Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > The suction pipe of a pump rises at a slope ...
Start Learning for Free
The suction pipe of a pump rises at a slope of 2 vertically in 3 along the pipe, which is 10 cm in diameter. The pipe is 6 m long; its lower end being just below the surface of water in the reservoir. For design reasons, it is undesirable that pressure at inlet to the pump fall more than 75 kN⁄m2 below atmospheric pressure. Neglecting friction, make calculations for the maximum discharge (in L/s) that the pump may deliver.
Take atmospheric pressure = 100 kN⁄m2
Correct answer is 'Range: 66 to 67'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
The suction pipe of a pump rises at a slope of 2 vertically in 3 alon...
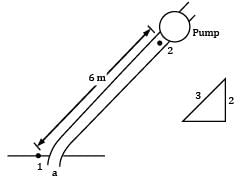
Let us consider a point a at the inlet of section pipe where the fluid is actually moving. Applying Bernoulli’s equation between a and 2
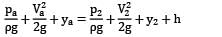
Where h represents any kind of losses in the flow. In this equation, ?? cannot be predicted as the fluid is moving, hence let us take point 1 on the free surface where the fluid particles start moving.
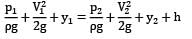

If we neglect friction loss
h = 0
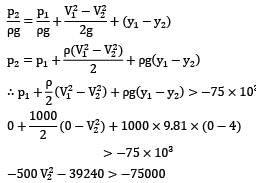
V2 < 8.457="" />
Thus maximum possible discharge is
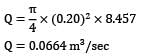
= 66.4 Lt/sec
Most Upvoted Answer
The suction pipe of a pump rises at a slope of 2 vertically in 3 alon...

Let us consider a point a at the inlet of section pipe where the fluid is actually moving. Applying Bernoulli’s equation between a and 2
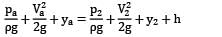
Where h represents any kind of losses in the flow. In this equation, ?? cannot be predicted as the fluid is moving, hence let us take point 1 on the free surface where the fluid particles start moving.
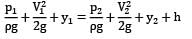

If we neglect friction loss
h = 0
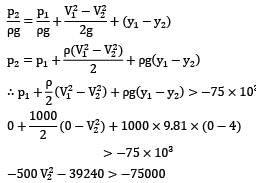
V2 < 8.457="" />
Thus maximum possible discharge is
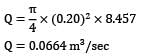
= 66.4 Lt/sec
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The suction pipe of a pump rises at a slope of 2 vertically in 3 alon...
Given data:
- Slope of the suction pipe: 2 vertically in 3 horizontally
- Diameter of the pipe: 10 cm
- Length of the pipe: 6 m
- Pressure limit: 75 kN/m2 below atmospheric pressure
Calculations:
1. Convert the slope to an angle:
- The slope is given as 2 vertically in 3 horizontally.
- This can be written as a ratio of rise to run: 2/3.
- The angle θ can be calculated using the tangent function: tan(θ) = rise/run.
- Plugging in the values, we get: tan(θ) = 2/3.
- Solving for θ, we find: θ = arctan(2/3).
- Using a scientific calculator, we get: θ ≈ 33.69°.
2. Calculate the height difference between the lower end of the pipe and the water surface:
- The length of the pipe is given as 6 m.
- The rise of the pipe can be calculated using the angle θ: rise = 6 * tan(θ).
- Plugging in the values, we get: rise = 6 * tan(33.69°).
- Using a scientific calculator, we get: rise ≈ 4.84 m.
- Since the lower end of the pipe is just below the water surface, the height difference is equal to the rise: h = 4.84 m.
3. Calculate the pressure at the inlet to the pump:
- The pressure at the inlet to the pump is given by the difference in height between the water surface and the pump inlet, multiplied by the unit weight of water: P = h * γ.
- The unit weight of water is equal to the density of water multiplied by the acceleration due to gravity: γ = ρ * g.
- The density of water is approximately 1000 kg/m3, and the acceleration due to gravity is approximately 9.81 m/s2.
- Plugging in the values, we get: γ ≈ 1000 * 9.81 ≈ 9810 N/m3.
- Plugging in the height difference, we get: P = 4.84 * 9810 ≈ 47444.4 N/m2.
- Converting to kN/m2, we get: P ≈ 47.44 kN/m2.
4. Calculate the maximum pressure drop allowed:
- The pressure drop allowed is 75 kN/m2 below atmospheric pressure.
- Since atmospheric pressure is given as 100 kN/m2, the maximum pressure drop allowed is 100 - 75 = 25 kN/m2.
