Class 7 Exam > Class 7 Questions > Differentiate between cincave lens and convex...
Start Learning for Free
Differentiate between cincave lens and convex lens?
Verified Answer
Differentiate between cincave lens and convex lens?
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 7 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 7 courses
Most Upvoted Answer
Differentiate between cincave lens and convex lens?
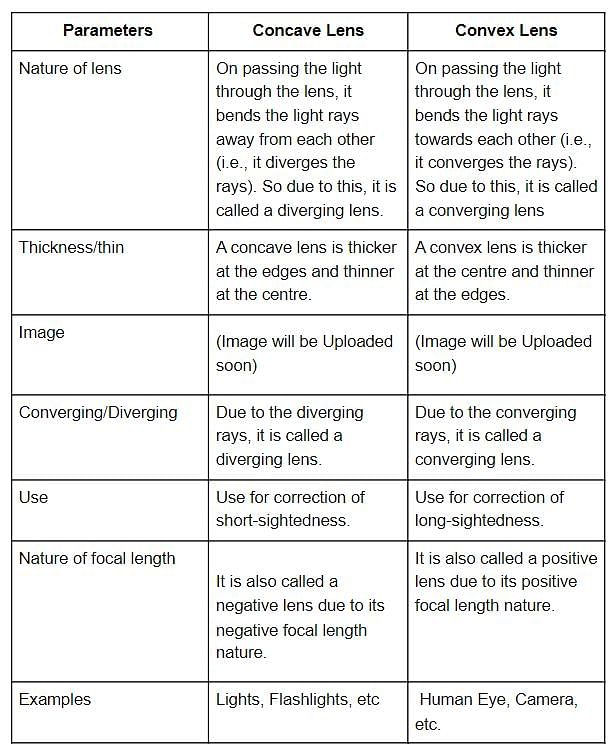
Difference between Concave Lens and Convex Lens
Concave and convex lenses are two types of optical lenses that are used in various optical systems. They have different shapes and properties, which result in different behaviors when it comes to the refraction of light. Let's explore the differences between these two lenses in detail:
Concave Lens
A concave lens is also known as a diverging lens due to its ability to diverge light rays. It is thinner at the center and thicker towards the edges, causing parallel light rays to spread out. This lens is thicker at the edges and thinner at the center.
Behavior of Concave Lens:
1. Divergence of Light: When a parallel beam of light passes through a concave lens, the rays bend away from the principal axis. This is because the lens is thinner at the center, causing the light rays to spread out.
2. Focal Point: Concave lenses have a virtual focal point located on the same side as the incident light. This focal point is the point where parallel light rays appear to converge after passing through the lens. The focal point is virtual because the light rays do not actually converge but only appear to do so.
3. Image Formation: Concave lenses create virtual and diminished images. The image formed by a concave lens is virtual, as the light rays do not actually meet. The image is also diminished, meaning it is smaller than the object.
4. Diverging Power: The diverging power of a concave lens is always negative because it causes the light rays to diverge.
Convex Lens
A convex lens is also known as a converging lens due to its ability to converge light rays. It is thicker at the center and thinner towards the edges, causing parallel light rays to come together. This lens is thicker at the center and thinner at the edges.
Behavior of Convex Lens:
1. Convergence of Light: When a parallel beam of light passes through a convex lens, the rays converge towards the principal axis. This is because the lens is thicker at the center, causing the light rays to bend towards each other.
2. Focal Point: Convex lenses have a real focal point located on the opposite side of the incident light. This focal point is the point where parallel light rays actually converge after passing through the lens.
3. Image Formation: Convex lenses create real and inverted images. The image formed by a convex lens is real because the light rays actually converge at a point. The image is also inverted, meaning it is upside down compared to the object.
4. Converging Power: The converging power of a convex lens is always positive because it causes the light rays to converge.
Conclusion
In summary, the key differences between concave and convex lenses lie in their shapes and behaviors. Concave lenses diverge light, have a virtual focal point, create virtual and diminished images, and have negative diverging power. On the other hand, convex lenses converge light, have a real focal point, create real and inverted images, and have positive converging power. Understanding these differences is essential for utilizing the correct lens in various optical systems.
Concave and convex lenses are two types of optical lenses that are used in various optical systems. They have different shapes and properties, which result in different behaviors when it comes to the refraction of light. Let's explore the differences between these two lenses in detail:
Concave Lens
A concave lens is also known as a diverging lens due to its ability to diverge light rays. It is thinner at the center and thicker towards the edges, causing parallel light rays to spread out. This lens is thicker at the edges and thinner at the center.
Behavior of Concave Lens:
1. Divergence of Light: When a parallel beam of light passes through a concave lens, the rays bend away from the principal axis. This is because the lens is thinner at the center, causing the light rays to spread out.
2. Focal Point: Concave lenses have a virtual focal point located on the same side as the incident light. This focal point is the point where parallel light rays appear to converge after passing through the lens. The focal point is virtual because the light rays do not actually converge but only appear to do so.
3. Image Formation: Concave lenses create virtual and diminished images. The image formed by a concave lens is virtual, as the light rays do not actually meet. The image is also diminished, meaning it is smaller than the object.
4. Diverging Power: The diverging power of a concave lens is always negative because it causes the light rays to diverge.
Convex Lens
A convex lens is also known as a converging lens due to its ability to converge light rays. It is thicker at the center and thinner towards the edges, causing parallel light rays to come together. This lens is thicker at the center and thinner at the edges.
Behavior of Convex Lens:
1. Convergence of Light: When a parallel beam of light passes through a convex lens, the rays converge towards the principal axis. This is because the lens is thicker at the center, causing the light rays to bend towards each other.
2. Focal Point: Convex lenses have a real focal point located on the opposite side of the incident light. This focal point is the point where parallel light rays actually converge after passing through the lens.
3. Image Formation: Convex lenses create real and inverted images. The image formed by a convex lens is real because the light rays actually converge at a point. The image is also inverted, meaning it is upside down compared to the object.
4. Converging Power: The converging power of a convex lens is always positive because it causes the light rays to converge.
Conclusion
In summary, the key differences between concave and convex lenses lie in their shapes and behaviors. Concave lenses diverge light, have a virtual focal point, create virtual and diminished images, and have negative diverging power. On the other hand, convex lenses converge light, have a real focal point, create real and inverted images, and have positive converging power. Understanding these differences is essential for utilizing the correct lens in various optical systems.

|
Explore Courses for Class 7 exam
|

|
Similar Class 7 Doubts
Differentiate between cincave lens and convex lens?
Question Description
Differentiate between cincave lens and convex lens? for Class 7 2025 is part of Class 7 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 7 exam syllabus. Information about Differentiate between cincave lens and convex lens? covers all topics & solutions for Class 7 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Differentiate between cincave lens and convex lens?.
Differentiate between cincave lens and convex lens? for Class 7 2025 is part of Class 7 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 7 exam syllabus. Information about Differentiate between cincave lens and convex lens? covers all topics & solutions for Class 7 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Differentiate between cincave lens and convex lens?.
Solutions for Differentiate between cincave lens and convex lens? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 7.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 7 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Differentiate between cincave lens and convex lens? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Differentiate between cincave lens and convex lens?, a detailed solution for Differentiate between cincave lens and convex lens? has been provided alongside types of Differentiate between cincave lens and convex lens? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Differentiate between cincave lens and convex lens? tests, examples and also practice Class 7 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 7 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























