Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > Read the passage given below and answer the f...
Start Learning for Free
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:
The reaction of phenol with aqueous sodium hydroxide indicates that phenols are stronger acids than alcohols and water. Due to the higher electronegativity of sp2 hybridised carbon of phenol to which –OH is attached, electron density decreases on oxygen. This increases the polarity of O–H bond and results in an increase in ionisation of phenols than that of alcohols. Now let us examine the stabilities of alkoxide and phenoxide ions. In alkoxide ion, the negative charge is localised on oxygen while in phenoxide ion, the charge is delocalised. The delocalisation of negative charge makes phenoxide ion more stable and favours the ionisation of phenol.
Q. Mark the correct order of decreasing acid strength of the following compounds.
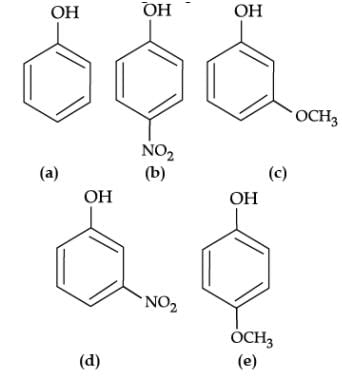
The reaction of phenol with aqueous sodium hydroxide indicates that phenols are stronger acids than alcohols and water. Due to the higher electronegativity of sp2 hybridised carbon of phenol to which –OH is attached, electron density decreases on oxygen. This increases the polarity of O–H bond and results in an increase in ionisation of phenols than that of alcohols. Now let us examine the stabilities of alkoxide and phenoxide ions. In alkoxide ion, the negative charge is localised on oxygen while in phenoxide ion, the charge is delocalised. The delocalisation of negative charge makes phenoxide ion more stable and favours the ionisation of phenol.
Q. Mark the correct order of decreasing acid strength of the following compounds.

- a)e > d > b > a > c
- b)b > d > a > c > e
- c)d > e > c > b > a
- d)e > d > c > b > a
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The re...
The correct order of decreasing acid strength is b>d>a>c>e p-nitrophenol is most acidic and p-methoxy phenol is least acidic. When an electron withdrawing group is para to OH group, the acidity is maximum. When an electron releasing group is para to OH group, the acidity is minimum.
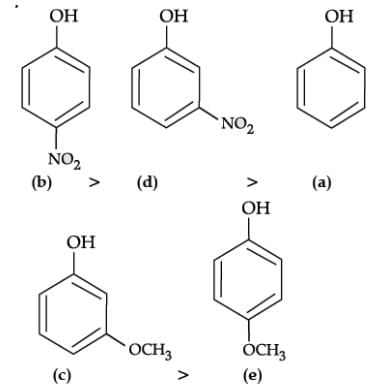
The presence of electron withdrawing group viz. −NO2 group increases the acidity of phenol due to −I effect and electron releasing group viz. −OCH3 group decreases the acidity of phenol due to +I effect. Moreover, p-nitrophenol is more acidic than m-nitrophenol. While, p-methoxyphenol is less acidic than m-methoxyphenol.

The presence of electron withdrawing group viz. −NO2 group increases the acidity of phenol due to −I effect and electron releasing group viz. −OCH3 group decreases the acidity of phenol due to +I effect. Moreover, p-nitrophenol is more acidic than m-nitrophenol. While, p-methoxyphenol is less acidic than m-methoxyphenol.
Most Upvoted Answer
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The re...
The correct order of decreasing acid strength is b>d>a>c>e p-nitrophenol is most acidic and p-methoxy phenol is least acidic. When an electron withdrawing group is para to OH group, the acidity is maximum. When an electron releasing group is para to OH group, the acidity is minimum.
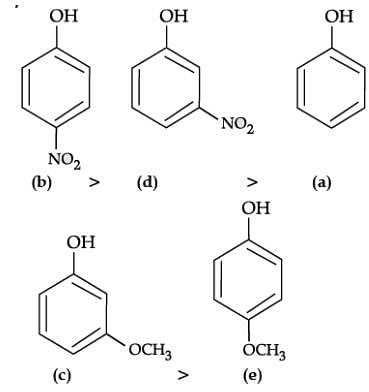
The presence of electron withdrawing group viz. −NO2 group increases the acidity of phenol due to −I effect and electron releasing group viz. −OCH3 group decreases the acidity of phenol due to +I effect. Moreover, p-nitrophenol is more acidic than m-nitrophenol. While, p-methoxyphenol is less acidic than m-methoxyphenol.

