Class 11 Exam > Class 11 Questions > Position of centre of massIn a uniform gravi...
Start Learning for Free
Position of centre of mass
In a uniform gravitational field the centre of mass coincide with the centre of gravity. But these two points do not always coincide, however. For example, the Moon’s centre of mass is very close to its geometric centre (it is not exact because the Moon is not a perfect uniform sphere), but its centre of gravity is slightly displaced towards Earth because of the stronger gravitational force on the Moon’s near side facing the earth. If an object does not have a uniform weight distribution then the center of mass will be closer to where most of the weight is located. For example, the center of gravity for a hammer is located close to where the head connects to the handle. The center of mass can be located at an empty point in space, such as the center of a hollow ball. The center of gravity can even be completely outside of an object, such as for a donut or a curved banana.

Standing upright, an adult human’s centre of mass is located roughly at the center of their torso. The centre of mass rises a few inches when with rising arms.
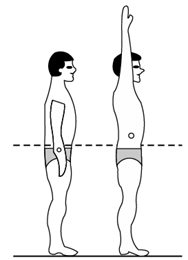
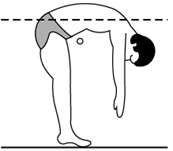
The center of gravity can even be at a point outside the body, such as when bent over in an inverted-U pose.
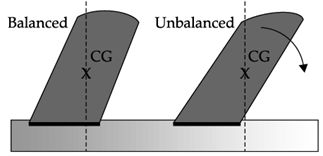
An object is in balanced position if its center of gravity is above its base of support. For the two cylinders below, the left cylinder’s CG is above the base of support so the upward support force from the base is aligned with the downward force of gravity. For the cylinder on the right the CG is not above the base of support so these two forces cannot align and instead create a torque that rotates the object, tipping it over.
The leaning tower of Pisa does not fall since
- a)Its center of mass is within its base.
- b)Its centre of mass is at the foot of the perpendicular dropped from the top.
- c)Its center of mass coincides with its centre of gravity.
- d)Its base is well concreted
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Position of centre of massIn a uniform gravitational field the centre...
The Leaning Tower of Pisa does not fall because its center of mass has been carefully kept within its base. Today, despite the inclination of about 4° (reduced from over 5° ), a vertical line drawn from the center of mass still falls inside the base.
View all questions of this test

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Similar Class 11 Doubts
Position of centre of massIn a uniform gravitational field the centre of mass coincide with the centre of gravity. But these two points do not always coincide, however. For example, the Moon’s centre of mass is very close to its geometric centre (it is not exact because the Moon is not a perfect uniform sphere), but its centre of gravity is slightly displaced towards Earth because of the stronger gravitational force on the Moon’s near side facing the earth. If an object does not have a uniform weight distribution then the center of mass will be closer to where most of the weight is located. For example, the center of gravity for a hammer is located close to where the head connects to the handle. The center of mass can be located at an empty point in space, such as the center of a hollow ball. The center of gravity can even be completely outside of an object, such as for a donut or a curved banana.Standing upright, an adult human’s centre of mass is located roughly at the center of their torso. The centre of mass rises a few inches when with rising arms.The center of gravity can even be at a point outside the body, such as when bent over in an inverted-U pose.An object is in balanced position if its center of gravity is above its base of support. For the two cylinders below, the left cylinder’s CG is above the base of support so the upward support force from the base is aligned with the downward force of gravity. For the cylinder on the right the CG is not above the base of support so these two forces cannot align and instead create a torque that rotates the object, tipping it over.The leaning tower of Pisa does not fall sincea)Its center of mass is within its base.b)Its centre of mass is at the foot of the perpendicular dropped from the top.c)Its center of mass coincides with its centre of gravity.d)Its base is well concretedCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Position of centre of massIn a uniform gravitational field the centre of mass coincide with the centre of gravity. But these two points do not always coincide, however. For example, the Moon’s centre of mass is very close to its geometric centre (it is not exact because the Moon is not a perfect uniform sphere), but its centre of gravity is slightly displaced towards Earth because of the stronger gravitational force on the Moon’s near side facing the earth. If an object does not have a uniform weight distribution then the center of mass will be closer to where most of the weight is located. For example, the center of gravity for a hammer is located close to where the head connects to the handle. The center of mass can be located at an empty point in space, such as the center of a hollow ball. The center of gravity can even be completely outside of an object, such as for a donut or a curved banana.Standing upright, an adult human’s centre of mass is located roughly at the center of their torso. The centre of mass rises a few inches