Chemical Engineering Exam > Chemical Engineering Questions > Two infinitely long cylinders are placed coax...
Start Learning for Free
Two infinitely long cylinders are placed coaxially. The inner cylinder has an outside diameter of 7.5 cm, and emissivity of 0.1 and is maintained at 1050 K. The outer cylinder has an inside diameter of 22.5 cm, an emissivity of 0.2 and is maintained at 315 K. A cylindrical shield (very thin so that its temperature is the same on both sides) is placed concentrically midway between the two cylinders and allowed to come to thermal equilibrium. It has an emissivity of 0.3 on both sides. Assuming that vacuum exists between the annular spaces. Find the steady state temperature attained by the cylindrical shield.
- a)715.0
- b)718.0
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Two infinitely long cylinders are placed coaxially. The inner cylinder...
Since the shield is placed midway between both the cylinders, therefore diameter of the shield
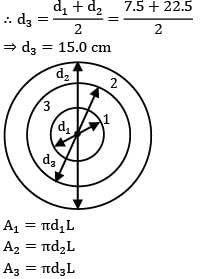
∴ d3 = d1+d2/2 = 7.5 + 22.5/2
⇒ d3 = 15.0 cm
A1 = πd1L
A2 = πd2L
A3 = πd3L
For the system to be steady,
(Q1➝3)net = (Q3➝2)net
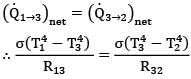
By thermal circuits
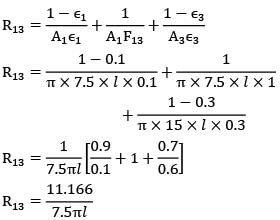
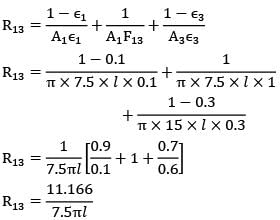
R13 = 11.166/7.5πl
Similarly,
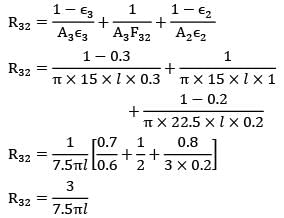
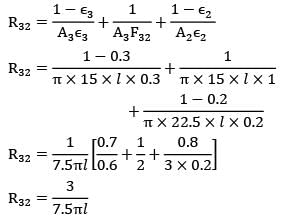
R32 = 3/7.5πl
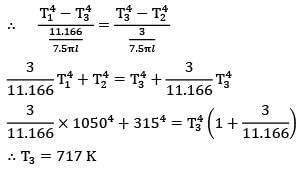
∴ T3 = 717 K
Question_type 5
Most Upvoted Answer
Two infinitely long cylinders are placed coaxially. The inner cylinder...
Since the shield is placed midway between both the cylinders, therefore diameter of the shield

∴ d3 = d1+d2/2 = 7.5 + 22.5/2
⇒ d3 = 15.0 cm
A1 = πd1L
A2 = πd2L
A3 = πd3L
For the system to be steady,
(Q1➝3)net = (Q3➝2)net
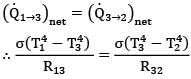
By thermal circuits
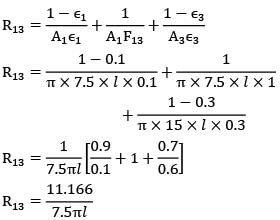
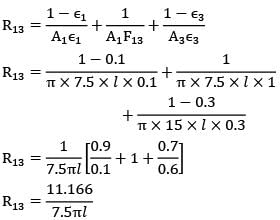
R13 = 11.166/7.5πl
Similarly,
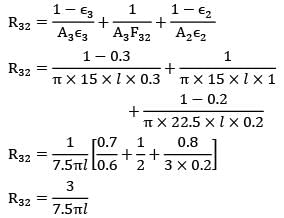
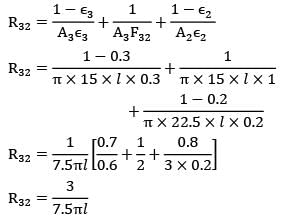
R32 = 3/7.5πl
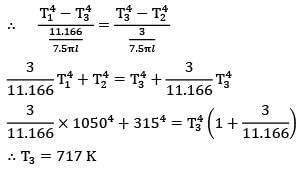
∴ T3 = 717 K
Question_type 5
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Two infinitely long cylinders are placed coaxially. The inner cylinder...