The presence of electron withdrawing group viz. −NO2 group increases the acidity of phenol due to −I effect and electron releasing group viz. −OCH3 group decreases the acidity of phenol due to +I effect. Moreover, p-nitrophenol is more acidic than m-nitrophenol. While, p-methoxyphenol is less acidic than m-methoxyphenol.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The reaction of phenol with aqueous sodium hydroxide indicates that phenols are stronger acids than alcohols and water. Due to the higher electronegativity of sp2 hybridised carbon of phenol to which –OH is attached, electron density decreases on oxygen. This increases the polarity of O–H bond and results in an increase in ionisation of phenols than that of alcohols. Now let us examine the stabilities of alkoxide and phenoxide ions. In alkoxide ion, the negative charge is localised on oxygen while in phenoxide ion, the charge is delocalised. The delocalisation of negative charge makes phenoxide ion more stable and favours the ionisation of phenol.Q. Mark the correct order of decreasing acid strength of the following compounds.a)e > d > b > a > cb)b > d > a > c > ec)d > e > c > b > ad)e > d > c > b > aCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The reaction of phenol with aqueous sodium hydroxide indicates that phenols are stronger acids than alcohols and water. Due to the higher electronegativity of sp2 hybridised carbon of phenol to which –OH is attached, electron density decreases on oxygen. This increases the polarity of O–H bond and results in an increase in ionisation of phenols than that of alcohols. Now let us examine the stabilities of alkoxide and phenoxide ions. In alkoxide ion, the negative charge is localised on oxygen while in phenoxide ion, the charge is delocalised. The delocalisation of negative charge makes phenoxide ion more stable and favours the ionisation of phenol.Q. Mark the correct order of decreasing acid strength of the following compounds.a)e > d > b > a > cb)b > d > a > c > ec)d > e > c > b > ad)e > d > c > b > aCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The reaction of phenol with aqueous sodium hydroxide indicates that phenols are stronger acids than alcohols and water. Due to the higher electronegativity of sp2 hybridised carbon of phenol to which –OH is attached, electron density decreases on oxygen. This increases the polarity of O–H bond and results in an increase in ionisation of phenols than that of alcohols. Now let us examine the stabilities of alkoxide and phenoxide ions. In alkoxide ion, the negative charge is localised on oxygen while in phenoxide ion, the charge is delocalised. The delocalisation of negative charge makes phenoxide ion more stable and favours the ionisation of phenol.Q. Mark the correct order of decreasing acid strength of the following compounds.a)e > d > b > a > cb)b > d > a > c > ec)d > e > c > b > ad)e > d > c > b > aCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The reaction of phenol with aqueous sodium hydroxide indicates that phenols are stronger acids than alcohols and water. Due to the higher electronegativity of sp2 hybridised carbon of phenol to which –OH is attached, electron density decreases on oxygen. This increases the polarity of O–H bond and results in an increase in ionisation of phenols than that of alcohols. Now let us examine the stabilities of alkoxide and phenoxide ions. In alkoxide ion, the negative charge is localised on oxygen while in phenoxide ion, the charge is delocalised. The delocalisation of negative charge makes phenoxide ion more stable and favours the ionisation of phenol.Q. Mark the correct order of decreasing acid strength of the following compounds.a)e > d > b > a > cb)b > d > a > c > ec)d > e > c > b > ad)e > d > c > b > aCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The reaction of phenol with aqueous sodium hydroxide indicates that phenols are stronger acids than alcohols and water. Due to the higher electronegativity of sp2 hybridised carbon of phenol to which –OH is attached, electron density decreases on oxygen. This increases the polarity of O–H bond and results in an increase in ionisation of phenols than that of alcohols. Now let us examine the stabilities of alkoxide and phenoxide ions. In alkoxide ion, the negative charge is localised on oxygen while in phenoxide ion, the charge is delocalised. The delocalisation of negative charge makes phenoxide ion more stable and favours the ionisation of phenol.Q. Mark the correct order of decreasing acid strength of the following compounds.a)e > d > b > a > cb)b > d > a > c > ec)d > e > c > b > ad)e > d > c > b > aCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The reaction of phenol with aqueous sodium hydroxide indicates that phenols are stronger acids than alcohols and water. Due to the higher electronegativity of sp2 hybridised carbon of phenol to which –OH is attached, electron density decreases on oxygen. This increases the polarity of O–H bond and results in an increase in ionisation of phenols than that of alcohols. Now let us examine the stabilities of alkoxide and phenoxide ions. In alkoxide ion, the negative charge is localised on oxygen while in phenoxide ion, the charge is delocalised. The delocalisation of negative charge makes phenoxide ion more stable and favours the ionisation of phenol.Q. Mark the correct order of decreasing acid strength of the following compounds.a)e > d > b > a > cb)b > d > a > c > ec)d > e > c > b > ad)e > d > c > b > aCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The reaction of phenol with aqueous sodium hydroxide indicates that phenols are stronger acids than alcohols and water. Due to the higher electronegativity of sp2 hybridised carbon of phenol to which –OH is attached, electron density decreases on oxygen. This increases the polarity of