JEE Exam > JEE Questions > When a metal surface is illuminated by light ...
Start Learning for Free
When a metal surface is illuminated by light of wavelengths 400 nm and 250 nm, the maximum velocities of the photoelectrons ejected are v and 2v respectively. The work function of the metal is (h - Planck's constant, c = velocity of light in air)
- a)2 hc x 106 J
- b)1.5 hc x 106 J
- c)hc x 106 J
- d)0.5 hc x 106 J
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
When a metal surface is illuminated by light of wavelengths 400 nm and...
We have,
E = W0 + K
E = W0 + K
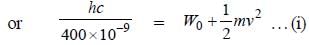
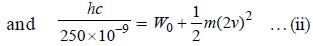
On simplifying above equations, we get
W0 = 2 hc x 106 J
W0 = 2 hc x 106 J
Most Upvoted Answer
When a metal surface is illuminated by light of wavelengths 400 nm and...
To understand this problem, let's consider the phenomenon of the photoelectric effect. When light of sufficient energy (or frequency) falls on a metal surface, it can cause the ejection of electrons from the metal. The energy required to remove an electron from the metal is called the work function (denoted by φ).
Key Concepts:
1. Photoelectric effect: The ejection of electrons from a metal surface when illuminated by light.
2. Work function (φ): The minimum energy required to remove an electron from the metal surface.
3. Maximum velocity of ejected electrons: The velocity of electrons that are ejected with maximum kinetic energy.
Given:
- Light of wavelengths 400 nm and 250 nm falls on a metal surface.
- The maximum velocity of photoelectrons ejected is v and 2v respectively.
Explanation:
1. Relationship between energy and wavelength: The energy (E) of a photon is inversely proportional to its wavelength (λ) according to the equation E = hc/λ, where h is Planck's constant and c is the velocity of light in air.
2. Calculation of energies: Convert the given wavelengths to meters and use the equation to calculate the energies of the photons corresponding to each wavelength.
- For 400 nm (wavelength), E1 = hc/λ1 = hc/(400 x 10^-9 m)
- For 250 nm (wavelength), E2 = hc/λ2 = hc/(250 x 10^-9 m)
3. Relationship between energy and work function: If the energy of a photon is greater than or equal to the work function (E ≥ φ), electrons will be ejected with some kinetic energy.
4. Calculation of work function: Since the maximum velocity of ejected electrons is proportional to the energy of the photons, we can compare the ratios of the energies to determine the relationship between the velocities.
- v/2v = E1/E2 = (hc/λ1)/(hc/λ2) = λ2/λ1 = (250 x 10^-9 m)/(400 x 10^-9 m)
- Simplifying, we get λ2/λ1 = 5/8
- Since the ratio of the velocities is inversely proportional to the ratio of the wavelengths, we can conclude that the ratio of the velocities is 8/5.
- Therefore, v/2v = 8/5, which means v = (8/5) * 2v = 16v/5.
5. Calculation of work function: The work function (φ) can be determined by comparing the energies of the photons.
- E1 = φ (for 400 nm wavelength)
- E2 = 16φ/5 (for 250 nm wavelength) (as v = 16v/5)
- Equating the two energies: E1 = E2, φ = (16φ/5)
- Solving the equation, we get φ = (5/16) * φ
- Therefore, φ = 5/16 * φ (equation 1)
- We know that E1 = φ, so E1 = hc/λ1 = φ (equation 2)
- From equations 1 and 2, we get φ = hc/λ1 = hc/400 x 10^-9 m
6. Final answer: Substituting the values of h and c, we get φ = 2hc x
Key Concepts:
1. Photoelectric effect: The ejection of electrons from a metal surface when illuminated by light.
2. Work function (φ): The minimum energy required to remove an electron from the metal surface.
3. Maximum velocity of ejected electrons: The velocity of electrons that are ejected with maximum kinetic energy.
Given:
- Light of wavelengths 400 nm and 250 nm falls on a metal surface.
- The maximum velocity of photoelectrons ejected is v and 2v respectively.
Explanation:
1. Relationship between energy and wavelength: The energy (E) of a photon is inversely proportional to its wavelength (λ) according to the equation E = hc/λ, where h is Planck's constant and c is the velocity of light in air.
2. Calculation of energies: Convert the given wavelengths to meters and use the equation to calculate the energies of the photons corresponding to each wavelength.
- For 400 nm (wavelength), E1 = hc/λ1 = hc/(400 x 10^-9 m)
- For 250 nm (wavelength), E2 = hc/λ2 = hc/(250 x 10^-9 m)
3. Relationship between energy and work function: If the energy of a photon is greater than or equal to the work function (E ≥ φ), electrons will be ejected with some kinetic energy.
4. Calculation of work function: Since the maximum velocity of ejected electrons is proportional to the energy of the photons, we can compare the ratios of the energies to determine the relationship between the velocities.
- v/2v = E1/E2 = (hc/λ1)/(hc/λ2) = λ2/λ1 = (250 x 10^-9 m)/(400 x 10^-9 m)
- Simplifying, we get λ2/λ1 = 5/8
- Since the ratio of the velocities is inversely proportional to the ratio of the wavelengths, we can conclude that the ratio of the velocities is 8/5.
- Therefore, v/2v = 8/5, which means v = (8/5) * 2v = 16v/5.
