JEE Exam > JEE Questions > In the figure a container is shown to have a ...
Start Learning for Free
In the figure a container is shown to have a movable (without friction) piston on top. The container and
the piston are all made of perfectly insulating material allowing no heat transfer between outside and
inside the container. The container is divided into two compartments by a rigid partition made of a
thermally conducting material that allows slow transfer of heat. The lower compartment of the container is filled with 2 moles of an ideal monatomic gas at 700 K and the upper compartment is filled with 2 moles of an ideal diatomic gas at 400 K. The heat capacities per mole of an ideal monatomic gas are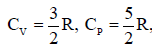 and those for an ideal diatomic gas are
and those for an ideal diatomic gas are 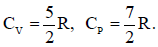
the piston are all made of perfectly insulating material allowing no heat transfer between outside and
inside the container. The container is divided into two compartments by a rigid partition made of a
thermally conducting material that allows slow transfer of heat. The lower compartment of the container is filled with 2 moles of an ideal monatomic gas at 700 K and the upper compartment is filled with 2 moles of an ideal diatomic gas at 400 K. The heat capacities per mole of an ideal monatomic gas are
Q.
Now consider the partition to be free to move without friction so that the pressure of gases in both
compartments is the same. Then total work done by the gases till the time they achieve equilibrium will be
compartments is the same. Then total work done by the gases till the time they achieve equilibrium will be
- a)250 R
- b)200 R
- c)100 R
- d)–100 R
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
In the figure a container is shown to have a movable (without friction...
Heat given by lower compartment = 
Heat obtained by upper compartment =
By equating (i) and (ii)
5(700 -T) = 7(T - 400)
3000 – 5T = 7T– 2800
6300 = 12 T
T = 525K
 Work done by lower gas = nRΔT = – 350 R
Work done by lower gas = nRΔT = – 350 R
Work done by upper gas = nRΔT = +250 R
Net work done - 100 R
5(700 -T) = 7(T - 400)
3000 – 5T = 7T– 2800
6300 = 12 T
T = 525K
Work done by upper gas = nRΔT = +250 R
Net work done - 100 R
Most Upvoted Answer
In the figure a container is shown to have a movable (without friction...
Heat given by lower compartment = 
Heat obtained by upper compartment =
By equating (i) and (ii)
5(700 -T) = 7(T - 400)
3000 – 5T = 7T– 2800
6300 = 12 T
T = 525K
 Work done by lower gas = nRΔT = – 350 R
Work done by lower gas = nRΔT = – 350 R
Work done by upper gas = nRΔT = +250 R
Net work done - 100 R
5(700 -T) = 7(T - 400)
3000 – 5T = 7T– 2800
6300 = 12 T
T = 525K
Work done by upper gas = nRΔT = +250 R
Net work done - 100 R
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
In the figure a container is shown to have a movable (without friction...
Heat given by lower compartment = 
Heat obtained by upper compartment =
By equating (i) and (ii)
5(700 -T) = 7(T - 400)
3000 – 5T = 7T– 2800
6300 = 12 T
T = 525K
 Work done by lower gas = nRΔT = – 350 R
Work done by lower gas = nRΔT = – 350 R
Work done by upper gas = nRΔT = +250 R
Net work done - 100 R
5(700 -T) = 7(T - 400)
3000 – 5T = 7T– 2800
6300 = 12 T
T = 525K
Work done by upper gas = nRΔT = +250 R
Net work done - 100 R

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
Question Description
In the figure a container is shown to have a movable (without friction) piston on top. The container andthe piston are all made of perfectly insulating material allowing no heat transfer between outside andinside the container. The container is divided into two compartments by a rigid partition made of athermally conducting material that allows slow transfer of heat. The lower compartment of the container is filled with 2 moles of an ideal monatomic gas at 700 K and the upper compartment is filled with 2 moles of an ideal diatomic gas at 400 K. The heat capacities per mole of an ideal monatomic gas areand those for an ideal diatomic gas are Q.Now consider the partition to be free to move without friction so that the pressure of gases in bothcompartments is the same. Then total work done by the gases till the time they achieve equilibrium will bea)250 Rb)200 Rc)100 Rd)–100 RCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about In the figure a container is shown to have a movable (without friction) piston on top. The container andthe piston are all made of perfectly insulating material allowing no heat transfer between outside andinside the container. The container is divided into two compartments by a rigid partition made of athermally conducting material that allows slow transfer of heat. The lower compartment of the container is filled with 2 moles of an ideal monatomic gas at 700 K and the upper compartment is filled with 2 moles of an ideal diatomic gas at 400 K. The