Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > In the saturation region, the ID- VGScharacte...
Start Learning for Free
In the saturation region, the ID - VGS characteristics of a MOSFET are
- a)linear
- b)quadratic
- c)exponential
- d)hyperbolic
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
In the saturation region, the ID- VGScharacteristics of a MOSFET area)...
For amplifier operation, MOSFET is always operated in saturation region.
Since,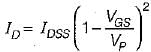 in saturation region,therefore the ID - VGS characteristics of a MOSFET are quadratic as evident from the above equation.
in saturation region,therefore the ID - VGS characteristics of a MOSFET are quadratic as evident from the above equation.
Since,
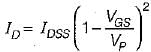 in saturation region,therefore the ID - VGS characteristics of a MOSFET are quadratic as evident from the above equation.
in saturation region,therefore the ID - VGS characteristics of a MOSFET are quadratic as evident from the above equation.Most Upvoted Answer
In the saturation region, the ID- VGScharacteristics of a MOSFET area)...
In the saturation region, the ID-VGS characteristics of a MOSFET are quadratic.
The saturation region is one of the three operating regions of a MOSFET, along with the cutoff and the triode regions. In the saturation region, the MOSFET operates as a voltage-controlled current source, and the drain current (ID) is relatively independent of the drain-to-source voltage (VDS). Instead, the drain current is primarily determined by the gate-to-source voltage (VGS).
Explanation:
In the saturation region, the MOSFET is fully turned on, and the channel between the drain and the source is pinched off. This means that the drain current is limited only by the applied gate-to-source voltage and the channel resistance. The drain current can be expressed by the quadratic equation:
ID = k * (VGS - Vth)^2
Where:
- ID is the drain current
- k is the transconductance parameter
- VGS is the gate-to-source voltage
- Vth is the threshold voltage
Key Points:
- In the saturation region, the drain current is relatively independent of the drain-to-source voltage.
- The drain current in the saturation region is primarily determined by the gate-to-source voltage.
- The drain current can be expressed by the quadratic equation ID = k * (VGS - Vth)^2.
- The quadratic relationship between ID and VGS in the saturation region is a result of the pinched-off channel and the transconductance parameter (k) of the MOSFET.
Overall, the quadratic relationship between ID and VGS in the saturation region of a MOSFET is due to the channel pinchoff and the dependence of the drain current on the gate-to-source voltage. This relationship is essential for understanding the behavior and characteristics of MOSFETs in various applications, such as amplifiers and digital circuits.
The saturation region is one of the three operating regions of a MOSFET, along with the cutoff and the triode regions. In the saturation region, the MOSFET operates as a voltage-controlled current source, and the drain current (ID) is relatively independent of the drain-to-source voltage (VDS). Instead, the drain current is primarily determined by the gate-to-source voltage (VGS).
Explanation:
In the saturation region, the MOSFET is fully turned on, and the channel between the drain and the source is pinched off. This means that the drain current is limited only by the applied gate-to-source voltage and the channel resistance. The drain current can be expressed by the quadratic equation:
ID = k * (VGS - Vth)^2
Where:
- ID is the drain current
- k is the transconductance parameter
- VGS is the gate-to-source voltage
- Vth is the threshold voltage
Key Points:
- In the saturation region, the drain current is relatively independent of the drain-to-source voltage.
- The drain current in the saturation region is primarily determined by the gate-to-source voltage.
- The drain current can be expressed by the quadratic equation ID = k * (VGS - Vth)^2.
- The quadratic relationship between ID and VGS in the saturation region is a result of the pinched-off channel and the transconductance parameter (k) of the MOSFET.
Overall, the quadratic relationship between ID and VGS in the saturation region of a MOSFET is due to the channel pinchoff and the dependence of the drain current on the gate-to-source voltage. This relationship is essential for understanding the behavior and characteristics of MOSFETs in various applications, such as amplifiers and digital circuits.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Question Description
In the saturation region, the ID- VGScharacteristics of a MOSFET area)linear b)quadraticc)exponential d)hyperbolicCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about In the saturation region, the ID- VGScharacteristics of a MOSFET area)linear b)quadraticc)exponential d)hyperbolicCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In the saturation region, the ID- VGScharacteristics of a MOSFET area)linear b)quadraticc)exponential d)hyperbolicCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
In the saturation region, the ID- VGScharacteristics of a MOSFET area)linear b)quadraticc)exponential d)hyperbolicCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about In the saturation region, the ID- VGScharacteristics of a MOSFET area)linear b)quadraticc)exponential d)hyperbolicCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In the saturation region, the ID- VGScharacteristics of a MOSFET area)linear b)quadraticc)exponential d)hyperbolicCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for In the saturation region, the ID- VGScharacteristics of a MOSFET area)linear b)quadraticc)exponential d)hyperbolicCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In the saturation region, the ID- VGScharacteristics of a MOSFET area)linear b)quadraticc)exponential d)hyperbolicCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In the saturation region, the ID- VGScharacteristics of a MOSFET area)linear b)quadraticc)exponential d)hyperbolicCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for In the saturation region, the ID- VGScharacteristics of a MOSFET area)linear b)quadraticc)exponential d)hyperbolicCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of In the saturation region, the ID- VGScharacteristics of a MOSFET area)linear b)quadraticc)exponential d)hyperbolicCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In the saturation region, the ID- VGScharacteristics of a MOSFET area)linear b)quadraticc)exponential d)hyperbolicCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