O–H bond and results in an increase in ionisation of phenols than that of alcohols. Now let us examine the stabilities of alkoxide and phenoxide ions. In alkoxide ion, the negative charge is localised on oxygen while in phenoxide ion, the charge is delocalised. The delocalisation of negative charge makes phenoxide ion more stable and favours the ionisation of phenol.Q. Mark the correct order of decreasing acid strength of the following compounds.a)e > d > b > a > cb)b > d > a > c > ec)d > e > c > b > ad)e > d > c > b > aCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The reaction of phenol with aqueous sodium hydroxide indicates that phenols are stronger acids than alcohols and water. Due to the higher electronegativity of sp2 hybridised carbon of phenol to which –OH is attached, electron density decreases on oxygen. This increases the polarity of O–H bond and results in an increase in ionisation of phenols than that of alcohols. Now let us examine the stabilities of alkoxide and phenoxide ions. In alkoxide ion, the negative charge is localised on oxygen while in phenoxide ion, the charge is delocalised. The delocalisation of negative charge makes phenoxide ion more stable and favours the ionisation of phenol.Q. Mark the correct order of decreasing acid strength of the following compounds.a)e > d > b > a > cb)b > d > a > c > ec)d > e > c > b > ad)e > d > c > b > aCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The reaction of phenol with aqueous sodium hydroxide indicates that phenols are stronger acids than alcohols and water. Due to the higher electronegativity of sp2 hybridised carbon of phenol to which –OH is attached, electron density decreases on oxygen. This increases the polarity of O–H bond and results in an increase in ionisation of phenols than that of alcohols. Now let us examine the stabilities of alkoxide and phenoxide ions. In alkoxide ion, the negative charge is localised on oxygen while in phenoxide ion, the charge is delocalised. The delocalisation of negative charge makes phenoxide ion more stable and favours the ionisation of phenol.Q. Mark the correct order of decreasing acid strength of the following compounds.a)e > d > b > a > cb)b > d > a > c > ec)d > e > c > b > ad)e > d > c > b > aCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The reaction of phenol with aqueous sodium hydroxide indicates that phenols are stronger acids than alcohols and water. Due to the higher electronegativity of sp2 hybridised carbon of phenol to which –OH is attached, electron density decreases on oxygen. This increases the polarity of O–H bond and results in an increase in ionisation of phenols than that of alcohols. Now let us examine the stabilities of alkoxide and phenoxide ions. In alkoxide ion, the negative charge is localised on oxygen while in phenoxide ion, the charge is delocalised. The delocalisation of negative charge makes phenoxide ion more stable and favours the ionisation of phenol.Q. Mark the correct order of decreasing acid strength of the following compounds.a)e > d > b > a > cb)b > d > a > c > ec)d > e > c > b > ad)e > d > c > b > aCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The reaction of phenol with aqueous sodium hydroxide indicates that phenols are stronger acids than alcohols and water. Due to the higher electronegativity of sp2 hybridised carbon of phenol to which –OH is attached, electron density decreases on oxygen. This increases the polarity of O–H bond and results in an increase in ionisation of phenols than that of alcohols. Now let us examine the stabilities of alkoxide and phenoxide ions. In alkoxide ion, the negative charge is localised on oxygen while in phenoxide ion, the charge is delocalised. The delocalisation of negative charge makes phenoxide ion more stable and favours the ionisation of phenol.Q. Mark the correct order of decreasing acid strength of the following compounds.a)e > d > b > a > cb)b > d > a > c > ec)d > e > c > b > ad)e > d > c > b > aCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The reaction of phenol with aqueous sodium hydroxide indicates that phenols are stronger acids than alcohols and water. Due to the higher electronegativity of sp2 hybridised carbon of phenol to which –OH is attached, electron density decreases on oxygen. This increases the polarity of O–H bond and results in an increase in ionisation of phenols than that of alcohols. Now let us examine the stabilities of alkoxide and phenoxide ions. In alkoxide ion, the negative charge is localised on oxygen while in phenoxide ion, the charge is delocalised. The delocalisation of negative charge makes phenoxide ion more stable and favours the ionisation of phenol.Q. Mark the correct order of decreasing acid strength of the following compounds.a)e > d > b > a > cb)b > d > a > c > ec)d > e > c > b > ad)e > d > c > b > aCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Read the passage given below and answer the following questions:The reaction of phenol with aqueous sodium hydroxide indicates that phenols are stronger acids than alcohols and water. Due to the higher electronegativity of sp2 hybridised carbon of phenol to which –OH is attached, electron density decreases on oxygen. This increases the polarity of O–H bond and results in an increase in ionisation of phenols than that of alcohols. Now let us examine the stabilities of alkoxide and phenoxide ions. In alkoxide ion, the negative charge is localised on oxygen while in phenoxide ion, the charge is delocalised. The delocalisation of negative charge makes phenoxide ion more stable and favours the ionisation of phenol.Q. Mark the correct order of decreasing acid strength of the following compounds.a)e > d > b > a > cb)b > d > a > c > ec)d > e > c > b > ad)e > d > c > b > aCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