5. Calculate the maximum discharge:
- The maximum discharge can be calculated using Bernoulli's equation: Q = A1 * v1 = A2 * v2.
- Since the diameter of the pipe is given as 10 cm, the radius is 5 cm or 0.05 m.
- The cross-sectional area of the pipe is given by A = π * r2.
- Plugging in the values, we get: A = π * (0.05)2 ≈ 0.00785 m2.
- The velocity of the fluid can be calculated using the volumetric flow rate equation: Q = A * v.
-
- Slope of the suction pipe: 2 vertically in 3 horizontally
- Diameter of the pipe: 10 cm
- Length of the pipe: 6 m
- Pressure limit: 75 kN/m2 below atmospheric pressure
Calculations:
1. Convert the slope to an angle:
- The slope is given as 2 vertically in 3 horizontally.
- This can be written as a ratio of rise to run: 2/3.
- The angle θ can be calculated using the tangent function: tan(θ) = rise/run.
- Plugging in the values, we get: tan(θ) = 2/3.
- Solving for θ, we find: θ = arctan(2/3).
- Using a scientific calculator, we get: θ ≈ 33.69°.
2. Calculate the height difference between the lower end of the pipe and the water surface:
- The length of the pipe is given as 6 m.
- The rise of the pipe can be calculated using the angle θ: rise = 6 * tan(θ).
- Plugging in the values, we get: rise = 6 * tan(33.69°).
- Using a scientific calculator, we get: rise ≈ 4.84 m.
- Since the lower end of the pipe is just below the water surface, the height difference is equal to the rise: h = 4.84 m.
3. Calculate the pressure at the inlet to the pump:
- The pressure at the inlet to the pump is given by the difference in height between the water surface and the pump inlet, multiplied by the unit weight of water: P = h * γ.
- The unit weight of water is equal to the density of water multiplied by the acceleration due to gravity: γ = ρ * g.
- The density of water is approximately 1000 kg/m3, and the acceleration due to gravity is approximately 9.81 m/s2.
- Plugging in the values, we get: γ ≈ 1000 * 9.81 ≈ 9810 N/m3.
- Plugging in the height difference, we get: P = 4.84 * 9810 ≈ 47444.4 N/m2.
- Converting to kN/m2, we get: P ≈ 47.44 kN/m2.
4. Calculate the maximum pressure drop allowed:
- The pressure drop allowed is 75 kN/m2 below atmospheric pressure.
- Since atmospheric pressure is given as 100 kN/m2, the maximum pressure drop allowed is 100 - 75 = 25 kN/m2.
5. Calculate the maximum discharge:
- The maximum discharge can be calculated using Bernoulli's equation: Q = A1 * v1 = A2 * v2.
- Since the diameter of the pipe is given as 10 cm, the radius is 5 cm or 0.05 m.
- The cross-sectional area of the pipe is given by A = π * r2.
- Plugging in the values, we get: A = π * (0.05)2 ≈ 0.00785 m2.
- The velocity of the fluid can be calculated using the volumetric flow rate equation: Q = A * v.
-

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Question Description
The suction pipe of a pump rises at a slope of 2 vertically in 3 along the pipe, which is 10 cm in diameter. The pipe is 6 m long; its lower end being just below the surface of water in the reservoir. For design reasons, it is undesirable that pressure at inlet to the pump fall more than 75 kN⁄m2 below atmospheric pressure. Neglecting friction, make calculations for the maximum discharge (in L/s) that the pump may deliver.Take atmospheric pressure = 100 kN⁄m2Correct answer is 'Range: 66 to 67'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about The suction pipe of a pump rises at a slope of 2 vertically in 3 along the pipe, which is 10 cm in diameter. The pipe is 6 m long; its lower end being just below the surface of water in the reservoir. For design reasons, it is undesirable that pressure at inlet to the pump fall more than 75 kN⁄m2 below atmospheric pressure. Neglecting friction, make calculations for the maximum discharge (in L/s) that the pump may deliver.Take atmospheric pressure = 100 kN⁄m2Correct answer is 'Range: 66 to 67'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The suction pipe of a pump rises at a slope of 2 vertically in 3 along the pipe, which is 10 cm in diameter. The pipe is 6 m long; its lower end being just below the surface of water in the reservoir. For design reasons, it is undesirable that pressure at inlet to the pump fall more than 75 kN⁄m2 below atmospheric pressure. Neglecting friction, make calculations for the maximum discharge (in L/s) that the pump may deliver.Take atmospheric pressure = 100 kN⁄m2Correct answer is 'Range: 66 to 67'. Can you explain this answer?.
