Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Questions > When a gas jar full of air is placed upside ...
Start Learning for Free
When a gas jar full of air is placed upside down on a gas jar full of bromine vapours, the red–brown vapours of bromine from the lower jar go upward into the jar containing air. In this experiment
- a)Bromine is heavier than air
- b)Air is heavier than bromine
- c)Coth air and bromine have the same density
- d)Bromine cannot be heavier than air because it is going upwards against gravity
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
When a gas jar full of air is placed upside down on a gas jar full of...
Explanation:
When a gas jar full of air is placed upside down on a gas jar full of bromine vapours, the red–brown vapours of bromine from the lower jar go upward into the jar containing air. This phenomenon can be explained by the difference in density between bromine and air.
Density of Bromine:
Bromine is a dense liquid, with a density of about 3.1 grams per cubic centimeter. This means that a given volume of bromine is much heavier than the same volume of air.
Density of Air:
Air, on the other hand, is a mixture of gases, primarily nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2), with a density of about 1.2 grams per cubic centimeter. This means that a given volume of air is lighter than the same volume of bromine.
Why does bromine go upward into the jar containing air?
The movement of bromine vapours from the lower jar into the jar containing air can be explained by the principle of diffusion. Diffusion is the process by which particles move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
In this case, the jar containing bromine vapours has a higher concentration of bromine molecules compared to the jar containing air. As a result, the bromine molecules tend to spread out or diffuse into the jar with lower bromine concentration, which is the jar containing air.
Since bromine is heavier than air, it might be expected that the bromine vapours would sink down instead of rising up. However, diffusion is driven by the random motion of particles, and the motion of gas particles is influenced by factors such as temperature and pressure.
In this experiment, the movement of bromine vapours upwards against gravity can be explained by the fact that the bromine molecules are highly volatile and have a higher vapor pressure compared to the air molecules. As a result, the bromine molecules are able to overcome the force of gravity and rise up into the jar containing air.
Therefore, the correct answer to the question is option 'A': Bromine is heavier than air.
When a gas jar full of air is placed upside down on a gas jar full of bromine vapours, the red–brown vapours of bromine from the lower jar go upward into the jar containing air. This phenomenon can be explained by the difference in density between bromine and air.
Density of Bromine:
Bromine is a dense liquid, with a density of about 3.1 grams per cubic centimeter. This means that a given volume of bromine is much heavier than the same volume of air.
Density of Air:
Air, on the other hand, is a mixture of gases, primarily nitrogen (N2) and oxygen (O2), with a density of about 1.2 grams per cubic centimeter. This means that a given volume of air is lighter than the same volume of bromine.
Why does bromine go upward into the jar containing air?
The movement of bromine vapours from the lower jar into the jar containing air can be explained by the principle of diffusion. Diffusion is the process by which particles move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
In this case, the jar containing bromine vapours has a higher concentration of bromine molecules compared to the jar containing air. As a result, the bromine molecules tend to spread out or diffuse into the jar with lower bromine concentration, which is the jar containing air.
Since bromine is heavier than air, it might be expected that the bromine vapours would sink down instead of rising up. However, diffusion is driven by the random motion of particles, and the motion of gas particles is influenced by factors such as temperature and pressure.
In this experiment, the movement of bromine vapours upwards against gravity can be explained by the fact that the bromine molecules are highly volatile and have a higher vapor pressure compared to the air molecules. As a result, the bromine molecules are able to overcome the force of gravity and rise up into the jar containing air.
Therefore, the correct answer to the question is option 'A': Bromine is heavier than air.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
When a gas jar full of air is placed upside down on a gas jar full of...
