Mechanical Engineering Exam > Mechanical Engineering Questions > Assertion (A): Soderberg relation is used fo...
Start Learning for Free
Assertion (A): Soderberg relation is used for design against fatigue.
Reason (R): Soderberg relation is based on yield strength of the material whereas all other failure relations for dynamic loading are based on ultimate strength of the material.
- a)both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A
- b)both A and R are individually true but R is not the correct explanation of A
- c)A is true but R is false
- d)A is false but R is true
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Assertion (A): Soderberg relation is used for design against fatigue....
Soderberg’s equation:
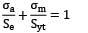
For fatigue load we use Soderberg, Gerber, Goodman criteria for the design.
⇒When there is a combination of variable stress with the mean stress, then we use the above three design parameters.
⇒So, both Assertion and Reason are correct but Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion.
Most Upvoted Answer
Assertion (A): Soderberg relation is used for design against fatigue....
Assertion (A): Soderberg relation is used for design against fatigue.
Reason (R): Soderberg relation is based on yield strength of the material whereas all other failure relations for dynamic loading are based on ultimate strength of the material.
Explanation:
The Soderberg relation is a commonly used method for designing against fatigue failure. It takes into account the yield strength of the material, which is the maximum stress that a material can withstand without permanent deformation.
Fatigue failure occurs when a material is subjected to repeated loading and unloading cycles, leading to crack initiation and propagation. The Soderberg relation considers the yield strength of the material and the alternating stress level to determine whether the design is safe against fatigue failure.
Explanation of Assertion (A):
The assertion states that the Soderberg relation is used for design against fatigue, which is true. The Soderberg relation provides a conservative estimate of the allowable stress range by considering the yield strength of the material. It ensures that the design does not exceed the material's yield strength and prevents the initiation and propagation of cracks under cyclic loading.
Explanation of Reason (R):
The reason states that the Soderberg relation is based on the yield strength of the material while other failure relations for dynamic loading are based on the ultimate strength of the material. This is also true. The ultimate strength of a material is the maximum stress it can withstand before failure, while the yield strength is the stress at which the material begins to exhibit plastic deformation.
In the context of dynamic loading, such as fatigue, it is more conservative to use the yield strength in design calculations. This is because the alternating stress levels in cyclic loading are typically much lower than the ultimate strength of the material. By using the yield strength, the design ensures that the material remains in the elastic range and does not experience permanent deformation or failure.
Explanation of the Correct Answer:
Both the assertion and the reason are individually true. The Soderberg relation is indeed used for design against fatigue, and it is based on the yield strength of the material. Additionally, the reason correctly explains why the Soderberg relation is based on yield strength rather than ultimate strength. Therefore, the correct answer is option B.
Reason (R): Soderberg relation is based on yield strength of the material whereas all other failure relations for dynamic loading are based on ultimate strength of the material.
Explanation:
The Soderberg relation is a commonly used method for designing against fatigue failure. It takes into account the yield strength of the material, which is the maximum stress that a material can withstand without permanent deformation.
Fatigue failure occurs when a material is subjected to repeated loading and unloading cycles, leading to crack initiation and propagation. The Soderberg relation considers the yield strength of the material and the alternating stress level to determine whether the design is safe against fatigue failure.
Explanation of Assertion (A):
The assertion states that the Soderberg relation is used for design against fatigue, which is true. The Soderberg relation provides a conservative estimate of the allowable stress range by considering the yield strength of the material. It ensures that the design does not exceed the material's yield strength and prevents the initiation and propagation of cracks under cyclic loading.
Explanation of Reason (R):
The reason states that the Soderberg relation is based on the yield strength of the material while other failure relations for dynamic loading are based on the ultimate strength of the material. This is also true. The ultimate strength of a material is the maximum stress it can withstand before failure, while the yield strength is the stress at which the material begins to exhibit plastic deformation.
In the context of dynamic loading, such as fatigue, it is more conservative to use the yield strength in design calculations. This is because the alternating stress levels in cyclic loading are typically much lower than the ultimate strength of the material. By using the yield strength, the design ensures that the material remains in the elastic range and does not experience permanent deformation or failure.
Explanation of the Correct Answer:
Both the assertion and the reason are individually true. The Soderberg relation is indeed used for design against fatigue, and it is based on the yield strength of the material. Additionally, the reason correctly explains why the Soderberg relation is based on yield strength rather than ultimate strength. Therefore, the correct answer is option B.
