JEE Exam > JEE Questions > Shown in the figure is a semicircular metalli...
Start Learning for Free
Shown in the figure is a semicircular metallic strip that has thickness t and resistivity ρ. Its inner radius is R1 and outer radius is R2. If a voltage V0 is applied between its two ends, a current I flows in it. In addition, it is observed that a transverse voltage ΔV develops between its inner and outer surfaces due to purely kinetic effects of moving electrons (ignore any role of the magnetic field due to the current). Then (figure is schematic and not drawn to scale)-
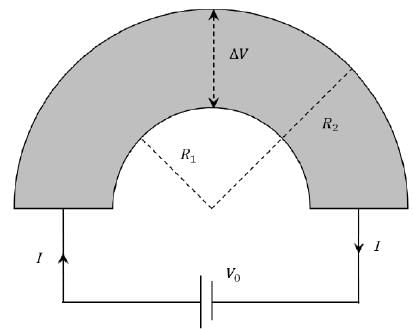

- a)
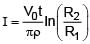
- b)the outer surface is at a higher voltage than the inner surface
- c)the outer surface is at a lower voltage than the inner surface
- d)ΔV ∝ I2
Correct answer is option 'A,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Shown in the figure is a semicircular metallic strip that has thicknes...
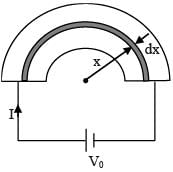
All the elements are in parallel
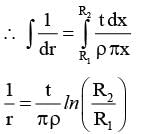
Resistance
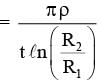
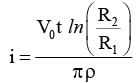 (A)
(A)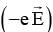 will be inward direction in order to provide centripetal acceleration. Therefore electric field will be radially outward
will be inward direction in order to provide centripetal acceleration. Therefore electric field will be radially outward Vouter < Vinner (C)
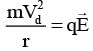
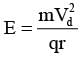 (I = neAVd ⇒ Vd ∝ i)
(I = neAVd ⇒ Vd ∝ i)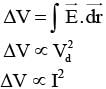

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
Shown in the figure is a semicircular metallic strip that has thickness t and resistivity ρ. Its inner radius is R1 and outer radius is R2. If a voltage V0 is applied between its two ends, a current I flows in it. In addition, it is observed that a transverse voltage ΔV develops between its inner and outer surfaces due to purely kinetic effects of moving electrons (ignore any role of the magnetic field due to the current). Then (figure is schematic and not drawn to scale)-a)b)the outer surface is at a higher voltage than the inner surfacec)the outer surface is at a lower voltage than the inner surfaced)ΔV ∝ I2Correct answer is option 'A,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Shown in the figure is a semicircular metallic strip that has thickness t and resistivity ρ. Its inner radius is R1 and outer radius is R2. If a voltage V0 is applied between its two ends, a current I flows in it. In addition, it is observed that a transverse voltage ΔV develops between its inner and outer surfaces due to purely kinetic effects of moving electrons (ignore any role of the magnetic field due to the current). Then (figure is schematic and not drawn to scale)-a)b)the outer surface is at a higher voltage than the inner surfacec)the outer surface is at a lower voltage than the inner surfaced)ΔV ∝ I2Correct answer is option 'A,C,D'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Shown in the figure is a semicircular metallic strip that has thickness t and resistivity ρ. Its inner radius is R1 and outer radius is R2. If a voltage V0 is applied between its two ends, a current I flows in it. In addition, it is observed that a transverse voltage ΔV develops between its inner and outer surfaces due to purely kinetic effects of moving electrons (ignore any role of the magnetic field due to the current). Then (figure is schematic and not drawn to scale)-a)b)the outer surface is at a higher voltage than the inner surfacec)the outer surface is at a lower voltage than the inner surfaced)ΔV ∝ I2Correct answer is option 'A,C,D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Shown in the figure is a semicircular metallic strip that has thickness t and resistivity ρ. Its inner radius is R1 and outer radius is R2. If a voltage V0 is applied between its two ends, a current I flows in it. In addition, it is observed that a transverse voltage ΔV develops between its inner and outer surfaces due to purely kinetic effects of moving electrons (ignore any role of the magnetic field due to the current). Then (figure is schematic and not drawn to scale)-a)b)the outer surface is at a higher voltage than the inner surfacec)the outer surface is at a lower voltage than the inner surfaced)ΔV ∝ I2Correct answer is option 'A,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Shown in the figure is a semicircular metallic strip that has thickness t and resistivity ρ. Its inner radius is R1 and outer radius is R2. If a voltage V0 is applied between its two ends, a current I flows in it. In addition, it is observed that a transverse voltage ΔV develops between its inner and outer surfaces due to purely kinetic effects of moving electrons (ignore any role of the magnetic field due to the current). Then (figure is schematic and not drawn to scale)-a)b)the outer surface is at a higher voltage than the inner surfacec)the outer surface is at a lower voltage than the inner surfaced)ΔV ∝ I2Correct answer is option 'A,C,D'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Shown in the figure is a semicircular metallic strip that has thickness t and resistivity ρ. Its inner radius is R1 and outer radius is R2. If a voltage V0 is applied between its two ends, a current I flows in