Mechanical Engineering Exam > Mechanical Engineering Questions > Strain energy stored in a solid circular sha...
Start Learning for Free
Strain energy stored in a solid circular shaft subjected to torsion is proportional to
- a)GJ
- b)(GJ)2
- c)1/GJ
- d)1/(GJ)2
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Strain energy stored in a solid circular shaft subjected to torsion i...
Strain energy due to torsion
View all questions of this test
U = 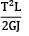
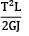
∴ U ∝ 1/GJ
Most Upvoted Answer
Strain energy stored in a solid circular shaft subjected to torsion i...
Strain energy due to torsion
U = 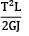
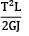
∴ U ∝ 1/GJ
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Strain energy stored in a solid circular shaft subjected to torsion i...
Strain Energy in a Solid Circular Shaft Subjected to Torsion
Torsion is a type of mechanical loading that causes twisting of an object around its longitudinal axis. When a circular shaft is subjected to torsion, it experiences shear stress distribution across its cross-section, resulting in the deformation of the material. This deformation results in the storage of strain energy within the shaft.
Strain Energy Proportional to 1/GJ
The strain energy stored in a solid circular shaft subjected to torsion is proportional to 1/GJ, where G is the shear modulus of the material and J is the polar moment of inertia of the shaft's cross-section.
Let's understand why the strain energy is proportional to 1/GJ in more detail:
Shear Strain Energy
When a shaft is subjected to torsion, shear stress is induced in the material. This shear stress causes shear strain, which is the angular deformation of the shaft. The work done by the shear stress in deforming the material results in the storage of strain energy.
Shear Modulus (G)
The shear modulus (G) is a material property that represents the ratio of shear stress to shear strain within the elastic range. It quantifies the material's resistance to deformation under shear stress. A higher shear modulus indicates a stiffer material.
Polar Moment of Inertia (J)
The polar moment of inertia (J) is a geometric property of the shaft's cross-section that determines its resistance to torsional deformation. It is analogous to the moment of inertia in bending. A larger J value indicates a greater resistance to torsion.
Proportional Relationship
The strain energy stored in a circular shaft subjected to torsion is directly proportional to the shear modulus (G) and inversely proportional to the polar moment of inertia (J). Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
Strain Energy ∝ 1/(GJ)
This relationship implies that increasing the shear modulus or decreasing the polar moment of inertia will result in a higher strain energy storage in the shaft.
Conclusion
In summary, the strain energy stored in a solid circular shaft subjected to torsion is proportional to 1/(GJ), where G is the shear modulus and J is the polar moment of inertia. This relationship highlights the importance of material stiffness and shaft geometry in determining the amount of strain energy stored during torsional loading.
Torsion is a type of mechanical loading that causes twisting of an object around its longitudinal axis. When a circular shaft is subjected to torsion, it experiences shear stress distribution across its cross-section, resulting in the deformation of the material. This deformation results in the storage of strain energy within the shaft.
Strain Energy Proportional to 1/GJ
The strain energy stored in a solid circular shaft subjected to torsion is proportional to 1/GJ, where G is the shear modulus of the material and J is the polar moment of inertia of the shaft's cross-section.
Let's understand why the strain energy is proportional to 1/GJ in more detail:
Shear Strain Energy
When a shaft is subjected to torsion, shear stress is induced in the material. This shear stress causes shear strain, which is the angular deformation of the shaft. The work done by the shear stress in deforming the material results in the storage of strain energy.
Shear Modulus (G)
The shear modulus (G) is a material property that represents the ratio of shear stress to shear strain within the elastic range. It quantifies the material's resistance to deformation under shear stress. A higher shear modulus indicates a stiffer material.
Polar Moment of Inertia (J)
The polar moment of inertia (J) is a geometric property of the shaft's cross-section that determines its resistance to torsional deformation. It is analogous to the moment of inertia in bending. A larger J value indicates a greater resistance to torsion.
Proportional Relationship
The strain energy stored in a circular shaft subjected to torsion is directly proportional to the shear modulus (G) and inversely proportional to the polar moment of inertia (J). Mathematically, it can be expressed as:
Strain Energy ∝ 1/(GJ)
This relationship implies that increasing the shear modulus or decreasing the polar moment of inertia will result in a higher strain energy storage in the shaft.
Conclusion
In summary, the strain energy stored in a solid circular shaft subjected to torsion is proportional to 1/(GJ), where G is the shear modulus and J is the polar moment of inertia. This relationship highlights the importance of material stiffness and shaft geometry in determining the amount of strain energy stored during torsional loading.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Question Description
Strain energy stored in a solid circular shaft subjected to torsion is proportional toa) GJb) (GJ)2c) 1/GJd) 1/(GJ)2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about Strain energy stored in a solid circular shaft subjected to torsion is proportional toa) GJb) (GJ)2c) 1/GJd) 1/(GJ)2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Strain energy stored in a solid circular shaft subjected to torsion is proportional toa) GJb) (GJ)2c) 1/GJd) 1/(GJ)2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Strain energy stored in a solid circular shaft subjected to torsion is proportional toa) GJb) (GJ)2c) 1/GJd) 1/(GJ)2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2025 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about Strain energy stored in a solid circular shaft subjected to torsion is proportional toa) GJb) (GJ)2c) 1/GJd) 1/(GJ)2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Strain energy stored in a solid circular shaft subjected to torsion is proportional toa) GJb) (GJ)2c) 1/GJd) 1/(GJ)2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Strain energy stored in a solid circular shaft subjected to torsion is proportional toa) GJb) (GJ)2c) 1/GJd) 1/(GJ)2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Mechanical Engineering.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Strain energy stored in a solid circular shaft subjected to torsion is proportional toa) GJb) (GJ)2c) 1/GJd) 1/(GJ)2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Strain energy stored in a solid circular shaft subjected to torsion is proportional toa) GJb) (GJ)2c) 1/GJd) 1/(GJ)2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Strain energy stored in a solid circular shaft subjected to torsion is proportional toa) GJb) (GJ)2c) 1/GJd) 1/(GJ)2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Strain energy stored in a solid circular shaft subjected to torsion is proportional toa) GJb) (GJ)2c) 1/GJd) 1/(GJ)2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Strain energy stored in a solid circular shaft subjected to torsion is proportional toa) GJb) (GJ)2c) 1/GJd) 1/(GJ)2Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Mechanical Engineering tests.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















