Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > Water flows from a large tank, open to the a...
Start Learning for Free
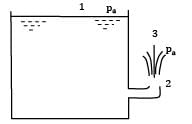
Water flows from a large tank, open to the atmosphere, through a 10 cm diameter well rounded aperture in its side. The free surface of water is 5 m above the centerline of the aperture. Calculate the velocity of jet issuing from the hole and the discharge. If a 90° elbow is placed at exit from the aperture, determine how high the water will reach.
- a)0.07 m3/s, 5 m
- b)5 m3/s, 0.7 m
- c)0.7 m3/s, 5 m
- d)0.5 m3/s, 0.7 m
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Water flows from a large tank, open to the atmosphere, through a 10 c...
(i)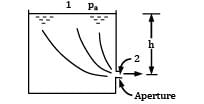
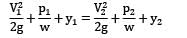
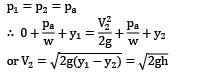
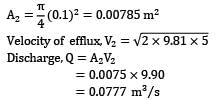
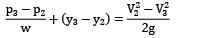
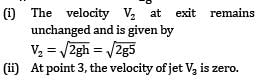
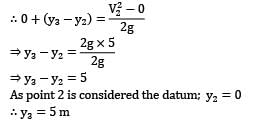
View all questions of this test

Apply Bernoulli’s equation between a point (1) on the water surface and a point (2) downstream from the aperture.
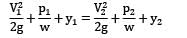
Velocity V1 on the water surface in the reservoir is practically zero because the cross sectional area of the tank is much greater than that of the aperture.
Pressure is atmospheric both at the free water surface and at the center line of the jet
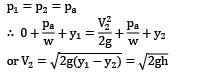
i.e., velocity of efflux from the aperture is equal to the velocity of the free fall from the surface of the reservoir. This is known as Torricelli’s Theorem.
Now: h = 5 m
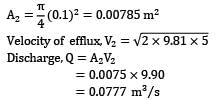
(ii)

Apply Bernoulli’s equation between point 2 and 3; the point 3 refers to the position of maximum elevation of the jet.
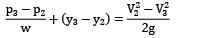
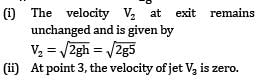
(iii) Pressure is atmospheric both at points 2 and 3, i.e., P2 = P3 = Pa
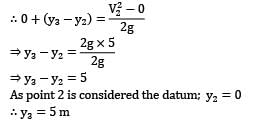
Thus if there are no losses, the water jet would reach the initial level of water in the tank and this is the height to which the water may be sprayed.
Most Upvoted Answer
Water flows from a large tank, open to the atmosphere, through a 10 c...
(i)
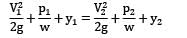
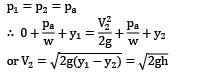
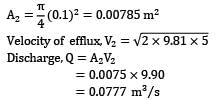

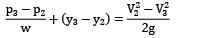
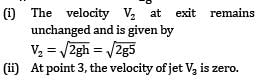
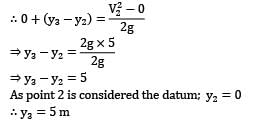

Apply Bernoulli’s equation between a point (1) on the water surface and a point (2) downstream from the aperture.
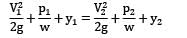
Velocity V1 on the water surface in the reservoir is practically zero because the cross sectional area of the tank is much greater than that of the aperture.
Pressure is atmospheric both at the free water surface and at the center line of the jet
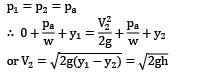
i.e., velocity of efflux from the aperture is equal to the velocity of the free fall from the surface of the reservoir. This is known as Torricelli’s Theorem.
Now: h = 5 m
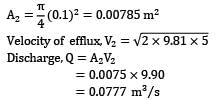
(ii)