5. Calculation of work function: The work function (φ) can be determined by comparing the energies of the photons.
- E1 = φ (for 400 nm wavelength)
- E2 = 16φ/5 (for 250 nm wavelength) (as v = 16v/5)
- Equating the two energies: E1 = E2, φ = (16φ/5)
- Solving the equation, we get φ = (5/16) * φ
- Therefore, φ = 5/16 * φ (equation 1)
- We know that E1 = φ, so E1 = hc/λ1 = φ (equation 2)
- From equations 1 and 2, we get φ = hc/λ1 = hc/400 x 10^-9 m
6. Final answer: Substituting the values of h and c, we get φ = 2hc x
Attention JEE Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed JEE study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in JEE.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
When a metal surface is illuminated by light of wavelengths 400 nm and 250 nm, the maximum velocities of the photoelectrons ejected are v and 2v respectively. The work function of the metal is (h - Plancks constant, c = velocity of light in air)a)2 hc x 106 Jb)1.5 hc x 106 Jc)hc x 106 Jd)0.5 hc x 106 JCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
When a metal surface is illuminated by light of wavelengths 400 nm and 250 nm, the maximum velocities of the photoelectrons ejected are v and 2v respectively. The work function of the metal is (h - Plancks constant, c = velocity of light in air)a)2 hc x 106 Jb)1.5 hc x 106 Jc)hc x 106 Jd)0.5 hc x 106 JCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about When a metal surface is illuminated by light of wavelengths 400 nm and 250 nm, the maximum velocities of the photoelectrons ejected are v and 2v respectively. The work function of the metal is (h - Plancks constant, c = velocity of light in air)a)2 hc x 106 Jb)1.5 hc x 106 Jc)hc x 106 Jd)0.5 hc x 106 JCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for When a metal surface is illuminated by light of wavelengths 400 nm and 250 nm, the maximum velocities of the photoelectrons ejected are v and 2v respectively. The work function of the metal is (h - Plancks constant, c = velocity of light in air)a)2 hc x 106 Jb)1.5 hc x 106 Jc)hc x 106 Jd)0.5 hc x 106 JCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
When a metal surface is illuminated by light of wavelengths 400 nm and 250 nm, the maximum velocities of the photoelectrons ejected are v and 2v respectively. The work function of the metal is (h - Plancks constant, c = velocity of light in air)a)2 hc x 106 Jb)1.5 hc x 106 Jc)hc x 106 Jd)0.5 hc x 106 JCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about When a metal surface is illuminated by light of wavelengths 400 nm and 250 nm, the maximum velocities of the photoelectrons ejected are v and 2v respectively. The work function of the metal is (h - Plancks constant, c = velocity of light in air)a)2 hc x 106 Jb)1.5 hc x 106 Jc)hc x 106 Jd)0.5 hc x 106 JCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for When a metal surface is illuminated by light of wavelengths 400 nm and 250 nm, the maximum velocities of the photoelectrons ejected are v and 2v respectively. The work function of the metal is (h - Plancks constant, c = velocity of light in air)a)2 hc x 106 Jb)1.5 hc x 106 Jc)hc x 106 Jd)0.5 hc x 106 JCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for When a metal surface is illuminated by light of wavelengths 400 nm and 250 nm, the maximum velocities of the photoelectrons ejected are v and 2v respectively. The work function of the metal is (h - Plancks constant, c = velocity of light in air)a)2 hc x 106 Jb)1.5 hc x 106 Jc)hc x 106 Jd)0.5 hc x 106 JCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of When a metal surface is illuminated by light of wavelengths 400 nm and 250 nm, the maximum velocities of the photoelectrons ejected are v and 2v respectively. The work function of the metal is (h - Plancks constant, c = velocity of light in air)a)2 hc x 106 Jb)1.5 hc x 106 Jc)hc x 106 Jd)0.5 hc x 106 JCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
When a metal surface is illuminated by light of wavelengths 400 nm and 250 nm, the maximum velocities of the photoelectrons ejected are v and 2v respectively. The work function of the metal is (h - Plancks constant, c = velocity of light in air)a)2 hc x 106 Jb)1.5 hc x 106 Jc)hc x 106 Jd)0.5 hc x 106 JCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for When a metal surface is illuminated by light of wavelengths 400 nm and 250 nm, the maximum velocities of the photoelectrons ejected are v and 2v respectively. The work function of the metal is (h - Plancks constant, c = velocity of light in air)a)2 hc x 106 Jb)1.5 hc x 106 Jc)hc x 106 Jd)0.5 hc x 106 JCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of When a metal surface is illuminated by light of wavelengths 400 nm and 250 nm, the maximum velocities of the photoelectrons ejected are v and 2v respectively. The work function of the metal is (h - Plancks constant, c = velocity of light in air)a)2 hc x 106 Jb)1.5 hc x 106 Jc)hc x 106 Jd)0.5 hc x 106 JCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice When a metal surface is illuminated by light of wavelengths 400 nm and 250 nm, the maximum velocities of the photoelectrons ejected are v and 2v respectively. The work function of the metal is (h - Plancks constant, c = velocity of light in air)a)2 hc x 106 Jb)1.5 hc x 106 Jc)hc x 106 Jd)0.5 hc x 106 JCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