Given:
- Inner cylinder: outside diameter = 7.5 cm, emissivity = 0.1, temperature = 1050 K
- Outer cylinder: inside diameter = 22.5 cm, emissivity = 0.2, temperature = 315 K
- Shield: emissivity = 0.3 on both sides
Assumptions:
- The system is in steady state.
- Vacuum exists between the annular spaces.
- The entire system is cylindrical and coaxial.
Approach:
1. Calculate the radiation heat transfer rates between the inner and outer cylinders and the shield.
2. Determine the net radiation heat transfer rate between the inner and outer cylinders.
3. Apply the energy balance equation to evaluate the steady-state temperature of the shield.
Solution:
Step 1: Radiation heat transfer rates
- The radiation heat transfer rate between two surfaces is given by the equation:
q = εσA(T₁⁴ - T₂⁴)
where q is the heat transfer rate, ε is the emissivity, σ is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant, A is the surface area, and T₁ and T₂ are the temperatures of the two surfaces.
- The heat transfer rate between the inner and outer cylinders can be calculated as:
q₁₂ = ε₁₂σA₁₂(T₁² - T₂²)
where ε₁₂ = (ε₁ + ε₂ - 1)/[(1/ε₁) + (1/ε₂) - 1] is the effective emissivity, A₁₂ is the surface area between the cylinders, and T₁ and T₂ are the temperatures of the inner and outer cylinders, respectively.
- The heat transfer rate between the shield and the inner cylinder can be calculated as:
q₁s = ε₁sσA₁s(T₁² - Ts²)
where ε₁s is the emissivity of the inner side of the shield, A₁s is the surface area between the inner cylinder and the shield, and Ts is the temperature of the shield.
- The heat transfer rate between the shield and the outer cylinder can be calculated as:
qs₂ = εs₂σAs₂(Ts² - T₂²)
where εs₂ is the emissivity of the outer side of the shield, As₂ is the surface area between the outer cylinder and the shield, and Ts is the temperature of the shield.
Step 2: Net radiation heat transfer rate
- The net radiation heat transfer rate between the inner and outer cylinders is given by the difference in heat transfer rates:
q_net = q₁₂ - q₁s - qs₂
Step 3: Energy balance equation
- The energy balance equation for the shield can be written as:
q_net = mcΔT
where mc is the mass of the shield and ΔT is the change in temperature.
- Since the shield is in thermal equilibrium, the change in temperature is zero (ΔT = 0).
- Therefore, the net radiation heat transfer rate is also zero (q_net = 0).
- Substituting the values of the heat transfer rates, we can solve for Ts.
Detailed Calculation:
1. Calculation of surface areas:
- The surface
- Inner cylinder: outside diameter = 7.5 cm, emissivity = 0.1, temperature = 1050 K
- Outer cylinder: inside diameter = 22.5 cm, emissivity = 0.2, temperature = 315 K
- Shield: emissivity = 0.3 on both sides
Assumptions:
- The system is in steady state.
- Vacuum exists between the annular spaces.
- The entire system is cylindrical and coaxial.
Approach:
1. Calculate the radiation heat transfer rates between the inner and outer cylinders and the shield.
2. Determine the net radiation heat transfer rate between the inner and outer cylinders.
3. Apply the energy balance equation to evaluate the steady-state temperature of the shield.
Solution:
Step 1: Radiation heat transfer rates
- The radiation heat transfer rate between two surfaces is given by the equation:
q = εσA(T₁⁴ - T₂⁴)
where q is the heat transfer rate, ε is the emissivity, σ is the Stefan-Boltzmann constant, A is the surface area, and T₁ and T₂ are the temperatures of the two surfaces.
- The heat transfer rate between the inner and outer cylinders can be calculated as:
q₁₂ = ε₁₂σA₁₂(T₁² - T₂²)
where ε₁₂ = (ε₁ + ε₂ - 1)/[(1/ε₁) + (1/ε₂) - 1] is the effective emissivity, A₁₂ is the surface area between the cylinders, and T₁ and T₂ are the temperatures of the inner and outer cylinders, respectively.
