fuel cells offer the possibility of achieving high thermodynamic efficiency in the conversion of Gibbs energy into mechanical work. Internal combustion engines at best convert only the fraction (T2 T1)/T2 of the heat of combustion into mechanical work.While the thermodynamic efficiency of the fuel cell is given by, is theGibbs energy change for the cell reaction and H is the enthalpy change of the cell reaction.A hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell may have an acidic or alkaline electrolyte.Pt|H2(g)|H+(aq.)||H2O( l )|O2(g)|Pt; The above fuel cell is used to produce constant current supply under constant temperature 30 atm constant total pressure condition in a cylinder. If 10 moles H2 and 5 moles of O2 were taken initially. Rate of combustion of O2 is 10 milli moles per minute. The half cell reactions areTo maximize the power per unit mass of an electrochemical cell, the electronic and electrolytic resistances of the cell must be minimized. Since fused salts have lower electrolytic resistances than aqueous solutions, high-temperature electrochemical cells are of special interest for practical applications.Calculate e.m.f. of the given cell at t = 0. (log 2 = 0.3).a)1.255 Vb)1.35 Vc)1.3 Vd)1.246 VCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A fuel cell is a cell that is continuously supplied with an oxidant and a reductant so that it can deliver a current indefinitely.Fuel cells offer the possibility of achieving high thermodynamic efficiency in the conversion of Gibbs energy into mechanical work. Internal combustion engines at best convert only the fraction (T2 T1)/T2 of the heat of combustion into mechanical work.While the thermodynamic efficiency of the fuel cell is given by, is theGibbs energy change for the cell reaction and H is the enthalpy change of the cell reaction.A hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell may have an acidic or alkaline electrolyte.Pt|H2(g)|H+(aq.)||H2O( l )|O2(g)|Pt; The above fuel cell is used to produce constant current supply under constant temperature 30 atm constant total pressure condition in a cylinder. If 10 moles H2 and 5 moles of O2 were taken initially. Rate of combustion of O2 is 10 milli moles per minute. The half cell reactions areTo maximize the power per unit mass of an electrochemical cell, the electronic and electrolytic resistances of the cell must be minimized. Since fused salts have lower electrolytic resistances than aqueous solutions, high-temperature electrochemical cells are of special interest for practical applications.Calculate e.m.f. of the given cell at t = 0. (log 2 = 0.3).a)1.255 Vb)1.35 Vc)1.3 Vd)1.246 VCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A fuel cell is a cell that is continuously supplied with an oxidant and a reductant so that it can deliver a current indefinitely.Fuel cells offer the possibility of achieving high thermodynamic efficiency in the conversion of Gibbs energy into mechanical work. Internal combustion engines at best convert only the fraction (T2 T1)/T2 of the heat of combustion into mechanical work.While the thermodynamic efficiency of the fuel cell is given by, is theGibbs energy change for the cell reaction and H is the enthalpy change of the cell reaction.A hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell may have an acidic or alkaline electrolyte.Pt|H2(g)|H+(aq.)||H2O( l )|O2(g)|Pt; The above fuel cell is used to produce constant current supply under constant temperature 30 atm constant total pressure condition in a cylinder. If 10 moles H2 and 5 moles of O2 were taken initially. Rate of combustion of O2 is 10 milli moles per minute. The half cell reactions areTo maximize the power per unit mass of an electrochemical cell, the electronic and electrolytic resistances of the cell must be minimized. Since fused salts have lower electrolytic resistances than aqueous solutions, high-temperature electrochemical cells are of special interest for practical applications.Calculate e.m.f. of the given cell at t = 0. (log 2 = 0.3).a)1.255 Vb)1.35 Vc)1.3 Vd)1.246 VCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A fuel cell is a cell that is continuously supplied with an oxidant and a reductant so that it can deliver a current indefinitely.Fuel cells offer the possibility of achieving high thermodynamic efficiency in the conversion of Gibbs energy into mechanical work. Internal combustion engines at best convert only the fraction (T2 T1)/T2 of the heat of combustion into mechanical work.While the thermodynamic efficiency of the fuel cell is given by, is theGibbs energy change for the cell reaction and H is the enthalpy change of the cell reaction.A hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell may have an acidic or alkaline electrolyte.Pt|H2(g)|H+(aq.)||H2O( l )|O2(g)|Pt; The above fuel cell is used to produce constant current supply under constant temperature 30 atm constant total pressure condition in a cylinder. If 10 moles H2 and 5 moles of O2 were taken initially. Rate of combustion of O2 is 10 milli moles per minute. The half cell reactions areTo maximize the power per unit mass of an electrochemical cell, the electronic and electrolytic resistances of the cell must be minimized. Since fused salts have lower electrolytic resistances than aqueous solutions, high-temperature electrochemical cells are of special interest for practical applications.Calculate e.m.f. of the given cell at t = 0. (log 2 = 0.3).a)1.255 Vb)1.35 Vc)1.3 Vd)1.246 VCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A fuel cell is a cell that is continuously supplied with an oxidant and a reductant so that it can deliver a current indefinitely.Fuel cells offer the possibility of achieving high thermodynamic efficiency in the conversion of Gibbs energy into mechanical work. Internal combustion engines at best convert only the fraction (T2 T1)/T2 of the heat of combustion into mechanical work.While the thermodynamic efficiency of the fuel cell is given by, is theGibbs energy change for the cell reaction and H is the enthalpy change of the cell reaction.A hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell may have an acidic or alkaline electrolyte.Pt|H2(g)|H+(aq.)||H2O( l )|O2(g)|Pt; The above fuel cell is used to produce constant current supply under constant temperature 30 atm constant total pressure condition in a cylinder. If 10 moles H2 and 5 moles of O2 were taken initially. Rate of combustion of O2 is 10 milli moles per minute. The half cell reactions areTo maximize the power per unit mass of an electrochemical cell, the electronic and electrolytic resistances of the cell must be minimized. Since fused salts have lower electrolytic resistances than aqueous solutions, high-temperature electrochemical cells are of special interest for practical applications.Calculate e.m.f. of the given cell at t = 0. (log 2 = 0.3).a)1.255 Vb)1.35 Vc)1.3 Vd)1.246 VCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A fuel cell is a cell that is continuously supplied with an oxidant and a reductant so that it can deliver a current indefinitely.Fuel cells offer the possibility of achieving high thermodynamic efficiency in the conversion of Gibbs energy into mechanical work. Internal combustion engines at best convert only the fraction (T2 T1)/T2 of the heat of combustion into mechanical work.While the thermodynamic efficiency of the fuel cell is given by, is theGibbs energy change for the cell reaction and H is the enthalpy change of the cell reaction.A hydrogen-oxygen fuel cell may have an acidic or alkaline electrolyte.Pt|H2(g)|H+(aq.)||H2O( l )|O2(g)|Pt; The above fuel cell is used to produce constant current supply under constant temperature 30 atm constant total pressure condition in a cylinder. If 10 moles H2 and 5 moles of O2 were taken initially. Rate of combustion of O2 is 10 milli moles per minute. The half cell reactions areTo maximize the power per unit mass of an electrochemical cell, the electronic and electrolytic resistances of the cell must be minimized. Since fused salts have lower electrolytic resistances than aqueous solutions, high-temperature electrochemical cells are of special interest for practical applications.Calculate e.m.f. of the given cell at t = 0. (log 2 = 0.3).a)1.255 Vb)1.35 Vc)1.3 Vd)1.246 VCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