The suction pipe of a pump rises at a slope of 2 vertically in 3 along the pipe, which is 10 cm in diameter. The pipe is 6 m long; its lower end being just below the surface of water in the reservoir. For design reasons, it is undesirable that pressure at inlet to the pump fall more than 75 kN⁄m2 below atmospheric pressure. Neglecting friction, make calculations for the maximum discharge (in L/s) that the pump may deliver.Take atmospheric pressure = 100 kN⁄m2Correct answer is 'Range: 66 to 67'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about The suction pipe of a pump rises at a slope of 2 vertically in 3 along the pipe, which is 10 cm in diameter. The pipe is 6 m long; its lower end being just below the surface of water in the reservoir. For design reasons, it is undesirable that pressure at inlet to the pump fall more than 75 kN⁄m2 below atmospheric pressure. Neglecting friction, make calculations for the maximum discharge (in L/s) that the pump may deliver.Take atmospheric pressure = 100 kN⁄m2Correct answer is 'Range: 66 to 67'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The suction pipe of a pump rises at a slope of 2 vertically in 3 along the pipe, which is 10 cm in diameter. The pipe is 6 m long; its lower end being just below the surface of water in the reservoir. For design reasons, it is undesirable that pressure at inlet to the pump fall more than 75 kN⁄m2 below atmospheric pressure. Neglecting friction, make calculations for the maximum discharge (in L/s) that the pump may deliver.Take atmospheric pressure = 100 kN⁄m2Correct answer is 'Range: 66 to 67'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The suction pipe of a pump rises at a slope of 2 vertically in 3 along the pipe, which is 10 cm in diameter. The pipe is 6 m long; its lower end being just below the surface of water in the reservoir. For design reasons, it is undesirable that pressure at inlet to the pump fall more than 75 kN⁄m2 below atmospheric pressure. Neglecting friction, make calculations for the maximum discharge (in L/s) that the pump may deliver.Take atmospheric pressure = 100 kN⁄m2Correct answer is 'Range: 66 to 67'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The suction pipe of a pump rises at a slope of 2 vertically in 3 along the pipe, which is 10 cm in diameter. The pipe is 6 m long; its lower end being just below the surface of water in the reservoir. For design reasons, it is undesirable that pressure at inlet to the pump fall more than 75 kN⁄m2 below atmospheric pressure. Neglecting friction, make calculations for the maximum discharge (in L/s) that the pump may deliver.Take atmospheric pressure = 100 kN⁄m2Correct answer is 'Range: 66 to 67'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The suction pipe of a pump rises at a slope of 2 vertically in 3 along the pipe, which is 10 cm in diameter. The pipe is 6 m long; its lower end being just below the surface of water in the reservoir. For design reasons, it is undesirable that pressure at inlet to the pump fall more than 75 kN⁄m2 below atmospheric pressure. Neglecting friction, make calculations for the maximum discharge (in L/s) that the pump may deliver.Take atmospheric pressure = 100 kN⁄m2Correct answer is 'Range: 66 to 67'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The suction pipe of a pump rises at a slope of 2 vertically in 3 along the pipe, which is 10 cm in diameter. The pipe is 6 m long; its lower end being just below the surface of water in the reservoir. For design reasons, it is undesirable that pressure at inlet to the pump fall more than 75 kN⁄m2 below atmospheric pressure. Neglecting friction, make calculations for the maximum discharge (in L/s) that the pump may deliver.Take atmospheric pressure = 100 kN⁄m2Correct answer is 'Range: 66 to 67'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The suction pipe of a pump rises at a slope of 2 vertically in 3 along the pipe, which is 10 cm in diameter. The pipe is 6 m long; its lower end being just below the surface of water in the reservoir. For design reasons, it is undesirable that pressure at inlet to the pump fall more than 75 kN⁄m2 below atmospheric pressure. Neglecting friction, make calculations for the maximum discharge (in L/s) that the pump may deliver.Take atmospheric pressure = 100 kN⁄m2Correct answer is 'Range: 66 to 67'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The suction pipe of a pump rises at a slope of 2 vertically in 3 along the pipe, which is 10 cm in diameter. The pipe is 6 m long; its lower end being just below the surface of water in the reservoir. For design reasons, it is undesirable that pressure at inlet to the pump fall more than 75 kN⁄m2 below atmospheric pressure. Neglecting friction, make calculations for the maximum discharge (in L/s) that the pump may deliver.Take atmospheric pressure = 100 kN⁄m2Correct answer is 'Range: 66 to 67'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