- The heat transfer rate between the shield and the inner cylinder can be calculated as:
q₁s = ε₁sσA₁s(T₁² - Ts²)
where ε₁s is the emissivity of the inner side of the shield, A₁s is the surface area between the inner cylinder and the shield, and Ts is the temperature of the shield.
- The heat transfer rate between the shield and the outer cylinder can be calculated as:
qs₂ = εs₂σAs₂(Ts² - T₂²)
where εs₂ is the emissivity of the outer side of the shield, As₂ is the surface area between the outer cylinder and the shield, and Ts is the temperature of the shield.
Step 2: Net radiation heat transfer rate
- The net radiation heat transfer rate between the inner and outer cylinders is given by the difference in heat transfer rates:
q_net = q₁₂ - q₁s - qs₂
Step 3: Energy balance equation
- The energy balance equation for the shield can be written as:
q_net = mcΔT
where mc is the mass of the shield and ΔT is the change in temperature.
- Since the shield is in thermal equilibrium, the change in temperature is zero (ΔT = 0).
- Therefore, the net radiation heat transfer rate is also zero (q_net = 0).
- Substituting the values of the heat transfer rates, we can solve for Ts.
Detailed Calculation:
1. Calculation of surface areas:
- The surface

|
Explore Courses for Chemical Engineering exam
|

|
Question Description
Two infinitely long cylinders are placed coaxially. The inner cylinder has an outside diameter of 7.5 cm, and emissivity of 0.1 and is maintained at 1050 K. The outer cylinder has an inside diameter of 22.5 cm, an emissivity of 0.2 and is maintained at 315 K. A cylindrical shield (very thin so that its temperature is the same on both sides) is placed concentrically midway between the two cylinders and allowed to come to thermal equilibrium. It has an emissivity of 0.3 on both sides. Assuming that vacuum exists between the annular spaces. Find the steady state temperature attained by the cylindrical shield.a)715.0b)718.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Chemical Engineering 2025 is part of Chemical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Chemical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about Two infinitely long cylinders are placed coaxially. The inner cylinder has an outside diameter of 7.5 cm, and emissivity of 0.1 and is maintained at 1050 K. The outer cylinder has an inside diameter of 22.5 cm, an emissivity of 0.2 and is maintained at 315 K. A cylindrical shield (very thin so that its temperature is the same on both sides) is placed concentrically midway between the two cylinders and allowed to come to thermal equilibrium. It has an emissivity of 0.3 on both sides. Assuming that vacuum exists between the annular spaces. Find the steady state temperature attained by the cylindrical shield.a)715.0b)718.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Chemical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Two infinitely long cylinders are placed coaxially. The inner cylinder has an outside diameter of 7.5 cm, and emissivity of 0.1 and is maintained at 1050 K. The outer cylinder has an inside diameter of 22.5 cm, an emissivity of 0.2 and is maintained at 315 K. A cylindrical shield (very thin so that its temperature is the same on both sides) is placed concentrically midway between the two cylinders and allowed to come to thermal equilibrium. It has an emissivity of 0.3 on both sides. Assuming that vacuum exists between the annular spaces. Find the steady state temperature attained by the cylindrical shield.a)715.0b)718.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Two infinitely long cylinders are placed coaxially. The inner cylinder has an outside diameter of 7.5 cm, and emissivity of 0.1 and is maintained at 1050 K. The outer cylinder has an inside diameter of 22.5 cm, an emissivity of 0.2 and is maintained at 315 K. A cylindrical shield (very thin so that its temperature is the same on both sides) is placed concentrically midway between the two cylinders and allowed to come to thermal equilibrium. It has an emissivity of 0.3 on both sides. Assuming that vacuum exists between the annular spaces. Find the steady state temperature attained by the cylindrical shield.a)715.0b)718.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Chemical Engineering 2025 is part of Chemical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Chemical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about Two infinitely long cylinders are placed coaxially. The inner cylinder has an outside diameter of 7.5 cm, and emissivity of 0.1 and is maintained at 1050 K. The outer cylinder has an inside diameter of 22.5 cm, an emissivity of 0.2 and is maintained at 315 K. A cylindrical shield (very thin so that its temperature is the same on both sides) is placed concentrically midway between the two cylinders and allowed to come to thermal equilibrium. It has an emissivity of 0.3 on both sides. Assuming that vacuum exists between the annular spaces. Find the steady state temperature attained by the cylindrical shield.a)715.0b)718.