Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > how to convert propanamine to ethanoic acid ?
Start Learning for Free
how to convert propanamine to ethanoic acid ?
Most Upvoted Answer
how to convert propanamine to ethanoic acid ?
Converting Propanamine to Ethanoic Acid
Converting propanamine to ethanoic acid involves a series of chemical reactions. The following steps can be taken:
Step 1: Oxidation of Propanamine
The first step is to oxidize propanamine to form propanone. This can be achieved using an oxidizing agent like potassium permanganate (KMnO4) or hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) in the presence of an acid catalyst like sulfuric acid (H2SO4).
Propanamine + KMnO4 + H2SO4 → Propanone + MnSO4 + K2SO4 + H2O
Step 2: Conversion of Propanone to Propanoic Acid
The next step is to convert propanone to propanoic acid. This can be achieved using a reducing agent like lithium aluminum hydride (LiAlH4) or sodium borohydride (NaBH4) in the presence of an acid catalyst like acetic acid (CH3COOH).
Propanone + LiAlH4 + CH3COOH → Propanoic acid + Al(OH)3 + LiCH3COO
Step 3: Conversion of Propanoic Acid to Ethanoic Acid
The final step is to convert propanoic acid to ethanoic acid. This can be achieved using an oxidizing agent like potassium permanganate (KMnO4) or sodium dichromate (Na2Cr2O7) in the presence of an acid catalyst like sulfuric acid (H2SO4).
Propanoic acid + KMnO4 + H2SO4 → Ethanoic acid + MnSO4 + K2SO4 + H2O
Overall Reaction
The overall reaction can be represented as:
Propanamine + KMnO4 + H2SO4 → Propanone + MnSO4 + K2SO4 + H2O
Propanone + LiAlH4 + CH3COOH → Propanoic acid + Al(OH)3 + LiCH3COO
Propanoic acid + KMnO4 + H2SO4 → Ethanoic acid + MnSO4 + K2SO4 + H2O
Community Answer
how to convert propanamine to ethanoic acid ?
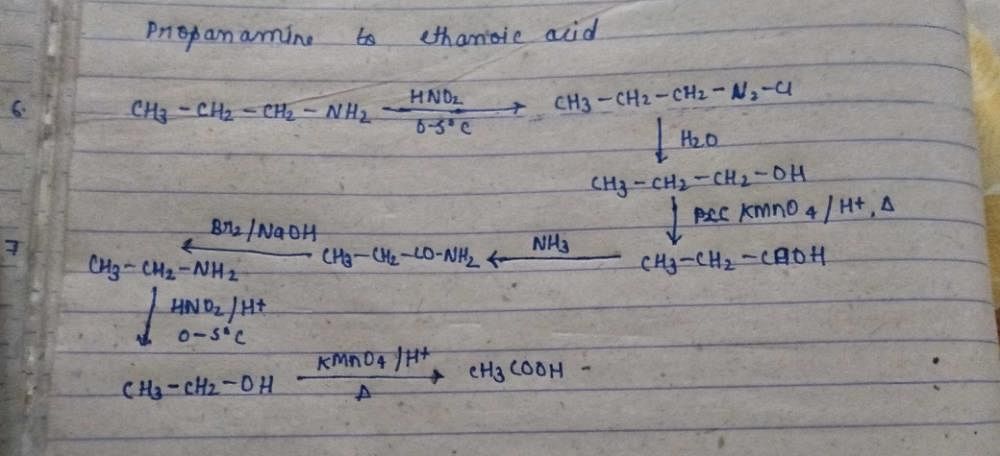

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
how to convert propanamine to ethanoic acid ?
Question Description
how to convert propanamine to ethanoic acid ? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about how to convert propanamine to ethanoic acid ? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for how to convert propanamine to ethanoic acid ?.
how to convert propanamine to ethanoic acid ? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about how to convert propanamine to ethanoic acid ? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for how to convert propanamine to ethanoic acid ?.
Solutions for how to convert propanamine to ethanoic acid ? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of how to convert propanamine to ethanoic acid ? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
how to convert propanamine to ethanoic acid ?, a detailed solution for how to convert propanamine to ethanoic acid ? has been provided alongside types of how to convert propanamine to ethanoic acid ? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice how to convert propanamine to ethanoic acid ? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



















