Mechanical Engineering Exam > Mechanical Engineering Questions > Which one of the following refrigerants has t...
Start Learning for Free
Which one of the following refrigerants has the highest critical temperature?
- a)Water
- b)Carbon dioxide
- c)Freon 12
- d)Ammonia
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Which one of the following refrigerants has the highest critical tempe...
Most Upvoted Answer
Which one of the following refrigerants has the highest critical tempe...
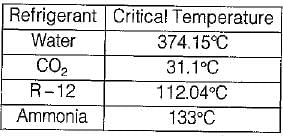
Critical Temperature of Refrigerants
The critical temperature of a refrigerant is the temperature above which the refrigerant cannot be liquefied, no matter how much pressure is applied to it. It is an important parameter to consider when selecting a refrigerant for a particular application.
Refrigerants and their Critical Temperatures
a) Water: Water has the highest critical temperature among the given options. Its critical temperature is 374°C. Due to its high critical temperature, water is not suitable for use in most refrigeration and air conditioning applications.
b) Carbon dioxide: Carbon dioxide has a critical temperature of 31°C. It is commonly used as a refrigerant in low-temperature applications, such as in food processing and storage.
c) Freon 12: Freon 12, also known as dichlorodifluoromethane, has a critical temperature of 111.4°C. It was widely used as a refrigerant in the past, but its production and use have been phased out due to its harmful effects on the environment.
d) Ammonia: Ammonia has a critical temperature of 132.4°C. It is commonly used as a refrigerant in industrial applications, such as in large refrigeration systems for food processing and storage.
Conclusion
Water has the highest critical temperature among the given options, making it unsuitable for most refrigeration and air conditioning applications. Carbon dioxide, Freon 12, and ammonia have lower critical temperatures and are commonly used as refrigerants in various applications.
The critical temperature of a refrigerant is the temperature above which the refrigerant cannot be liquefied, no matter how much pressure is applied to it. It is an important parameter to consider when selecting a refrigerant for a particular application.
Refrigerants and their Critical Temperatures
a) Water: Water has the highest critical temperature among the given options. Its critical temperature is 374°C. Due to its high critical temperature, water is not suitable for use in most refrigeration and air conditioning applications.
b) Carbon dioxide: Carbon dioxide has a critical temperature of 31°C. It is commonly used as a refrigerant in low-temperature applications, such as in food processing and storage.
c) Freon 12: Freon 12, also known as dichlorodifluoromethane, has a critical temperature of 111.4°C. It was widely used as a refrigerant in the past, but its production and use have been phased out due to its harmful effects on the environment.
d) Ammonia: Ammonia has a critical temperature of 132.4°C. It is commonly used as a refrigerant in industrial applications, such as in large refrigeration systems for food processing and storage.
Conclusion
Water has the highest critical temperature among the given options, making it unsuitable for most refrigeration and air conditioning applications. Carbon dioxide, Freon 12, and ammonia have lower critical temperatures and are commonly used as refrigerants in various applications.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Question Description
Which one of the following refrigerants has the highest critical temperature?a)Waterb)Carbon dioxidec)Freon 12d)AmmoniaCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about Which one of the following refrigerants has the highest critical temperature?a)Waterb)Carbon dioxidec)Freon 12d)AmmoniaCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which one of the following refrigerants has the highest critical temperature?a)Waterb)Carbon dioxidec)Freon 12d)AmmoniaCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Which one of the following refrigerants has the highest critical temperature?a)Waterb)Carbon dioxidec)Freon 12d)AmmoniaCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about Which one of the following refrigerants has the highest critical temperature?a)Waterb)Carbon dioxidec)Freon 12d)AmmoniaCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which one of the following refrigerants has the highest critical temperature?a)Waterb)Carbon dioxidec)Freon 12d)AmmoniaCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Which one of the following refrigerants has the highest critical temperature?a)Waterb)Carbon dioxidec)Freon 12d)AmmoniaCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Mechanical Engineering.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Which one of the following refrigerants has the highest critical temperature?a)Waterb)Carbon dioxidec)Freon 12d)AmmoniaCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Which one of the following refrigerants has the highest critical temperature?a)Waterb)Carbon dioxidec)Freon 12d)AmmoniaCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Which one of the following refrigerants has the highest critical temperature?a)Waterb)Carbon dioxidec)Freon 12d)AmmoniaCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Which one of the following refrigerants has the highest critical temperature?a)Waterb)Carbon dioxidec)Freon 12d)AmmoniaCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Which one of the following refrigerants has the highest critical temperature?a)Waterb)Carbon dioxidec)Freon 12d)AmmoniaCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Mechanical Engineering tests.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























