Mechanical Engineering Exam > Mechanical Engineering Questions > For good weldability, the carbon equivalent (...
Start Learning for Free
For good weldability, the carbon equivalent (%) of steel should be in the range of
- a)0.2 - 0.4
- b)0.5 - 0.8
- c)0.7 - 0.8
- d)0.9 - 1.0
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
For good weldability, the carbon equivalent (%) of steel should be in ...
Hypo eutectoid steel 0.008 - 0,76
Hyper eutectoid steel 0.76 - 2.1
Hypo eutectic steel 2.1 - 4.3
Hyper eutectic steel 4.3 - 6.64
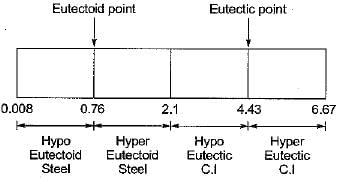
Hyper eutectoid steel 0.76 - 2.1
Hypo eutectic steel 2.1 - 4.3
Hyper eutectic steel 4.3 - 6.64

Most Upvoted Answer
For good weldability, the carbon equivalent (%) of steel should be in ...
Carbon Equivalent and Weldability of Steel
The carbon equivalent (CE) is a parameter used to measure the weldability of steel. Weldability refers to the ease with which a material can be welded without developing defects or experiencing problems during the welding process. The carbon equivalent value helps to predict the risk of cracking and other issues that may arise during welding.
Definition of Carbon Equivalent (CE)
The carbon equivalent is calculated based on the chemical composition of the steel, particularly the carbon content and the presence of other alloying elements. It is a numerical value that indicates the relative contribution of carbon and other elements to the weldability of the steel.
Range of Carbon Equivalent for Good Weldability
For good weldability, the carbon equivalent (%) of steel should be in the range of 0.2 - 0.4. This means that if the carbon equivalent value falls within this range, the steel is considered to have good weldability.
Explanation of the Correct Answer
The correct answer, option 'A' (0.2 - 0.4), is the range of carbon equivalent values that indicate good weldability. This range is widely accepted and used in various welding codes and standards.
Reason for the Range of 0.2 - 0.4
- Low Carbon Equivalent: A low carbon equivalent value indicates a low risk of cracking and other welding-related issues. This is because a lower carbon equivalent means a lower carbon content in the steel, which reduces the likelihood of hardening and cracking during welding.
- Optimum Carbon Equivalent: The range of 0.2 - 0.4 is considered the optimum range for good weldability. It strikes a balance between reducing the risk of welding defects and maintaining desirable mechanical properties in the welded joint.
- Effect of Alloying Elements: The presence of alloying elements such as manganese, silicon, and other elements affects the carbon equivalent value. These elements can help reduce the carbon equivalent and improve the weldability of the steel.
- Consideration of Welding Process: The carbon equivalent value is also influenced by the specific welding process being used. Some welding processes, such as high heat input processes, may require a lower carbon equivalent to ensure good weldability.
Conclusion
In summary, the carbon equivalent is an important parameter for assessing the weldability of steel. A carbon equivalent value in the range of 0.2 - 0.4 indicates good weldability, as it reduces the risk of welding defects while maintaining desirable mechanical properties in the welded joint. It is crucial to consider the carbon equivalent when selecting steel for welding applications to ensure successful and reliable welds.
The carbon equivalent (CE) is a parameter used to measure the weldability of steel. Weldability refers to the ease with which a material can be welded without developing defects or experiencing problems during the welding process. The carbon equivalent value helps to predict the risk of cracking and other issues that may arise during welding.
Definition of Carbon Equivalent (CE)
The carbon equivalent is calculated based on the chemical composition of the steel, particularly the carbon content and the presence of other alloying elements. It is a numerical value that indicates the relative contribution of carbon and other elements to the weldability of the steel.
Range of Carbon Equivalent for Good Weldability
For good weldability, the carbon equivalent (%) of steel should be in the range of 0.2 - 0.4. This means that if the carbon equivalent value falls within this range, the steel is considered to have good weldability.
Explanation of the Correct Answer
The correct answer, option 'A' (0.2 - 0.4), is the range of carbon equivalent values that indicate good weldability. This range is widely accepted and used in various welding codes and standards.
Reason for the Range of 0.2 - 0.4
- Low Carbon Equivalent: A low carbon equivalent value indicates a low risk of cracking and other welding-related issues. This is because a lower carbon equivalent means a lower carbon content in the steel, which reduces the likelihood of hardening and cracking during welding.
- Optimum Carbon Equivalent: The range of 0.2 - 0.4 is considered the optimum range for good weldability. It strikes a balance between reducing the risk of welding defects and maintaining desirable mechanical properties in the welded joint.
- Effect of Alloying Elements: The presence of alloying elements such as manganese, silicon, and other elements affects the carbon equivalent value. These elements can help reduce the carbon equivalent and improve the weldability of the steel.
- Consideration of Welding Process: The carbon equivalent value is also influenced by the specific welding process being used. Some welding processes, such as high heat input processes, may require a lower carbon equivalent to ensure good weldability.
Conclusion
In summary, the carbon equivalent is an important parameter for assessing the weldability of steel. A carbon equivalent value in the range of 0.2 - 0.4 indicates good weldability, as it reduces the risk of welding defects while maintaining desirable mechanical properties in the welded joint. It is crucial to consider the carbon equivalent when selecting steel for welding applications to ensure successful and reliable welds.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Question Description
For good weldability, the carbon equivalent (%) of steel should be in the range ofa)0.2 - 0.4b)0.5 - 0.8c)0.7 - 0.8d)0.9 - 1.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about For good weldability, the carbon equivalent (%) of steel should be in the range ofa)0.2 - 0.4b)0.5 - 0.8c)0.7 - 0.8d)0.9 - 1.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for For good weldability, the carbon equivalent (%) of steel should be in the range ofa)0.2 - 0.4b)0.5 - 0.8c)0.7 - 0.8d)0.9 - 1.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
For good weldability, the carbon equivalent (%) of steel should be in the range ofa)0.2 - 0.4b)0.5 - 0.8c)0.7 - 0.8d)0.9 - 1.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about For good weldability, the carbon equivalent (%) of steel should be in the range ofa)0.2 - 0.4b)0.5 - 0.8c)0.7 - 0.8d)0.9 - 1.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for For good weldability, the carbon equivalent (%) of steel should be in the range ofa)0.2 - 0.4b)0.5 - 0.8c)0.7 - 0.8d)0.9 - 1.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for For good weldability, the carbon equivalent (%) of steel should be in the range ofa)0.2 - 0.4b)0.5 - 0.8c)0.7 - 0.8d)0.9 - 1.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Mechanical Engineering.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of For good weldability, the carbon equivalent (%) of steel should be in the range ofa)0.2 - 0.4b)0.5 - 0.8c)0.7 - 0.8d)0.9 - 1.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
For good weldability, the carbon equivalent (%) of steel should be in the range ofa)0.2 - 0.4b)0.5 - 0.8c)0.7 - 0.8d)0.9 - 1.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for For good weldability, the carbon equivalent (%) of steel should be in the range ofa)0.2 - 0.4b)0.5 - 0.8c)0.7 - 0.8d)0.9 - 1.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of For good weldability, the carbon equivalent (%) of steel should be in the range ofa)0.2 - 0.4b)0.5 - 0.8c)0.7 - 0.8d)0.9 - 1.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice For good weldability, the carbon equivalent (%) of steel should be in the range ofa)0.2 - 0.4b)0.5 - 0.8c)0.7 - 0.8d)0.9 - 1.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Mechanical Engineering tests.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