it. In addition, it is observed that a transverse voltage ΔV develops between its inner and outer surfaces due to purely kinetic effects of moving electrons (ignore any role of the magnetic field due to the current). Then (figure is schematic and not drawn to scale)-a)b)the outer surface is at a higher voltage than the inner surfacec)the outer surface is at a lower voltage than the inner surfaced)ΔV ∝ I2Correct answer is option 'A,C,D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Shown in the figure is a semicircular metallic strip that has thickness t and resistivity ρ. Its inner radius is R1 and outer radius is R2. If a voltage V0 is applied between its two ends, a current I flows in it. In addition, it is observed that a transverse voltage ΔV develops between its inner and outer surfaces due to purely kinetic effects of moving electrons (ignore any role of the magnetic field due to the current). Then (figure is schematic and not drawn to scale)-a)b)the outer surface is at a higher voltage than the inner surfacec)the outer surface is at a lower voltage than the inner surfaced)ΔV ∝ I2Correct answer is option 'A,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Shown in the figure is a semicircular metallic strip that has thickness t and resistivity ρ. Its inner radius is R1 and outer radius is R2. If a voltage V0 is applied between its two ends, a current I flows in it. In addition, it is observed that a transverse voltage ΔV develops between its inner and outer surfaces due to purely kinetic effects of moving electrons (ignore any role of the magnetic field due to the current). Then (figure is schematic and not drawn to scale)-a)b)the outer surface is at a higher voltage than the inner surfacec)the outer surface is at a lower voltage than the inner surfaced)ΔV ∝ I2Correct answer is option 'A,C,D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Shown in the figure is a semicircular metallic strip that has thickness t and resistivity ρ. Its inner radius is R1 and outer radius is R2. If a voltage V0 is applied between its two ends, a current I flows in it. In addition, it is observed that a transverse voltage ΔV develops between its inner and outer surfaces due to purely kinetic effects of moving electrons (ignore any role of the magnetic field due to the current). Then (figure is schematic and not drawn to scale)-a)b)the outer surface is at a higher voltage than the inner surfacec)the outer surface is at a lower voltage than the inner surfaced)ΔV ∝ I2Correct answer is option 'A,C,D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Shown in the figure is a semicircular metallic strip that has thickness t and resistivity ρ. Its inner radius is R1 and outer radius is R2. If a voltage V0 is applied between its two ends, a current I flows in it. In addition, it is observed that a transverse voltage ΔV develops between its inner and outer surfaces due to purely kinetic effects of moving electrons (ignore any role of the magnetic field due to the current). Then (figure is schematic and not drawn to scale)-a)b)the outer surface is at a higher voltage than the inner surfacec)the outer surface is at a lower voltage than the inner surfaced)ΔV ∝ I2Correct answer is option 'A,C,D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Shown in the figure is a semicircular metallic strip that has thickness t and resistivity ρ. Its inner radius is R1 and outer radius is R2. If a voltage V0 is applied between its two ends, a current I flows in it. In addition, it is observed that a transverse voltage ΔV develops between its inner and outer surfaces due to purely kinetic effects of moving electrons (ignore any role of the magnetic field due to the current). Then (figure is schematic and not drawn to scale)-a)b)the outer surface is at a higher voltage than the inner surfacec)the outer surface is at a lower voltage than the inner surfaced)ΔV ∝ I2Correct answer is option 'A,C,D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Shown in the figure is a semicircular metallic strip that has thickness t and resistivity ρ. Its inner radius is R1 and outer radius is R2. If a voltage V0 is applied between its two ends, a current I flows in it. In addition, it is observed that a transverse voltage ΔV develops between its inner and outer surfaces due to purely kinetic effects of moving electrons (ignore any role of the magnetic field due to the current). Then (figure is schematic and not drawn to scale)-a)b)the outer surface is at a higher voltage than the inner surfacec)the outer surface is at a lower voltage than the inner surfaced)ΔV ∝ I2Correct answer is option 'A,C,D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Shown in the figure is a semicircular metallic strip that has thickness t and resistivity ρ. Its inner radius is R1 and outer radius is R2. If a voltage V0 is applied between its two ends, a current I flows in it. In addition, it is observed that a transverse voltage ΔV develops between its inner and outer surfaces due to purely kinetic effects of moving electrons (ignore any role of the magnetic field due to the current). Then (figure is schematic and not drawn to scale)-a)b)the outer surface is at a higher voltage than the inner surfacec)the outer surface is at a lower voltage than the inner surfaced)ΔV ∝ I2Correct answer is option 'A,C,D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























