NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Quick notes on "biological classification" pa...
Start Learning for Free
Quick notes on "biological classification" part-1?
Most Upvoted Answer
Quick notes on "biological classification" part-1?
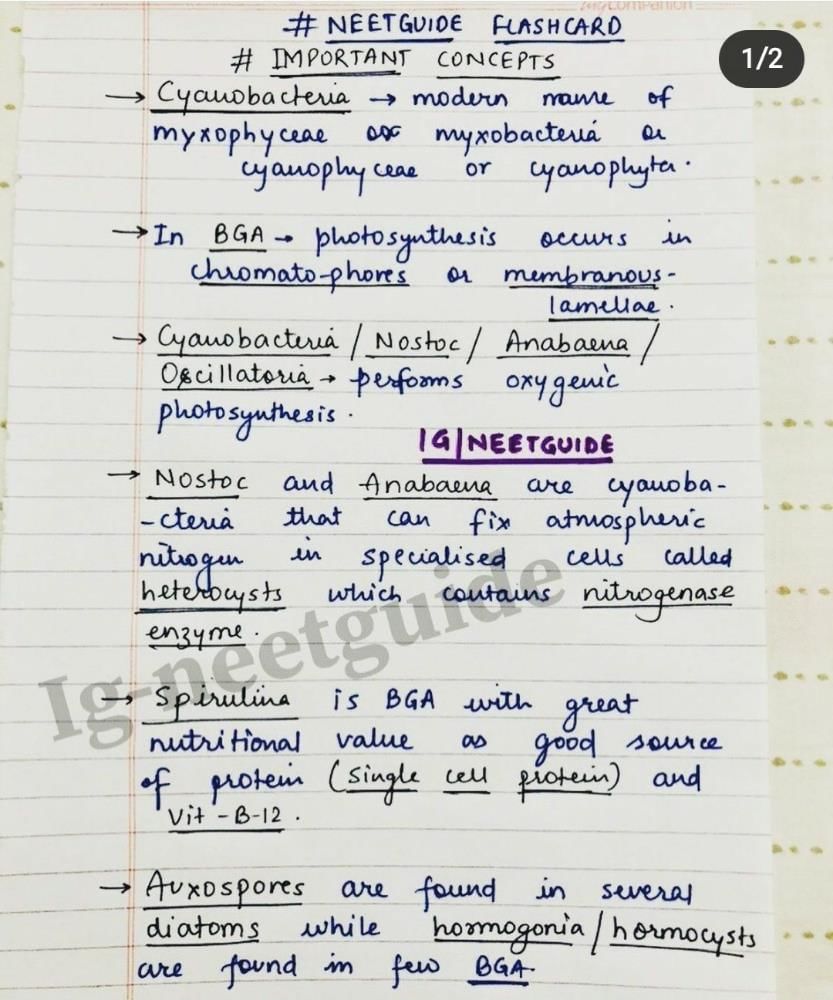
Community Answer
Quick notes on "biological classification" part-1?
Biological Classification
Biological classification is the process of categorizing and organizing living organisms based on their characteristics and relationships. It involves classifying organisms into different groups and subgroups based on their similarities and differences. This classification helps in understanding the diversity of life on Earth and provides a systematic and organized way of studying and categorizing living organisms.
Importance of Biological Classification
Biological classification is essential for several reasons:
1. Identification and Naming: Classification helps in identifying and naming new organisms. It provides a standardized system of naming and categorizing organisms, known as the binomial nomenclature.
2. Understanding Diversity: Classification helps in understanding the vast diversity of life on Earth. It allows scientists to study and compare different organisms and their characteristics.
3. Evolutionary Relationships: Classification helps in determining the evolutionary relationships between organisms. By studying similarities and differences, scientists can infer the evolutionary history and relatedness of different species.
Levels of Biological Classification
Biological classification is hierarchical and consists of various levels or categories. The main levels of classification, from the broadest to the most specific, are:
1. Domain: The highest level of classification, which categorizes organisms into three domains: Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya.