when with rising arms.The center of gravity can even be at a point outside the body, such as when bent over in an inverted-U pose.An object is in balanced position if its center of gravity is above its base of support. For the two cylinders below, the left cylinder’s CG is above the base of support so the upward support force from the base is aligned with the downward force of gravity. For the cylinder on the right the CG is not above the base of support so these two forces cannot align and instead create a torque that rotates the object, tipping it over.The leaning tower of Pisa does not fall sincea)Its center of mass is within its base.b)Its centre of mass is at the foot of the perpendicular dropped from the top.c)Its center of mass coincides with its centre of gravity.d)Its base is well concretedCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 11 2024 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Position of centre of massIn a uniform gravitational field the centre of mass coincide with the centre of gravity. But these two points do not always coincide, however. For example, the Moon’s centre of mass is very close to its geometric centre (it is not exact because the Moon is not a perfect uniform sphere), but its centre of gravity is slightly displaced towards Earth because of the stronger gravitational force on the Moon’s near side facing the earth. If an object does not have a uniform weight distribution then the center of mass will be closer to where most of the weight is located. For example, the center of gravity for a hammer is located close to where the head connects to the handle. The center of mass can be located at an empty point in space, such as the center of a hollow ball. The center of gravity can even be completely outside of an object, such as for a donut or a curved banana.Standing upright, an adult human’s centre of mass is located roughly at the center of their torso. The centre of mass rises a few inches when with rising arms.The center of gravity can even be at a point outside the body, such as when bent over in an inverted-U pose.An object is in balanced position if its center of gravity is above its base of support. For the two cylinders below, the left cylinder’s CG is above the base of support so the upward support force from the base is aligned with the downward force of gravity. For the cylinder on the right the CG is not above the base of support so these two forces cannot align and instead create a torque that rotates the object, tipping it over.The leaning tower of Pisa does not fall sincea)Its center of mass is within its base.b)Its centre of mass is at the foot of the perpendicular dropped from the top.c)Its center of mass coincides with its centre of gravity.d)Its base is well concretedCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Position of centre of massIn a uniform gravitational field the centre of mass coincide with the centre of gravity. But these two points do not always coincide, however. For example, the Moon’s centre of mass is very close to its geometric centre (it is not exact because the Moon is not a perfect uniform sphere), but its centre of gravity is slightly displaced towards Earth because of the stronger gravitational force on the Moon’s near side facing the earth. If an object does not have a uniform weight distribution then the center of mass will be closer to where most of the weight is located. For example, the center of gravity for a hammer is located close to where the head connects to the handle. The center of mass can be located at an empty point in space, such as the center of a hollow ball. The center of gravity can even be completely outside of an object, such as for a donut or a curved banana.Standing upright, an adult human’s centre of mass is located roughly at the center of their torso. The centre of mass rises a few inches when with rising arms.The center of gravity can even be at a point outside the body, such as when bent over in an inverted-U pose.An object is in balanced position if its center of gravity is above its base of support. For the two cylinders below, the left cylinder’s CG is above the base of support so the upward support force from the base is aligned with the downward force of gravity. For the cylinder on the right the CG is not above the base of support so these two forces cannot align and instead create a torque that rotates the object, tipping it over.The leaning tower of Pisa does not fall sincea)Its center of mass is within its base.b)Its centre of mass is at the foot of the perpendicular dropped from the top.c)Its center of mass coincides with its centre of gravity.d)Its base is well concretedCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Position of centre of massIn a uniform gravitational field the centre of mass coincide with the centre of gravity. But these two points do not always coincide, however. For example, the Moon’s centre of mass is very close to its geometric centre (it is not exact because the Moon is not a perfect uniform sphere), but its centre of gravity is slightly displaced towards Earth because of the stronger gravitational force on the Moon’s near side facing the earth. If an object does not have a uniform weight distribution then the center of mass will be closer to where most of the weight is located. For example, the center of gravity for a hammer is located close to where the head connects to the handle. The center of mass can be located at an empty point in space, such as the center of a hollow