Attention Mechanical Engineering Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Mechanical Engineering study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Mechanical Engineering.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Similar Mechanical Engineering Doubts
Assertion (A): Soderberg relation is used for design against fatigue.Reason (R): Soderberg relation is based on yield strength of the material whereas all other failure relations for dynamic loading are based on ultimate strength of the material.a) both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of Ab) both A and R are individually true but R is not the correct explanation of Ac) A is true but R is falsed) A is false but R is trueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Assertion (A): Soderberg relation is used for design against fatigue.Reason (R): Soderberg relation is based on yield strength of the material whereas all other failure relations for dynamic loading are based on ultimate strength of the material.a) both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of Ab) both A and R are individually true but R is not the correct explanation of Ac) A is true but R is falsed) A is false but R is trueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2024 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about Assertion (A): Soderberg relation is used for design against fatigue.Reason (R): Soderberg relation is based on yield strength of the material whereas all other failure relations for dynamic loading are based on ultimate strength of the material.a) both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of Ab) both A and R are individually true but R is not the correct explanation of Ac) A is true but R is falsed) A is false but R is trueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Assertion (A): Soderberg relation is used for design against fatigue.Reason (R): Soderberg relation is based on yield strength of the material whereas all other failure relations for dynamic loading are based on ultimate strength of the material.a) both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of Ab) both A and R are individually true but R is not the correct explanation of Ac) A is true but R is falsed) A is false but R is trueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Assertion (A): Soderberg relation is used for design against fatigue.Reason (R): Soderberg relation is based on yield strength of the material whereas all other failure relations for dynamic loading are based on ultimate strength of the material.a) both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of Ab) both A and R are individually true but R is not the correct explanation of Ac) A is true but R is falsed) A is false but R is trueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2024 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about Assertion (A): Soderberg relation is used for design against fatigue.Reason (R): Soderberg relation is based on yield strength of the material whereas all other failure relations for dynamic loading are based on ultimate strength of the material.a) both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of Ab) both A and R are individually true but R is not the correct explanation of Ac) A is true but R is falsed) A is false but R is trueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Assertion (A): Soderberg relation is used for design against fatigue.Reason (R): Soderberg relation is based on yield strength of the material whereas all other failure relations for dynamic loading are based on ultimate strength of the material.a) both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of Ab) both A and R are individually true but R is not the correct explanation of Ac) A is true but R is falsed) A is false but R is trueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Assertion (A): Soderberg relation is used for design against fatigue.Reason (R): Soderberg relation is based on yield strength of the material whereas all other failure relations for dynamic loading are based on ultimate strength of the material.a) both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of Ab) both A and R are individually true but R is not the correct explanation of Ac) A is true but R is falsed) A is false but R is trueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Mechanical Engineering.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Assertion (A): Soderberg relation is used for design against fatigue.Reason (R): Soderberg relation is based on yield strength of the material whereas all other failure relations for dynamic loading are based on ultimate strength of the material.a) both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of Ab) both A and R are individually true but R is not the correct explanation of Ac) A is true but R is falsed) A is false but R is trueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Assertion (A): Soderberg relation is used for design against fatigue.Reason (R): Soderberg relation is based on yield strength of the material whereas all other failure relations for dynamic loading are based on ultimate strength of the material.a) both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of Ab) both A and R are individually true but R is not the correct explanation of Ac) A is true but R is falsed) A is false but R is trueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Assertion (A): Soderberg relation is used for design against fatigue.Reason (R): Soderberg relation is based on yield strength of the material whereas all other failure relations for dynamic loading are based on ultimate strength of the material.a) both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of Ab) both A and R are individually true but R is not the correct explanation of Ac) A is true but R is falsed) A is false but R is trueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Assertion (A): Soderberg relation is used for design against fatigue.Reason (R): Soderberg relation is based on yield strength of the material whereas all other failure relations for dynamic loading are based on ultimate strength of the material.a) both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of Ab) both A and R are individually true but R is not the correct explanation of Ac) A is true but R is falsed) A is false but R is trueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Assertion (A): Soderberg relation is used for design against fatigue.Reason (R): Soderberg relation is based on yield strength of the material whereas all other failure relations for dynamic loading are based on ultimate strength of the material.a) both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of Ab) both A and R are individually true but R is not the correct explanation of Ac) A is true but R is falsed) A is false but R is trueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Mechanical Engineering tests.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