2. Kingdom: The second level of classification, which groups organisms into five kingdoms: Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia.
3. Phylum: The third level of classification, which further divides organisms within each kingdom based on their body plans and characteristics.
4. Class: The fourth level of classification, which divides organisms within each phylum based on additional characteristics.
5. Order: The fifth level of classification, which further divides organisms within each class based on specific features.
6. Family: The sixth level of classification, which groups organisms within each order based on similarities in anatomy and genetics.
7. Genus: The seventh level of classification, which categorizes organisms within each family based on shared characteristics.
8. Species: The lowest and most specific level of classification, which identifies individual organisms with similar characteristics that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring.
The Linnaean System
The Linnaean system, developed by Carl Linnaeus, is the most widely used system of biological classification. It is based on a hierarchical structure and uses a binomial nomenclature to name and categorize organisms. The system assigns a unique two-part Latin name to each species, consisting of the genus and species names. For example, Homo sapiens is the binomial name for humans.
Overall, biological classification is a vital tool for scientists to understand and study the diversity of life. It provides a systematic framework for organizing and categorizing organisms, allowing for easier identification, comparison, and analysis.
Biological classification is the process of categorizing and organizing living organisms based on their characteristics and relationships. It involves classifying organisms into different groups and subgroups based on their similarities and differences. This classification helps in understanding the diversity of life on Earth and provides a systematic and organized way of studying and categorizing living organisms.
Importance of Biological Classification
Biological classification is essential for several reasons:
1. Identification and Naming: Classification helps in identifying and naming new organisms. It provides a standardized system of naming and categorizing organisms, known as the binomial nomenclature.
2. Understanding Diversity: Classification helps in understanding the vast diversity of life on Earth. It allows scientists to study and compare different organisms and their characteristics.
3. Evolutionary Relationships: Classification helps in determining the evolutionary relationships between organisms. By studying similarities and differences, scientists can infer the evolutionary history and relatedness of different species.
Levels of Biological Classification
Biological classification is hierarchical and consists of various levels or categories. The main levels of classification, from the broadest to the most specific, are:
1. Domain: The highest level of classification, which categorizes organisms into three domains: Archaea, Bacteria, and Eukarya.
2. Kingdom: The second level of classification, which groups organisms into five kingdoms: Monera, Protista, Fungi, Plantae, and Animalia.
3. Phylum: The third level of classification, which further divides organisms within each kingdom based on their body plans and characteristics.
4. Class: The fourth level of classification, which divides organisms within each phylum based on additional characteristics.
5. Order: The fifth level of classification, which further divides organisms within each class based on specific features.
6. Family: The sixth level of classification, which groups organisms within each order based on similarities in anatomy and genetics.
7. Genus: The seventh level of classification, which categorizes organisms within each family based on shared characteristics.
8. Species: The lowest and most specific level of classification, which identifies individual organisms with similar characteristics that can interbreed and produce fertile offspring.
The Linnaean System
The Linnaean system, developed by Carl Linnaeus, is the most widely used system of biological classification. It is based on a hierarchical structure and uses a binomial nomenclature to name and categorize organisms. The system assigns a unique two-part Latin name to each species, consisting of the genus and species names. For example, Homo sapiens is the binomial name for humans.
Overall, biological classification is a vital tool for scientists to understand and study the diversity of life. It provides a systematic framework for organizing and categorizing organisms, allowing for easier identification, comparison, and analysis.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
Question Description
Quick notes on "biological classification" part-1? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Quick notes on "biological classification" part-1? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Quick notes on "biological classification" part-1?.
Quick notes on "biological classification" part-1? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Quick notes on "biological classification" part-1? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Quick notes on "biological classification" part-1?.
Solutions for Quick notes on "biological classification" part-1? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Quick notes on "biological classification" part-1? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Quick notes on "biological classification" part-1?, a detailed solution for Quick notes on "biological classification" part-1? has been provided alongside types of Quick notes on "biological classification" part-1? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Quick notes on "biological classification" part-1? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup to solve all Doubts
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.





















