Teaching Exam > Teaching Questions > Diagram with labelled of human respiratory sy...
Start Learning for Free
Diagram with labelled of human respiratory system?
Most Upvoted Answer
Diagram with labelled of human respiratory system?
Community Answer
Diagram with labelled of human respiratory system?
The human respiratory system is responsible for the exchange of gases between the body and the environment. It consists of several organs and structures that work together to facilitate the intake of oxygen and the removal of carbon dioxide.
The Organs of the Respiratory System
The respiratory system includes the following organs:
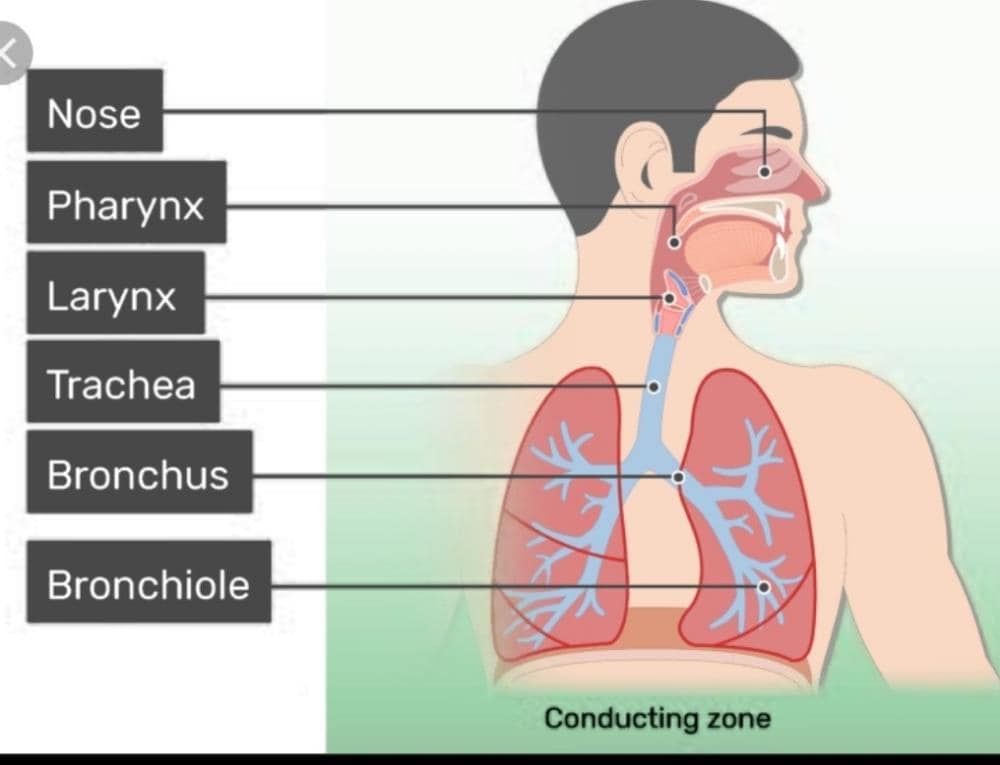
Nose and Nasal Cavity: The nose is the primary entrance for air into the respiratory system. It filters, warms, and moistens the incoming air. The nasal cavity is lined with tiny hairs called cilia, which trap dust particles and other pollutants.
Pharynx: The pharynx serves as a common passage for both air and food. It is divided into three regions: the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx.
Larynx: The larynx, commonly known as the voice box, is located at the top of the trachea. It houses the vocal cords, which vibrate to produce sound during speech.
Trachea: The trachea, or windpipe, is a tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi. It is lined with cilia and mucus-producing cells that help to trap and remove foreign particles.
Bronchi: The trachea branches into two bronchi, one leading to each lung. The bronchi further divide into smaller tubes called bronchioles, which eventually lead to the alveoli.
Lungs: The lungs are the main organs of respiration. They are located in the thoracic cavity and protected by the rib cage. The right lung is divided into three lobes, while the left lung has two lobes to accommodate the heart.
Alveoli: The alveoli are small, balloon-like structures within the lungs where the exchange of gases takes place. They are surrounded by a network of capillaries, allowing for the diffusion of oxygen into the bloodstream and the removal of carbon dioxide.
Diaphragm: The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle located at the base of the lungs. It plays a crucial role in the process of breathing by contracting and relaxing to facilitate the movement of air in and out of the lungs.
The Process of Respiration
The respiratory system operates through a process called respiration, which can be divided into two distinct phases:
Inhalation: During inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and moves downward, causing the volume of the thoracic cavity to increase. This creates a pressure gradient that allows air to rush into the lungs through the nose or mouth.
Exhalation: Exhalation occurs when the diaphragm relaxes and moves upward, decreasing the volume of the thoracic cavity. This leads to an increase in pressure within the lungs, forcing air out of the respiratory system.
Gas Exchange: The exchange of gases occurs in the alveoli, where oxygen diffuses from the air into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide moves from the bloodstream into the alveoli to be expelled during exhalation.
Conclusion
The human respiratory system is a complex network of organs and structures that work together to ensure the exchange of gases necessary for survival. Understanding the anatomy and function of this system is essential for teaching and learning about the vital process of respiration
The Organs of the Respiratory System
The respiratory system includes the following organs:
Nose and Nasal Cavity: The nose is the primary entrance for air into the respiratory system. It filters, warms, and moistens the incoming air. The nasal cavity is lined with tiny hairs called cilia, which trap dust particles and other pollutants.
Pharynx: The pharynx serves as a common passage for both air and food. It is divided into three regions: the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx.