When a gas jar full of air is placed upside down on a gas jar full of bromine vapours, the red-brown vapours of bromine from the lower jar go upward into the jar containing air. In this experiment, Bromine vapour (or bromine gas) is red-brown in colour, and it is heavier than air ; therefore it is settling in bottom of apparatus and air is rising at the top of apparatus.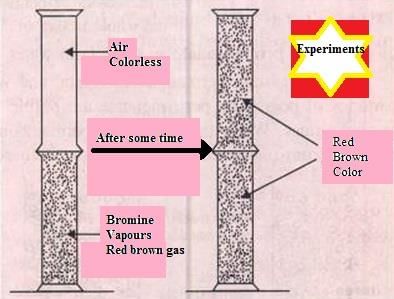


|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Similar Class 9 Doubts
Question Description
When a gas jar full of air is placed upside down on a gas jar full of bromine vapours, the red–brown vapours of bromine from the lower jar go upward into the jar containing air. In this experimenta)Bromine is heavier than airb)Air is heavier than brominec)Coth air and bromine have the same densityd)Bromine cannot be heavier than air because it is going upwards against gravityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 9 2025 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about When a gas jar full of air is placed upside down on a gas jar full of bromine vapours, the red–brown vapours of bromine from the lower jar go upward into the jar containing air. In this experimenta)Bromine is heavier than airb)Air is heavier than brominec)Coth air and bromine have the same densityd)Bromine cannot be heavier than air because it is going upwards against gravityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for When a gas jar full of air is placed upside down on a gas jar full of bromine vapours, the red–brown vapours of bromine from the lower jar go upward into the jar containing air. In this experimenta)Bromine is heavier than airb)Air is heavier than brominec)Coth air and bromine have the same densityd)Bromine cannot be heavier than air because it is going upwards against gravityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
When a gas jar full of air is placed upside down on a gas jar full of bromine vapours, the red–brown vapours of bromine from the lower jar go upward into the jar containing air. In this experimenta)Bromine is heavier than airb)Air is heavier than brominec)Coth air and bromine have the same densityd)Bromine cannot be heavier than air because it is going upwards against gravityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 9 2025 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about When a gas jar full of air is placed upside down on a gas jar full of bromine vapours, the red–brown vapours of bromine from the lower jar go upward into the jar containing air. In this experimenta)Bromine is heavier than airb)Air is heavier than brominec)Coth air and bromine have the same densityd)Bromine cannot be heavier than air because it is going upwards against gravityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for When a gas jar full of air is placed upside down on a gas jar full of bromine vapours, the red–brown vapours of bromine from the lower jar go upward into the jar containing air. In this experimenta)Bromine is heavier than airb)Air is heavier than brominec)Coth air and bromine have the same densityd)Bromine cannot be heavier than air because it is going upwards against gravityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for When a gas jar full of air is placed upside down on a gas jar full of bromine vapours, the red–brown vapours of bromine from the lower jar go upward into the jar containing air. In this experimenta)Bromine is heavier than airb)Air is heavier than brominec)Coth air and bromine have the same densityd)Bromine cannot be heavier than air because it is going upwards against gravityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 9.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of When a gas jar full of air is placed upside down on a gas jar full of bromine vapours, the red–brown vapours of bromine from the lower jar go upward into the jar containing air. In this experimenta)Bromine is heavier than airb)Air is heavier than brominec)Coth air and bromine have the same densityd)Bromine cannot be heavier than air because it is going upwards against gravityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
When a gas jar full of air is placed upside down on a gas jar full of bromine vapours, the red–brown vapours of bromine from the lower jar go upward into the jar containing air. In this experimenta)Bromine is heavier than airb)Air is heavier than brominec)Coth air and bromine have the same densityd)Bromine cannot be heavier than air because it is going upwards against gravityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for When a gas jar full of air is placed upside down on a gas jar full of bromine vapours, the red–brown vapours of bromine from the lower jar go upward into the jar containing air. In this experimenta)Bromine is heavier than airb)Air is heavier than brominec)Coth air and bromine have the same densityd)Bromine cannot be heavier than air because it is going upwards against gravityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of When a gas jar full of air is placed upside down on a gas jar full of bromine vapours, the red–brown vapours of bromine from the lower jar go upward into the jar containing air. In this experimenta)Bromine is heavier than airb)Air is heavier than brominec)Coth air and bromine have the same densityd)Bromine cannot be heavier than air because it is going upwards against gravityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice When a gas jar full of air is placed upside down on a gas jar full of bromine vapours, the red–brown vapours of bromine from the lower jar go upward into the jar containing air. In this experimenta)Bromine is heavier than airb)Air is heavier than brominec)Coth air and bromine have the same densityd)Bromine cannot be heavier than air because it is going upwards against gravityCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 9 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Signup to solve all Doubts
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



























