GATE Exam > GATE Questions > The flow in a rectangular channel is subcrit...
Start Learning for Free
The flow in a rectangular channel is subcritical. If width of the channel is reduced at a certain section, the water surface under no–choke condition will
- a)Drop at a downstream section
- b)Rise at a downstream section
- c)Rise at an upstream section
- d)Not undergo any change
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
The flow in a rectangular channel is subcritical. If width of the cha...
In the subcritical region of flow for a given specific energy, as the discharge per unit width q is increased due to reducing width at the section, the depth of flow will decrease.
Therefore water surface drop at a downstream section.
Alternately
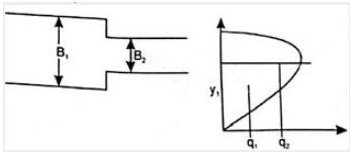
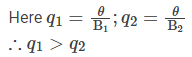
From the discharge diagram, it can be seen that, for subcritical flow as q increases, depth decreases.
Therefore at the reduced section, depth decreases.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The flow in a rectangular channel is subcritical. If width of the cha...
Introduction:
The flow in a rectangular channel is said to be subcritical when the flow velocity is less than the wave speed. In this scenario, if the width of the channel is reduced at a certain section, the water surface under no-choke condition will drop at a downstream section.
Explanation:
When the width of a rectangular channel is reduced at a certain section, it causes a decrease in the cross-sectional area of the channel. According to the continuity equation, which states that the product of velocity and cross-sectional area is constant, a decrease in cross-sectional area will result in an increase in flow velocity.
Reason for water surface drop:
1. Change in cross-sectional area: As the width of the channel is reduced, the cross-sectional area decreases.
2. Continuity equation: According to the continuity equation, the product of velocity and cross-sectional area is constant. Since the cross-sectional area decreases, the flow velocity must increase to maintain the constant product.
3. Subcritical flow: The flow in the channel is already subcritical, indicating that the flow velocity is less than the wave speed. Therefore, any increase in flow velocity will result in a drop in water surface elevation.
4. Conservation of energy: In subcritical flow, the water surface elevation is directly related to the specific energy of the flow. When the flow velocity increases due to the channel width reduction, the specific energy decreases. This leads to a drop in the water surface elevation.
Conclusion:
In summary, when the width of a rectangular channel is reduced at a certain section, the water surface under no-choke condition will drop at a downstream section. This is due to the decrease in cross-sectional area, resulting in an increase in flow velocity, which in turn leads to a decrease in water surface elevation.
The flow in a rectangular channel is said to be subcritical when the flow velocity is less than the wave speed. In this scenario, if the width of the channel is reduced at a certain section, the water surface under no-choke condition will drop at a downstream section.
Explanation:
When the width of a rectangular channel is reduced at a certain section, it causes a decrease in the cross-sectional area of the channel. According to the continuity equation, which states that the product of velocity and cross-sectional area is constant, a decrease in cross-sectional area will result in an increase in flow velocity.
Reason for water surface drop:
1. Change in cross-sectional area: As the width of the channel is reduced, the cross-sectional area decreases.
2. Continuity equation: According to the continuity equation, the product of velocity and cross-sectional area is constant. Since the cross-sectional area decreases, the flow velocity must increase to maintain the constant product.
3. Subcritical flow: The flow in the channel is already subcritical, indicating that the flow velocity is less than the wave speed. Therefore, any increase in flow velocity will result in a drop in water surface elevation.
4. Conservation of energy: In subcritical flow, the water surface elevation is directly related to the specific energy of the flow. When the flow velocity increases due to the channel width reduction, the specific energy decreases. This leads to a drop in the water surface elevation.
Conclusion:
In summary, when the width of a rectangular channel is reduced at a certain section, the water surface under no-choke condition will drop at a downstream section. This is due to the decrease in cross-sectional area, resulting in an increase in flow velocity, which in turn leads to a decrease in water surface elevation.

|
Explore Courses for GATE exam
|

|
Similar GATE Doubts
Question Description
The flow in a rectangular channel is subcritical. If width of the channel is reduced at a certain section, the water surface under no–choke condition willa)Drop at a downstream sectionb)Rise at a downstream sectionc)Rise at an upstream sectiond)Not undergo any changeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for GATE 2025 is part of GATE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the GATE exam syllabus. Information about The flow in a rectangular channel is subcritical. If width of the channel is reduced at a certain section, the water surface under no–choke condition willa)Drop at a downstream sectionb)Rise at a downstream sectionc)Rise at an upstream sectiond)Not undergo any changeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for GATE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The flow in a rectangular channel is subcritical. If width of the channel is reduced at a certain section, the water surface under no–choke condition willa)Drop at a downstream sectionb)Rise at a downstream sectionc)Rise at an upstream sectiond)Not undergo any changeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
The flow in a rectangular channel is subcritical. If width of the channel is reduced at a certain section, the water surface under no–choke condition willa)Drop at a downstream sectionb)Rise at a downstream sectionc)Rise at an upstream sectiond)Not undergo any changeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for GATE 2025 is part of GATE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the GATE exam syllabus. Information about The flow in a rectangular channel is subcritical. If width of the channel is reduced at a certain section, the water surface under no–choke condition willa)Drop at a downstream sectionb)Rise at a downstream sectionc)Rise at an upstream sectiond)Not undergo any changeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for GATE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The flow in a rectangular channel is subcritical. If width of the channel is reduced at a certain section, the water surface under no–choke condition willa)Drop at a downstream sectionb)Rise at a downstream sectionc)Rise at an upstream sectiond)Not undergo any changeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The flow in a rectangular channel is subcritical. If width of the channel is reduced at a certain section, the water surface under no–choke condition willa)Drop at a downstream sectionb)Rise at a downstream sectionc)Rise at an upstream sectiond)Not undergo any changeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for GATE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for GATE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The flow in a rectangular channel is subcritical. If width of the channel is reduced at a certain section, the water surface under no–choke condition willa)Drop at a downstream sectionb)Rise at a downstream sectionc)Rise at an upstream sectiond)Not undergo any changeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The flow in a rectangular channel is subcritical. If width of the channel is reduced at a certain section, the water surface under no–choke condition willa)Drop at a downstream sectionb)Rise at a downstream sectionc)Rise at an upstream sectiond)Not undergo any changeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The flow in a rectangular channel is subcritical. If width of the channel is reduced at a certain section, the water surface under no–choke condition willa)Drop at a downstream sectionb)Rise at a downstream sectionc)Rise at an upstream sectiond)Not undergo any changeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The flow in a rectangular channel is subcritical. If width of the channel is reduced at a certain section, the water surface under no–choke condition willa)Drop at a downstream sectionb)Rise at a downstream sectionc)Rise at an upstream sectiond)Not undergo any changeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The flow in a rectangular channel is subcritical. If width of the channel is reduced at a certain section, the water surface under no–choke condition willa)Drop at a downstream sectionb)Rise at a downstream sectionc)Rise at an upstream sectiond)Not undergo any changeCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice GATE tests.

|
Explore Courses for GATE exam
|

|
Signup to solve all Doubts
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.




















