Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > If the potential difference V applied across ...
Start Learning for Free
If the potential difference V applied across a conductor is increased to 2V with its temperature kept constant, the drift velocity of the free electrons in a conductor will:
- a)remain the same.
- b)become half of its previous value.
- c)be double of its initial value.
- d)become zero.
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
If the potential difference V applied across a conductor is increased ...
Introduction:
When a potential difference is applied across a conductor, it creates an electric field within the conductor which exerts a force on the free electrons present in the conductor. This force causes the electrons to drift in a particular direction, resulting in a net flow of charge or electric current.
Explanation:
To understand how the drift velocity of free electrons in a conductor changes when the potential difference is increased to 2V while keeping the temperature constant, let's consider the following points:
1. Relationship between drift velocity and applied potential difference:
The drift velocity of free electrons in a conductor is directly proportional to the applied potential difference. This means that as the potential difference increases, the drift velocity of the free electrons also increases.
2. Relationship between drift velocity and temperature:
The drift velocity of free electrons in a conductor is not directly affected by the temperature, as long as the temperature remains constant. Therefore, the drift velocity remains the same even when the temperature is constant.
3. Effect of increasing the potential difference:
When the potential difference across a conductor is increased to 2V, the electric field within the conductor becomes stronger. This stronger electric field exerts a greater force on the free electrons, causing them to accelerate and increase their drift velocity.
Conclusion:
Based on the above explanations, it can be concluded that when the potential difference applied across a conductor is increased to 2V while keeping the temperature constant, the drift velocity of the free electrons in the conductor will become double of its initial value. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C'.
When a potential difference is applied across a conductor, it creates an electric field within the conductor which exerts a force on the free electrons present in the conductor. This force causes the electrons to drift in a particular direction, resulting in a net flow of charge or electric current.
Explanation:
To understand how the drift velocity of free electrons in a conductor changes when the potential difference is increased to 2V while keeping the temperature constant, let's consider the following points:
1. Relationship between drift velocity and applied potential difference:
The drift velocity of free electrons in a conductor is directly proportional to the applied potential difference. This means that as the potential difference increases, the drift velocity of the free electrons also increases.
2. Relationship between drift velocity and temperature:
The drift velocity of free electrons in a conductor is not directly affected by the temperature, as long as the temperature remains constant. Therefore, the drift velocity remains the same even when the temperature is constant.
3. Effect of increasing the potential difference:
When the potential difference across a conductor is increased to 2V, the electric field within the conductor becomes stronger. This stronger electric field exerts a greater force on the free electrons, causing them to accelerate and increase their drift velocity.
Conclusion:
Based on the above explanations, it can be concluded that when the potential difference applied across a conductor is increased to 2V while keeping the temperature constant, the drift velocity of the free electrons in the conductor will become double of its initial value. Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C'.
Free Test
| FREE | Start Free Test |
Community Answer
If the potential difference V applied across a conductor is increased ...
We know
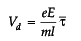
=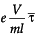
If temperature is kept constant, relaxation time τ - will remain constant and e, m are also constants.
Vd ∝ V
Vd ∝ 2V
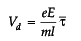
=
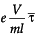
If temperature is kept constant, relaxation time τ - will remain constant and e, m are also constants.
Vd ∝ V
Vd ∝ 2V

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Question Description
If the potential difference V applied across a conductor is increased to 2V with its temperature kept constant, the drift velocity of the free electrons in a conductor will:a)remain the same.b)become half of its previous value.c)be double of its initial value.d)become zero.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about If the potential difference V applied across a conductor is increased to 2V with its temperature kept constant, the drift velocity of the free electrons in a conductor will:a)remain the same.b)become half of its previous value.c)be double of its initial value.d)become zero.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for If the potential difference V applied across a conductor is increased to 2V with its temperature kept constant, the drift velocity of the free electrons in a conductor will:a)remain the same.b)become half of its previous value.c)be double of its initial value.d)become zero.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
If the potential difference V applied across a conductor is increased to 2V with its temperature kept constant, the drift velocity of the free electrons in a conductor will:a)remain the same.b)become half of its previous value.c)be double of its initial value.d)become zero.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about If the potential difference V applied across a conductor is increased to 2V with its temperature kept constant, the drift velocity of the free electrons in a conductor will:a)remain the same.b)become half of its previous value.c)be double of its initial value.d)become zero.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for If the potential difference V applied across a conductor is increased to 2V with its temperature kept constant, the drift velocity of the free electrons in a conductor will:a)remain the same.b)become half of its previous value.c)be double of its initial value.d)become zero.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for If the potential difference V applied across a conductor is increased to 2V with its temperature kept constant, the drift velocity of the free electrons in a conductor will:a)remain the same.b)become half of its previous value.c)be double of its initial value.d)become zero.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of If the potential difference V applied across a conductor is increased to 2V with its temperature kept constant, the drift velocity of the free electrons in a conductor will:a)remain the same.b)become half of its previous value.c)be double of its initial value.d)become zero.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
If the potential difference V applied across a conductor is increased to 2V with its temperature kept constant, the drift velocity of the free electrons in a conductor will:a)remain the same.b)become half of its previous value.c)be double of its initial value.d)become zero.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for If the potential difference V applied across a conductor is increased to 2V with its temperature kept constant, the drift velocity of the free electrons in a conductor will:a)remain the same.b)become half of its previous value.c)be double of its initial value.d)become zero.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of If the potential difference V applied across a conductor is increased to 2V with its temperature kept constant, the drift velocity of the free electrons in a conductor will:a)remain the same.b)become half of its previous value.c)be double of its initial value.d)become zero.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice If the potential difference V applied across a conductor is increased to 2V with its temperature kept constant, the drift velocity of the free electrons in a conductor will:a)remain the same.b)become half of its previous value.c)be double of its initial value.d)become zero.Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























