Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > How Benzene convert into toluene
Start Learning for Free
How Benzene convert into toluene
Verified Answer
How Benzene convert into toluene
Benzene is reacted with chloromethane (CH3Cl) in the presence of dry aluminium chloride (AlCl3) as a catalyst to form toluene (C6H5CH3) in equilibrium and hydrochloric acid (HCl) as a waste product: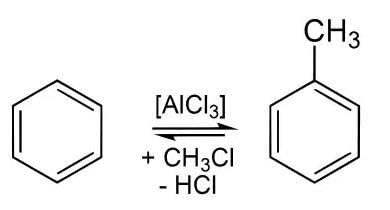

Toluene also goes by the name of Toluol, and is a colourless liquid used primarily as an industrial solvent. It is sometimes even used as a recreational inhalant, but can cause severe neurological damage if inhaled in high doses.
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 12 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 12 courses
Most Upvoted Answer
How Benzene convert into toluene
Benzene is an aromatic hydrocarbon with the molecular formula C6H6, while toluene is a compound with the molecular formula C7H8. Benzene can be converted into toluene through a process known as alkylation, specifically Friedel-Crafts alkylation. This reaction involves the substitution of a hydrogen atom on the benzene ring with an alkyl group, in this case, a methyl group (-CH3). The reaction is typically catalyzed by a Lewis acid, such as aluminum chloride (AlCl3).
The Friedel-Crafts Alkylation Reaction:
The Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction is a powerful method for introducing alkyl groups onto aromatic compounds. Here is how benzene can be converted into toluene using this reaction:
Step 1: Activation of the Lewis Acid Catalyst:
The first step involves the activation of the Lewis acid catalyst, typically aluminum chloride (AlCl3). This is achieved by adding a small amount of the catalyst to a solvent, such as anhydrous chloroform or dichloromethane. The Lewis acid catalyst functions by coordinating with the alkyl halide, making it more reactive.
Step 2: Formation of the Carbocation:
Next, the alkyl halide, in this case, methyl chloride (CH3Cl), is added to the reaction mixture. The Lewis acid catalyst activates the alkyl halide by polarizing the carbon-halogen bond, leading to the formation of a carbocation intermediate. The carbocation is a positively charged carbon atom.
Step 3: Attack of Benzene on the Carbocation:
Once the carbocation is formed, the benzene molecule acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbocation. The pi electrons of the benzene ring form a bond with the positively charged carbon atom of the carbocation, resulting in the substitution of a hydrogen atom on the benzene ring.
Step 4: Regeneration of the Catalyst:
Finally, the reaction mixture is quenched with water or a weak acid, which protonates the negatively charged complex formed between the catalyst and the alkyl group attached to the benzene ring. This leads to the formation of the final product, toluene, and regenerates the Lewis acid catalyst.
Overall Reaction:
The overall reaction can be represented as follows:
Benzene + Methyl Chloride (CH3Cl) + Lewis Acid Catalyst (AlCl3) → Toluene + Regenerated Catalyst
Summary:
- Benzene can be converted into toluene through Friedel-Crafts alkylation.
- The reaction involves the substitution of a hydrogen atom on the benzene ring with a methyl group.
- The process requires a Lewis acid catalyst, typically aluminum chloride (AlCl3).
- The reaction proceeds through the formation of a carbocation intermediate and the attack of benzene as a nucleophile.
- The reaction mixture is quenched to regenerate the catalyst and obtain the final product, toluene.
The Friedel-Crafts Alkylation Reaction:
The Friedel-Crafts alkylation reaction is a powerful method for introducing alkyl groups onto aromatic compounds. Here is how benzene can be converted into toluene using this reaction:
Step 1: Activation of the Lewis Acid Catalyst:
The first step involves the activation of the Lewis acid catalyst, typically aluminum chloride (AlCl3). This is achieved by adding a small amount of the catalyst to a solvent, such as anhydrous chloroform or dichloromethane. The Lewis acid catalyst functions by coordinating with the alkyl halide, making it more reactive.
Step 2: Formation of the Carbocation:
Next, the alkyl halide, in this case, methyl chloride (CH3Cl), is added to the reaction mixture. The Lewis acid catalyst activates the alkyl halide by polarizing the carbon-halogen bond, leading to the formation of a carbocation intermediate. The carbocation is a positively charged carbon atom.
Step 3: Attack of Benzene on the Carbocation:
Once the carbocation is formed, the benzene molecule acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbocation. The pi electrons of the benzene ring form a bond with the positively charged carbon atom of the carbocation, resulting in the substitution of a hydrogen atom on the benzene ring.
Step 4: Regeneration of the Catalyst:
Finally, the reaction mixture is quenched with water or a weak acid, which protonates the negatively charged complex formed between the catalyst and the alkyl group attached to the benzene ring. This leads to the formation of the final product, toluene, and regenerates the Lewis acid catalyst.
Overall Reaction:
The overall reaction can be represented as follows:
Benzene + Methyl Chloride (CH3Cl) + Lewis Acid Catalyst (AlCl3) → Toluene + Regenerated Catalyst
Summary:
- Benzene can be converted into toluene through Friedel-Crafts alkylation.
- The reaction involves the substitution of a hydrogen atom on the benzene ring with a methyl group.
- The process requires a Lewis acid catalyst, typically aluminum chloride (AlCl3).
- The reaction proceeds through the formation of a carbocation intermediate and the attack of benzene as a nucleophile.
- The reaction mixture is quenched to regenerate the catalyst and obtain the final product, toluene.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
How Benzene convert into toluene
Question Description
How Benzene convert into toluene for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about How Benzene convert into toluene covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for How Benzene convert into toluene.
How Benzene convert into toluene for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about How Benzene convert into toluene covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for How Benzene convert into toluene.
Solutions for How Benzene convert into toluene in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of How Benzene convert into toluene defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
How Benzene convert into toluene, a detailed solution for How Benzene convert into toluene has been provided alongside types of How Benzene convert into toluene theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice How Benzene convert into toluene tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



