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Chemical Engineering 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Two infinitely long cylinders are placed coaxially. The inner cylinder has an outside diameter of 7.5 cm, and emissivity of 0.1 and is maintained at 1050 K. The outer cylinder has an inside diameter of 22.5 cm, an emissivity of 0.2 and is maintained at 315 K. A cylindrical shield (very thin so that its temperature is the same on both sides) is placed concentrically midway between the two cylinders and allowed to come to thermal equilibrium. It has an emissivity of 0.3 on both sides. Assuming that vacuum exists between the annular spaces. Find the steady state temperature attained by the cylindrical shield.a)715.0b)718.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Two infinitely long cylinders are placed coaxially. The inner cylinder has an outside diameter of 7.5 cm, and emissivity of 0.1 and is maintained at 1050 K. The outer cylinder has an inside diameter of 22.5 cm, an emissivity of 0.2 and is maintained at 315 K. A cylindrical shield (very thin so that its temperature is the same on both sides) is placed concentrically midway between the two cylinders and allowed to come to thermal equilibrium. It has an emissivity of 0.3 on both sides. Assuming that vacuum exists between the annular spaces. Find the steady state temperature attained by the cylindrical shield.a)715.0b)718.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Chemical Engineering.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Chemical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Two infinitely long cylinders are placed coaxially. The inner cylinder has an outside diameter of 7.5 cm, and emissivity of 0.1 and is maintained at 1050 K. The outer cylinder has an inside diameter of 22.5 cm, an emissivity of 0.2 and is maintained at 315 K. A cylindrical shield (very thin so that its temperature is the same on both sides) is placed concentrically midway between the two cylinders and allowed to come to thermal equilibrium. It has an emissivity of 0.3 on both sides. Assuming that vacuum exists between the annular spaces. Find the steady state temperature attained by the cylindrical shield.a)715.0b)718.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Two infinitely long cylinders are placed coaxially. The inner cylinder has an outside diameter of 7.5 cm, and emissivity of 0.1 and is maintained at 1050 K. The outer cylinder has an inside diameter of 22.5 cm, an emissivity of 0.2 and is maintained at 315 K. A cylindrical shield (very thin so that its temperature is the same on both sides) is placed concentrically midway between the two cylinders and allowed to come to thermal equilibrium. It has an emissivity of 0.3 on both sides. Assuming that vacuum exists between the annular spaces. Find the steady state temperature attained by the cylindrical shield.a)715.0b)718.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Two infinitely long cylinders are placed coaxially. The inner cylinder has an outside diameter of 7.5 cm, and emissivity of 0.1 and is maintained at 1050 K. The outer cylinder has an inside diameter of 22.5 cm, an emissivity of 0.2 and is maintained at 315 K. A cylindrical shield (very thin so that its temperature is the same on both sides) is placed concentrically midway between the two cylinders and allowed to come to thermal equilibrium. It has an emissivity of 0.3 on both sides. Assuming that vacuum exists between the annular spaces. Find the steady state temperature attained by the cylindrical shield.a)715.0b)718.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Two infinitely long cylinders are placed coaxially. The inner cylinder has an outside diameter of 7.5 cm, and emissivity of 0.1 and is maintained at 1050 K. The outer cylinder has an inside diameter of 22.5 cm, an emissivity of 0.2 and is maintained at 315 K. A cylindrical shield (very thin so that its temperature is the same on both sides) is placed concentrically midway between the two cylinders and allowed to come to thermal equilibrium. It has an emissivity of 0.3 on both sides. Assuming that vacuum exists between the annular spaces. Find the steady state temperature attained by the cylindrical shield.a)715.0b)718.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Two infinitely long cylinders are placed coaxially. The inner cylinder has an outside diameter of 7.5 cm, and emissivity of 0.1 and is maintained at 1050 K. The outer cylinder has an inside diameter of 22.5 cm, an emissivity of 0.2 and is maintained at 315 K. A cylindrical shield (very thin so that its temperature is the same on both sides) is placed concentrically midway between the two cylinders and allowed to come to thermal equilibrium. It has an emissivity of 0.3 on both sides. Assuming that vacuum exists between the annular spaces. Find the steady state temperature attained by the cylindrical shield.a)715.0b)718.0Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Chemical Engineering tests.

|
Explore Courses for Chemical Engineering exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