Larynx: The larynx, commonly known as the voice box, is located at the top of the trachea. It houses the vocal cords, which vibrate to produce sound during speech.
Trachea: The trachea, or windpipe, is a tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi. It is lined with cilia and mucus-producing cells that help to trap and remove foreign particles.
Bronchi: The trachea branches into two bronchi, one leading to each lung. The bronchi further divide into smaller tubes called bronchioles, which eventually lead to the alveoli.
Lungs: The lungs are the main organs of respiration. They are located in the thoracic cavity and protected by the rib cage. The right lung is divided into three lobes, while the left lung has two lobes to accommodate the heart.
Alveoli: The alveoli are small, balloon-like structures within the lungs where the exchange of gases takes place. They are surrounded by a network of capillaries, allowing for the diffusion of oxygen into the bloodstream and the removal of carbon dioxide.
Diaphragm: The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle located at the base of the lungs. It plays a crucial role in the process of breathing by contracting and relaxing to facilitate the movement of air in and out of the lungs.
The Process of Respiration
The respiratory system operates through a process called respiration, which can be divided into two distinct phases:
Inhalation: During inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and moves downward, causing the volume of the thoracic cavity to increase. This creates a pressure gradient that allows air to rush into the lungs through the nose or mouth.
Exhalation: Exhalation occurs when the diaphragm relaxes and moves upward, decreasing the volume of the thoracic cavity. This leads to an increase in pressure within the lungs, forcing air out of the respiratory system.
Gas Exchange: The exchange of gases occurs in the alveoli, where oxygen diffuses from the air into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide moves from the bloodstream into the alveoli to be expelled during exhalation.
Conclusion
The human respiratory system is a complex network of organs and structures that work together to ensure the exchange of gases necessary for survival. Understanding the anatomy and function of this system is essential for teaching and learning about the vital process of respiration

|
Explore Courses for Teaching exam
|

|
Diagram with labelled of human respiratory system?
Question Description
Diagram with labelled of human respiratory system? for Teaching 2025 is part of Teaching preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Teaching exam syllabus. Information about Diagram with labelled of human respiratory system? covers all topics & solutions for Teaching 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Diagram with labelled of human respiratory system?.
Diagram with labelled of human respiratory system? for Teaching 2025 is part of Teaching preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Teaching exam syllabus. Information about Diagram with labelled of human respiratory system? covers all topics & solutions for Teaching 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Diagram with labelled of human respiratory system?.
Solutions for Diagram with labelled of human respiratory system? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Teaching.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Teaching Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Diagram with labelled of human respiratory system? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Diagram with labelled of human respiratory system?, a detailed solution for Diagram with labelled of human respiratory system? has been provided alongside types of Diagram with labelled of human respiratory system? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Diagram with labelled of human respiratory system? tests, examples and also practice Teaching tests.

|
Explore Courses for Teaching exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



