heat capacities per mole of an ideal monatomic gas areand those for an ideal diatomic gas are Q.Now consider the partition to be free to move without friction so that the pressure of gases in bothcompartments is the same. Then total work done by the gases till the time they achieve equilibrium will bea)250 Rb)200 Rc)100 Rd)–100 RCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In the figure a container is shown to have a movable (without friction) piston on top. The container andthe piston are all made of perfectly insulating material allowing no heat transfer between outside andinside the container. The container is divided into two compartments by a rigid partition made of athermally conducting material that allows slow transfer of heat. The lower compartment of the container is filled with 2 moles of an ideal monatomic gas at 700 K and the upper compartment is filled with 2 moles of an ideal diatomic gas at 400 K. The heat capacities per mole of an ideal monatomic gas areand those for an ideal diatomic gas are Q.Now consider the partition to be free to move without friction so that the pressure of gases in bothcompartments is the same. Then total work done by the gases till the time they achieve equilibrium will bea)250 Rb)200 Rc)100 Rd)–100 RCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
In the figure a container is shown to have a movable (without friction) piston on top. The container andthe piston are all made of perfectly insulating material allowing no heat transfer between outside andinside the container. The container is divided into two compartments by a rigid partition made of athermally conducting material that allows slow transfer of heat. The lower compartment of the container is filled with 2 moles of an ideal monatomic gas at 700 K and the upper compartment is filled with 2 moles of an ideal diatomic gas at 400 K. The heat capacities per mole of an ideal monatomic gas areand those for an ideal diatomic gas are Q.Now consider the partition to be free to move without friction so that the pressure of gases in bothcompartments is the same. Then total work done by the gases till the time they achieve equilibrium will bea)250 Rb)200 Rc)100 Rd)–100 RCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about In the figure a container is shown to have a movable (without friction) piston on top. The container andthe piston are all made of perfectly insulating material allowing no heat transfer between outside andinside the container. The container is divided into two compartments by a rigid partition made of athermally conducting material that allows slow transfer of heat. The lower compartment of the container is filled with 2 moles of an ideal monatomic gas at 700 K and the upper compartment is filled with 2 moles of an ideal diatomic gas at 400 K. The heat capacities per mole of an ideal monatomic gas areand those for an ideal diatomic gas are Q.Now consider the partition to be free to move without friction so that the pressure of gases in bothcompartments is the same. Then total work done by the gases till the time they achieve equilibrium will bea)250 Rb)200 Rc)100 Rd)–100 RCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In the figure a container is shown to have a movable (without friction) piston on top. The container andthe piston are all made of perfectly insulating material allowing no heat transfer between outside andinside the container. The container is divided into two compartments by a rigid partition made of athermally conducting material that allows slow transfer of heat. The lower compartment of the container is filled with 2 moles of an ideal monatomic gas at 700 K and the upper compartment is filled with 2 moles of an ideal diatomic gas at 400 K. The heat capacities per mole of an ideal monatomic gas areand those for an ideal diatomic gas are Q.Now consider the partition to be free to move without friction so that the pressure of gases in bothcompartments is the same. Then total work done by the gases till the time they achieve equilibrium will bea)250 Rb)200 Rc)100 Rd)–100 RCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for In the figure a container is shown to have a movable (without friction) piston on top. The container andthe piston are all made of perfectly insulating material allowing no heat transfer between outside andinside the container. The container is divided into two compartments by a rigid partition made of athermally conducting material that allows slow transfer of heat. The lower compartment of the container is filled with 2 moles of an ideal monatomic gas at 700 K and the upper compartment is filled with 2 moles of an ideal diatomic gas at 400 K. The heat capacities per mole of an ideal monatomic gas areand those for an ideal diatomic gas are Q.Now consider the partition to be free to move without friction so that the pressure of gases in bothcompartments is the same. Then total work