ball. The center of gravity can even be completely outside of an object, such as for a donut or a curved banana.Standing upright, an adult human’s centre of mass is located roughly at the center of their torso. The centre of mass rises a few inches when with rising arms.The center of gravity can even be at a point outside the body, such as when bent over in an inverted-U pose.An object is in balanced position if its center of gravity is above its base of support. For the two cylinders below, the left cylinder’s CG is above the base of support so the upward support force from the base is aligned with the downward force of gravity. For the cylinder on the right the CG is not above the base of support so these two forces cannot align and instead create a torque that rotates the object, tipping it over.The leaning tower of Pisa does not fall sincea)Its center of mass is within its base.b)Its centre of mass is at the foot of the perpendicular dropped from the top.c)Its center of mass coincides with its centre of gravity.d)Its base is well concretedCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 11 2024 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Position of centre of massIn a uniform gravitational field the centre of mass coincide with the centre of gravity. But these two points do not always coincide, however. For example, the Moon’s centre of mass is very close to its geometric centre (it is not exact because the Moon is not a perfect uniform sphere), but its centre of gravity is slightly displaced towards Earth because of the stronger gravitational force on the Moon’s near side facing the earth. If an object does not have a uniform weight distribution then the center of mass will be closer to where most of the weight is located. For example, the center of gravity for a hammer is located close to where the head connects to the handle. The center of mass can be located at an empty point in space, such as the center of a hollow ball. The center of gravity can even be completely outside of an object, such as for a donut or a curved banana.Standing upright, an adult human’s centre of mass is located roughly at the center of their torso. The centre of mass rises a few inches when with rising arms.The center of gravity can even be at a point outside the body, such as when bent over in an inverted-U pose.An object is in balanced position if its center of gravity is above its base of support. For the two cylinders below, the left cylinder’s CG is above the base of support so the upward support force from the base is aligned with the downward force of gravity. For the cylinder on the right the CG is not above the base of support so these two forces cannot align and instead create a torque that rotates the object, tipping it over.The leaning tower of Pisa does not fall sincea)Its center of mass is within its base.b)Its centre of mass is at the foot of the perpendicular dropped from the top.c)Its center of mass coincides with its centre of gravity.d)Its base is well concretedCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Position of centre of massIn a uniform gravitational field the centre of mass coincide with the centre of gravity. But these two points do not always coincide, however. For example, the Moon’s centre of mass is very close to its geometric centre (it is not exact because the Moon is not a perfect uniform sphere), but its centre of gravity is slightly displaced towards Earth because of the stronger gravitational force on the Moon’s near side facing the earth. If an object does not have a uniform weight distribution then the center of mass will be closer to where most of the weight is located. For example, the center of gravity for a hammer is located close to where the head connects to the handle. The center of mass can be located at an empty point in space, such as the center of a hollow ball. The center of gravity can even be completely outside of an object, such as for a donut or a curved banana.Standing upright, an adult human’s centre of mass is located roughly at the center of their torso. The centre of mass rises a few inches when with rising arms.The center of gravity can even be at a point outside the body, such as when bent over in an inverted-U pose.An object is in balanced position if its center of gravity is above its base of support. For the two cylinders below, the left cylinder’s CG is above the base of support so the upward support force from the base is aligned with the downward force of gravity. For the cylinder on the right the CG is not above the base of support so these two forces cannot align and instead create a torque that rotates the object, tipping it over.The leaning tower of Pisa does not fall sincea)Its center of mass is within its base.b)Its centre of mass is at the foot of the perpendicular dropped from the top.c)Its center of mass coincides with its centre of gravity.d)Its base is well concretedCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Position of centre of massIn a uniform gravitational field the centre of mass coincide with the centre of gravity. But these two points do not always coincide, however. For example, the Moon’s centre of mass is very close to its geometric centre (it is not exact because the Moon is not a perfect uniform sphere), but its centre of gravity is slightly displaced towards Earth because of the stronger gravitational force on the Moon’s near side facing the earth. If an object does not have a uniform weight distribution then the center of mass will be closer