Apply Bernoulli’s equation between point 2 and 3; the point 3 refers to the position of maximum elevation of the jet.
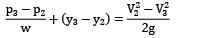
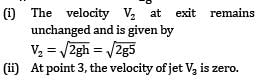
(iii) Pressure is atmospheric both at points 2 and 3, i.e., P2 = P3 = Pa
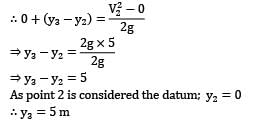
Thus if there are no losses, the water jet would reach the initial level of water in the tank and this is the height to which the water may be sprayed.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Question Description
Water flows from a large tank, open to the atmosphere, through a 10 cm diameter well rounded aperture in its side. The free surface of water is 5 m above the centerline of the aperture. Calculate the velocity of jet issuing from the hole and the discharge. If a 90° elbow is placed at exit from the aperture, determine how high the water will reach.a) 0.07 m3/s, 5 mb) 5 m3/s, 0.7 mc) 0.7 m3/s, 5 md) 0.5 m3/s, 0.7 mCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about Water flows from a large tank, open to the atmosphere, through a 10 cm diameter well rounded aperture in its side. The free surface of water is 5 m above the centerline of the aperture. Calculate the velocity of jet issuing from the hole and the discharge. If a 90° elbow is placed at exit from the aperture, determine how high the water will reach.a) 0.07 m3/s, 5 mb) 5 m3/s, 0.7 mc) 0.7 m3/s, 5 md) 0.5 m3/s, 0.7 mCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Water flows from a large tank, open to the atmosphere, through a 10 cm diameter well rounded aperture in its side. The free surface of water is 5 m above the centerline of the aperture. Calculate the velocity of jet issuing from the hole and the discharge. If a 90° elbow is placed at exit from the aperture, determine how high the water will reach.a) 0.07 m3/s, 5 mb) 5 m3/s, 0.7 mc) 0.7 m3/s, 5 md) 0.5 m3/s, 0.7 mCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Water flows from a large tank, open to the atmosphere, through a 10 cm diameter well rounded aperture in its side. The free surface of water is 5 m above the centerline of the aperture. Calculate the velocity of jet issuing from the hole and the discharge. If a 90° elbow is placed at exit from the aperture, determine how high the water will reach.a) 0.07 m3/s, 5 mb) 5 m3/s, 0.7 mc) 0.7 m3/s, 5 md) 0.5 m3/s, 0.7 mCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about Water flows from a large tank, open to the atmosphere, through a 10 cm diameter well rounded aperture in its side. The free surface of water is 5 m above the centerline of the aperture. Calculate the velocity of jet issuing from the hole and the discharge. If a 90° elbow is placed at exit from the aperture, determine how high the water will reach.a) 0.07 m3/s, 5 mb) 5 m3/s, 0.7 mc) 0.7 m3/s, 5 md) 0.5 m3/s, 0.7 mCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Water flows from a large tank, open to the atmosphere, through a 10 cm diameter well rounded aperture in its side. The free surface of water is 5 m above the centerline of the aperture. Calculate the velocity of jet issuing from the hole and the discharge. If a 90° elbow is placed at exit from the aperture, determine how high the water will reach.a) 0.07 m3/s, 5 mb) 5 m3/s, 0.7 mc) 0.7 m3/s, 5 md) 0.5 m3/s, 0.7 mCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Water flows from a large tank, open to the atmosphere, through a 10 cm diameter well rounded aperture in its side. The free surface of water is 5 m above the centerline of the aperture. Calculate the velocity of jet issuing from the hole and the discharge. If a 90° elbow is placed at exit from the aperture, determine how high the water will reach.a) 0.07 m3/s, 5 mb) 5 m3/s, 0.7 mc) 0.7 m3/s, 5 md) 0.5 m3/s, 0.7 mCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Water flows from a large tank, open to the atmosphere, through a 10 cm diameter well rounded aperture in its side. The free surface of water is 5 m above the centerline of the aperture. Calculate the velocity of jet issuing from the hole and the discharge. If a 90° elbow is placed at exit from the aperture, determine how high the water will reach.a) 0.07 m3/s, 5 mb) 5 m3/s, 0.7 mc) 0.7 m3/s, 5 md) 0.5 m3/s, 0.7 mCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Water flows from a large tank, open to the atmosphere, through a 10 cm diameter well rounded aperture in its side. The free surface of water is 5 m above the centerline of the aperture. Calculate the velocity of jet issuing from the hole and the discharge. If a 90° elbow is placed at exit from the aperture, determine how high the water will reach.a) 0.07 m3/s, 5 mb) 5 m3/s, 0.7 mc) 0.7 m3/s, 5 md) 0.5 m3/s, 0.7 mCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Water flows from a large tank, open to the atmosphere, through a 10 cm diameter well rounded aperture in its side. The free surface of water is 5 m above the centerline of the aperture. Calculate the velocity of jet issuing from the hole and the discharge. If a 90° elbow is placed at exit from the aperture, determine how high the water will reach.a) 0.07 m3/s, 5 mb) 5 m3/s, 0.7 mc) 0.7 m3/s, 5 md) 0.5 m3/s, 0.7 mCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Water flows from a large tank, open to the atmosphere, through a 10 cm diameter well rounded aperture in its side. The free surface of water is 5 m above the centerline of the aperture. Calculate the velocity of jet issuing from the hole and the discharge. If a 90° elbow is placed at exit from the aperture, determine how high the water will reach.a) 0.07 m3/s, 5 mb) 5 m3/s, 0.7 mc) 0.7 m3/s, 5 md) 0.5 m3/s, 0.7 mCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Water flows from a large tank, open to the atmosphere, through a 10 cm diameter well rounded aperture in its side. The free surface of water is 5 m above the centerline of the aperture. Calculate the velocity of jet issuing from the hole and the discharge. If a 90° elbow is placed at exit from the aperture, determine how high the water will reach.a) 0.07 m3/s, 5 mb) 5 m3/s, 0.7 mc) 0.7 m3/s, 5 md) 0.5 m3/s, 0.7 mCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















