NEET Exam > NEET Questions > Carbylamine reaction. It is all about to help...
Start Learning for Free
Carbylamine reaction. It is all about to help you so don't answer please?
Most Upvoted Answer
Carbylamine reaction. It is all about to help you so don't answer plea...
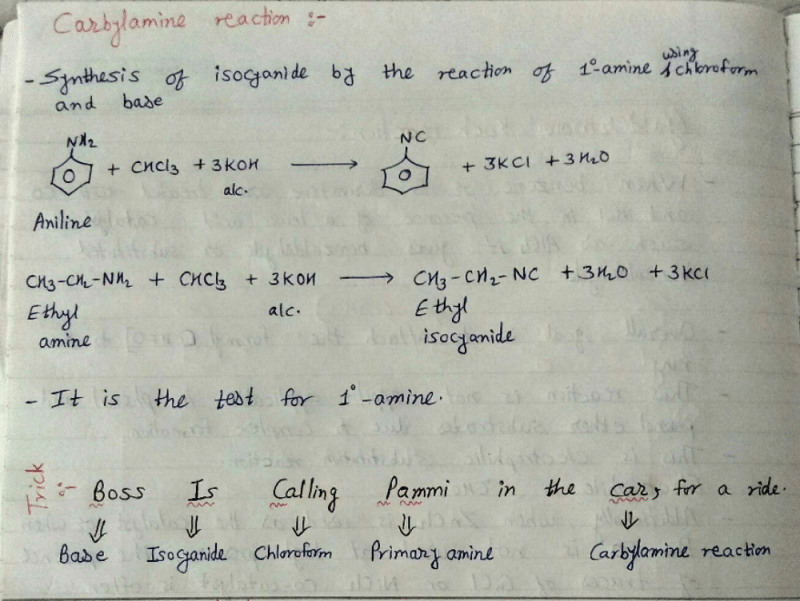
Community Answer
Carbylamine reaction. It is all about to help you so don't answer plea...
Carbylamine Reaction
The Carbylamine reaction, also known as the isocyanide test, is a chemical test used to detect the presence of primary amines in a compound. This test is based on the reaction of primary amines with chloroform and alcoholic potassium hydroxide to form foul-smelling isocyanides.
Mechanism
1. The primary amine reacts with chloroform (CHCl3) and alcoholic potassium hydroxide (KOH) to form an isocyanide.
2. The reaction proceeds through the formation of an intermediate isocyanate, which then rearranges to form the isocyanide.
3. The isocyanide produced in this reaction has a foul odor, hence the name "Carbylamine reaction."
Applications
1. The Carbylamine reaction is commonly used in organic chemistry labs to distinguish between primary, secondary, and tertiary amines.
2. Primary amines give a positive test in the Carbylamine reaction, while secondary and tertiary amines do not react.
3. This test is useful in the identification of primary amines in various organic compounds.
Limitations
1. The Carbylamine reaction is not specific for primary amines and can also give false-positive results with compounds containing other functional groups.
2. The foul odor produced in this reaction can be unpleasant, making it less desirable for use in certain environments.
In conclusion, the Carbylamine reaction is a simple and effective test for the detection of primary amines in organic compounds. It is commonly used in organic chemistry labs for qualitative analysis of amines.
The Carbylamine reaction, also known as the isocyanide test, is a chemical test used to detect the presence of primary amines in a compound. This test is based on the reaction of primary amines with chloroform and alcoholic potassium hydroxide to form foul-smelling isocyanides.
Mechanism
1. The primary amine reacts with chloroform (CHCl3) and alcoholic potassium hydroxide (KOH) to form an isocyanide.
2. The reaction proceeds through the formation of an intermediate isocyanate, which then rearranges to form the isocyanide.
3. The isocyanide produced in this reaction has a foul odor, hence the name "Carbylamine reaction."
Applications
1. The Carbylamine reaction is commonly used in organic chemistry labs to distinguish between primary, secondary, and tertiary amines.
2. Primary amines give a positive test in the Carbylamine reaction, while secondary and tertiary amines do not react.
3. This test is useful in the identification of primary amines in various organic compounds.
Limitations
1. The Carbylamine reaction is not specific for primary amines and can also give false-positive results with compounds containing other functional groups.
2. The foul odor produced in this reaction can be unpleasant, making it less desirable for use in certain environments.
In conclusion, the Carbylamine reaction is a simple and effective test for the detection of primary amines in organic compounds. It is commonly used in organic chemistry labs for qualitative analysis of amines.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Similar NEET Doubts
Question Description
Carbylamine reaction. It is all about to help you so don't answer please? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Carbylamine reaction. It is all about to help you so don't answer please? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Carbylamine reaction. It is all about to help you so don't answer please?.
Carbylamine reaction. It is all about to help you so don't answer please? for NEET 2025 is part of NEET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the NEET exam syllabus. Information about Carbylamine reaction. It is all about to help you so don't answer please? covers all topics & solutions for NEET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Carbylamine reaction. It is all about to help you so don't answer please?.
Solutions for Carbylamine reaction. It is all about to help you so don't answer please? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for NEET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for NEET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Carbylamine reaction. It is all about to help you so don't answer please? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Carbylamine reaction. It is all about to help you so don't answer please?, a detailed solution for Carbylamine reaction. It is all about to help you so don't answer please? has been provided alongside types of Carbylamine reaction. It is all about to help you so don't answer please? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Carbylamine reaction. It is all about to help you so don't answer please? tests, examples and also practice NEET tests.

|
Explore Courses for NEET exam
|

|
Signup to solve all Doubts
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



