to where most of the weight is located. For example, the center of gravity for a hammer is located close to where the head connects to the handle. The center of mass can be located at an empty point in space, such as the center of a hollow ball. The center of gravity can even be completely outside of an object, such as for a donut or a curved banana.Standing upright, an adult human’s centre of mass is located roughly at the center of their torso. The centre of mass rises a few inches when with rising arms.The center of gravity can even be at a point outside the body, such as when bent over in an inverted-U pose.An object is in balanced position if its center of gravity is above its base of support. For the two cylinders below, the left cylinder’s CG is above the base of support so the upward support force from the base is aligned with the downward force of gravity. For the cylinder on the right the CG is not above the base of support so these two forces cannot align and instead create a torque that rotates the object, tipping it over.The leaning tower of Pisa does not fall sincea)Its center of mass is within its base.b)Its centre of mass is at the foot of the perpendicular dropped from the top.c)Its center of mass coincides with its centre of gravity.d)Its base is well concretedCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 11.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 11 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Position of centre of massIn a uniform gravitational field the centre of mass coincide with the centre of gravity. But these two points do not always coincide, however. For example, the Moon’s centre of mass is very close to its geometric centre (it is not exact because the Moon is not a perfect uniform sphere), but its centre of gravity is slightly displaced towards Earth because of the stronger gravitational force on the Moon’s near side facing the earth. If an object does not have a uniform weight distribution then the center of mass will be closer to where most of the weight is located. For example, the center of gravity for a hammer is located close to where the head connects to the handle. The center of mass can be located at an empty point in space, such as the center of a hollow ball. The center of gravity can even be completely outside of an object, such as for a donut or a curved banana.Standing upright, an adult human’s centre of mass is located roughly at the center of their torso. The centre of mass rises a few inches when with rising arms.The center of gravity can even be at a point outside the body, such as when bent over in an inverted-U pose.An object is in balanced position if its center of gravity is above its base of support. For the two cylinders below, the left cylinder’s CG is above the base of support so the upward support force from the base is aligned with the downward force of gravity. For the cylinder on the right the CG is not above the base of support so these two forces cannot align and instead create a torque that rotates the object, tipping it over.The leaning tower of Pisa does not fall sincea)Its center of mass is within its base.b)Its centre of mass is at the foot of the perpendicular dropped from the top.c)Its center of mass coincides with its centre of gravity.d)Its base is well concretedCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Position of centre of massIn a uniform gravitational field the centre of mass coincide with the centre of gravity. But these two points do not always coincide, however. For example, the Moon’s centre of mass is very close to its geometric centre (it is not exact because the Moon is not a perfect uniform sphere), but its centre of gravity is slightly displaced towards Earth because of the stronger gravitational force on the Moon’s near side facing the earth. If an object does not have a uniform weight distribution then the center of mass will be closer to where most of the weight is located. For example, the center of gravity for a hammer is located close to where the head connects to the handle. The center of mass can be located at an empty point in space, such as the center of a hollow ball. The center of gravity can even be completely outside of an object, such as for a donut or a curved banana.Standing upright, an adult human’s centre of mass is located roughly at the center of their torso. The centre of mass rises a few inches when with rising arms.The center of gravity can even be at a point outside the body, such as when bent over in an inverted-U pose.An object is in balanced position if its center of gravity is above its base of support. For the two cylinders below, the left cylinder’s CG is above the base of support so the upward support force from the base is aligned with the downward force of gravity. For the cylinder on the right the CG is not above the base of support so these two forces cannot align and instead create a torque that rotates the object, tipping it over.The leaning tower of Pisa does not fall sincea)Its center of mass is within its base.b)Its centre of mass is at the foot of the perpendicular dropped from the top.c)Its center of mass coincides with its centre of gravity.d)Its base is well concretedCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Position of centre of massIn a uniform gravitational field the centre of mass coincide with the centre of gravity. But these two points do not always coincide, however. For example, the Moon’s centre of mass is very close to its geometric centre (it is not exact