Railways Exam > Railways Questions > This reversible cycle consists of constant v...
Start Learning for Free
This reversible cycle consists of constant volume heat addition, reversible adiabatic expansion and constant pressure heat rejection
- a)Otto cycle
- b)Lenoir cycle
- c)Atkinson cycle
- d)Brayton cycle
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
This reversible cycle consists of constant volume heat addition, reve...
Lenoir cycle consists of only 3 processes.
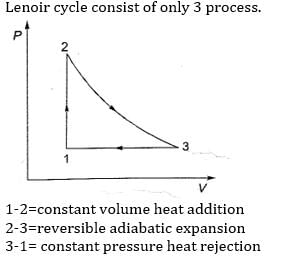
1-2 = constant volume heat addition
2-3= reversible adiabatic expansion
3-1 = constant pressure heat rejection
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
This reversible cycle consists of constant volume heat addition, reve...
Lenoir Cycle:
The Lenoir cycle is a thermodynamic cycle that describes the operation of a reciprocating internal combustion engine. It consists of the following processes:
1. Constant Volume Heat Addition:
In the Lenoir cycle, the first process is constant volume heat addition. During this process, the fuel-air mixture is ignited and combustion occurs at a constant volume. The heat released during combustion increases the temperature and pressure of the working fluid.
2. Reversible Adiabatic Expansion:
After the constant volume heat addition, the working fluid undergoes a reversible adiabatic expansion. This expansion is characterized by a decrease in pressure and temperature of the working fluid. The expansion is adiabatic, meaning there is no heat transfer during this process.
3. Constant Pressure Heat Rejection:
The third process in the Lenoir cycle is constant pressure heat rejection. During this process, the working fluid is cooled at a constant pressure. Heat is transferred from the working fluid to the surroundings, causing a decrease in temperature and pressure.
Explanation:
Among the given options, the Lenoir cycle is the only one that consists of a constant volume heat addition, reversible adiabatic expansion, and constant pressure heat rejection. Let's analyze the other options to understand why they are not the correct answers:
- Otto Cycle: The Otto cycle consists of constant volume heat addition, reversible adiabatic expansion, and constant volume heat rejection. Therefore, it does not match the description given in the question.
- Atkinson Cycle: The Atkinson cycle is an extension of the Otto cycle and also consists of constant volume heat addition, reversible adiabatic expansion, and constant volume heat rejection. Therefore, it does not match the description given in the question.
- Brayton Cycle: The Brayton cycle consists of constant pressure heat addition, reversible adiabatic expansion, and constant pressure heat rejection. Therefore, it does not match the description given in the question.
Based on the analysis above, the correct answer is option 'B' - Lenoir cycle, as it is the only one that matches the given description of the cycle consisting of constant volume heat addition, reversible adiabatic expansion, and constant pressure heat rejection.
The Lenoir cycle is a thermodynamic cycle that describes the operation of a reciprocating internal combustion engine. It consists of the following processes:
1. Constant Volume Heat Addition:
In the Lenoir cycle, the first process is constant volume heat addition. During this process, the fuel-air mixture is ignited and combustion occurs at a constant volume. The heat released during combustion increases the temperature and pressure of the working fluid.
2. Reversible Adiabatic Expansion:
After the constant volume heat addition, the working fluid undergoes a reversible adiabatic expansion. This expansion is characterized by a decrease in pressure and temperature of the working fluid. The expansion is adiabatic, meaning there is no heat transfer during this process.
3. Constant Pressure Heat Rejection:
The third process in the Lenoir cycle is constant pressure heat rejection. During this process, the working fluid is cooled at a constant pressure. Heat is transferred from the working fluid to the surroundings, causing a decrease in temperature and pressure.
Explanation:
Among the given options, the Lenoir cycle is the only one that consists of a constant volume heat addition, reversible adiabatic expansion, and constant pressure heat rejection. Let's analyze the other options to understand why they are not the correct answers:
- Otto Cycle: The Otto cycle consists of constant volume heat addition, reversible adiabatic expansion, and constant volume heat rejection. Therefore, it does not match the description given in the question.
- Atkinson Cycle: The Atkinson cycle is an extension of the Otto cycle and also consists of constant volume heat addition, reversible adiabatic expansion, and constant volume heat rejection. Therefore, it does not match the description given in the question.
- Brayton Cycle: The Brayton cycle consists of constant pressure heat addition, reversible adiabatic expansion, and constant pressure heat rejection. Therefore, it does not match the description given in the question.
Based on the analysis above, the correct answer is option 'B' - Lenoir cycle, as it is the only one that matches the given description of the cycle consisting of constant volume heat addition, reversible adiabatic expansion, and constant pressure heat rejection.

|
Explore Courses for Railways exam
|

|
Similar Railways Doubts
This reversible cycle consists of constant volume heat addition, reversible adiabatic expansion and constant pressure heat rejectiona)Otto cycleb)Lenoir cyclec)Atkinson cycled)Brayton cycleCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
This reversible cycle consists of constant volume heat addition, reversible adiabatic expansion and constant pressure heat rejectiona)Otto cycleb)Lenoir cyclec)Atkinson cycled)Brayton cycleCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Railways 2025 is part of Railways preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Railways exam syllabus. Information about This reversible cycle consists of constant volume heat addition, reversible adiabatic expansion and constant pressure heat rejectiona)Otto cycleb)Lenoir cyclec)Atkinson cycled)Brayton cycleCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Railways 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for This reversible cycle consists of constant volume heat addition, reversible adiabatic expansion and constant pressure heat rejectiona)Otto cycleb)Lenoir cyclec)Atkinson cycled)Brayton cycleCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
This reversible cycle consists of constant volume heat addition, reversible adiabatic expansion and constant pressure heat rejectiona)Otto cycleb)Lenoir cyclec)Atkinson cycled)Brayton cycleCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Railways 2025 is part of Railways preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Railways exam syllabus. Information about This reversible cycle consists of constant volume heat addition, reversible adiabatic expansion and constant pressure heat rejectiona)Otto cycleb)Lenoir cyclec)Atkinson cycled)Brayton cycleCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Railways 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for This reversible cycle consists of constant volume heat addition, reversible adiabatic expansion and constant pressure heat rejectiona)Otto cycleb)Lenoir cyclec)Atkinson cycled)Brayton cycleCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for This reversible cycle consists of constant volume heat addition, reversible adiabatic expansion and constant pressure heat rejectiona)Otto cycleb)Lenoir cyclec)Atkinson cycled)Brayton cycleCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Railways.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Railways Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of This reversible cycle consists of constant volume heat addition, reversible adiabatic expansion and constant pressure heat rejectiona)Otto cycleb)Lenoir cyclec)Atkinson cycled)Brayton cycleCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
This reversible cycle consists of constant volume heat addition, reversible adiabatic expansion and constant pressure heat rejectiona)Otto cycleb)Lenoir cyclec)Atkinson cycled)Brayton cycleCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for This reversible cycle consists of constant volume heat addition, reversible adiabatic expansion and constant pressure heat rejectiona)Otto cycleb)Lenoir cyclec)Atkinson cycled)Brayton cycleCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of This reversible cycle consists of constant volume heat addition, reversible adiabatic expansion and constant pressure heat rejectiona)Otto cycleb)Lenoir cyclec)Atkinson cycled)Brayton cycleCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice This reversible cycle consists of constant volume heat addition, reversible adiabatic expansion and constant pressure heat rejectiona)Otto cycleb)Lenoir cyclec)Atkinson cycled)Brayton cycleCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Railways tests.

|
Explore Courses for Railways exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