done by the gases till the time they achieve equilibrium will bea)250 Rb)200 Rc)100 Rd)–100 RCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In the figure a container is shown to have a movable (without friction) piston on top. The container andthe piston are all made of perfectly insulating material allowing no heat transfer between outside andinside the container. The container is divided into two compartments by a rigid partition made of athermally conducting material that allows slow transfer of heat. The lower compartment of the container is filled with 2 moles of an ideal monatomic gas at 700 K and the upper compartment is filled with 2 moles of an ideal diatomic gas at 400 K. The heat capacities per mole of an ideal monatomic gas areand those for an ideal diatomic gas are Q.Now consider the partition to be free to move without friction so that the pressure of gases in bothcompartments is the same. Then total work done by the gases till the time they achieve equilibrium will bea)250 Rb)200 Rc)100 Rd)–100 RCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In the figure a container is shown to have a movable (without friction) piston on top. The container andthe piston are all made of perfectly insulating material allowing no heat transfer between outside andinside the container. The container is divided into two compartments by a rigid partition made of athermally conducting material that allows slow transfer of heat. The lower compartment of the container is filled with 2 moles of an ideal monatomic gas at 700 K and the upper compartment is filled with 2 moles of an ideal diatomic gas at 400 K. The heat capacities per mole of an ideal monatomic gas areand those for an ideal diatomic gas are Q.Now consider the partition to be free to move without friction so that the pressure of gases in bothcompartments is the same. Then total work done by the gases till the time they achieve equilibrium will bea)250 Rb)200 Rc)100 Rd)–100 RCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for In the figure a container is shown to have a movable (without friction) piston on top. The container andthe piston are all made of perfectly insulating material allowing no heat transfer between outside andinside the container. The container is divided into two compartments by a rigid partition made of athermally conducting material that allows slow transfer of heat. The lower compartment of the container is filled with 2 moles of an ideal monatomic gas at 700 K and the upper compartment is filled with 2 moles of an ideal diatomic gas at 400 K. The heat capacities per mole of an ideal monatomic gas areand those for an ideal diatomic gas are Q.Now consider the partition to be free to move without friction so that the pressure of gases in bothcompartments is the same. Then total work done by the gases till the time they achieve equilibrium will bea)250 Rb)200 Rc)100 Rd)–100 RCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of In the figure a container is shown to have a movable (without friction) piston on top. The container andthe piston are all made of perfectly insulating material allowing no heat transfer between outside andinside the container. The container is divided into two compartments by a rigid partition made of athermally conducting material that allows slow transfer of heat. The lower compartment of the container is filled with 2 moles of an ideal monatomic gas at 700 K and the upper compartment is filled with 2 moles of an ideal diatomic gas at 400 K. The heat capacities per mole of an ideal monatomic gas areand those for an ideal diatomic gas are Q.Now consider the partition to be free to move without friction so that the pressure of gases in bothcompartments is the same. Then total work done by the gases till the time they achieve equilibrium will bea)250 Rb)200 Rc)100 Rd)–100 RCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In the figure a container is shown to have a movable (without friction) piston on top. The container andthe piston are all made of perfectly insulating material allowing no heat transfer between outside andinside the container. The container is divided into two compartments by a rigid partition made of athermally conducting material that allows slow transfer of heat. The lower compartment of the container is filled with 2 moles of an ideal monatomic gas at 700 K and the upper compartment is filled with 2 moles of an ideal diatomic gas at 400 K. The heat capacities per mole of an ideal monatomic gas areand those for an ideal diatomic gas are Q.Now consider the partition to be free to move without friction so that the pressure of gases in bothcompartments is the same. Then total work done by the gases till the time they achieve equilibrium will bea)250 Rb)200 Rc)100 Rd)–100 RCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Signup to solve all Doubts
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.





