because the Moon is not a perfect uniform sphere), but its centre of gravity is slightly displaced towards Earth because of the stronger gravitational force on the Moon’s near side facing the earth. If an object does not have a uniform weight distribution then the center of mass will be closer to where most of the weight is located. For example, the center of gravity for a hammer is located close to where the head connects to the handle. The center of mass can be located at an empty point in space, such as the center of a hollow ball. The center of gravity can even be completely outside of an object, such as for a donut or a curved banana.Standing upright, an adult human’s centre of mass is located roughly at the center of their torso. The centre of mass rises a few inches when with rising arms.The center of gravity can even be at a point outside the body, such as when bent over in an inverted-U pose.An object is in balanced position if its center of gravity is above its base of support. For the two cylinders below, the left cylinder’s CG is above the base of support so the upward support force from the base is aligned with the downward force of gravity. For the cylinder on the right the CG is not above the base of support so these two forces cannot align and instead create a torque that rotates the object, tipping it over.The leaning tower of Pisa does not fall sincea)Its center of mass is within its base.b)Its centre of mass is at the foot of the perpendicular dropped from the top.c)Its center of mass coincides with its centre of gravity.d)Its base is well concretedCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Position of centre of massIn a uniform gravitational field the centre of mass coincide with the centre of gravity. But these two points do not always coincide, however. For example, the Moon’s centre of mass is very close to its geometric centre (it is not exact because the Moon is not a perfect uniform sphere), but its centre of gravity is slightly displaced towards Earth because of the stronger gravitational force on the Moon’s near side facing the earth. If an object does not have a uniform weight distribution then the center of mass will be closer to where most of the weight is located. For example, the center of gravity for a hammer is located close to where the head connects to the handle. The center of mass can be located at an empty point in space, such as the center of a hollow ball. The center of gravity can even be completely outside of an object, such as for a donut or a curved banana.Standing upright, an adult human’s centre of mass is located roughly at the center of their torso. The centre of mass rises a few inches when with rising arms.The center of gravity can even be at a point outside the body, such as when bent over in an inverted-U pose.An object is in balanced position if its center of gravity is above its base of support. For the two cylinders below, the left cylinder’s CG is above the base of support so the upward support force from the base is aligned with the downward force of gravity. For the cylinder on the right the CG is not above the base of support so these two forces cannot align and instead create a torque that rotates the object, tipping it over.The leaning tower of Pisa does not fall sincea)Its center of mass is within its base.b)Its centre of mass is at the foot of the perpendicular dropped from the top.c)Its center of mass coincides with its centre of gravity.d)Its base is well concretedCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Position of centre of massIn a uniform gravitational field the centre of mass coincide with the centre of gravity. But these two points do not always coincide, however. For example, the Moon’s centre of mass is very close to its geometric centre (it is not exact because the Moon is not a perfect uniform sphere), but its centre of gravity is slightly displaced towards Earth because of the stronger gravitational force on the Moon’s near side facing the earth. If an object does not have a uniform weight distribution then the center of mass will be closer to where most of the weight is located. For example, the center of gravity for a hammer is located close to where the head connects to the handle. The center of mass can be located at an empty point in space, such as the center of a hollow ball. The center of gravity can even be completely outside of an object, such as for a donut or a curved banana.Standing upright, an adult human’s centre of mass is located roughly at the center of their torso. The centre of mass rises a few inches when with rising arms.The center of gravity can even be at a point outside the body, such as when bent over in an inverted-U pose.An object is in balanced position if its center of gravity is above its base of support. For the two cylinders below, the left cylinder’s CG is above the base of support so the upward support force from the base is aligned with the downward force of gravity. For the cylinder on the right the CG is not above the base of support so these two forces cannot align and instead create a torque that rotates the object, tipping it over.The leaning tower of Pisa does not fall sincea)Its center of mass is within its base.b)Its centre of mass is at the foot of the perpendicular dropped from the top.c)Its center of mass coincides with its centre of gravity.d)Its base is well concretedCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 11 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























