Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > A radio can tune to any station in the freque...
Start Learning for Free
A radio can tune to any station in the frequency range from 2.5 MHz to 15 MHz bands. What is the corresponding wavelength band?
- a)30 m to 130 m
- b)40 m to 140 m
- c)20 m to 120 m
- d)10 m to 110 m
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
A radio can tune to any station in the frequency range from 2.5 MHz to...
The wavelength band of the radio is from 20 m to 120 m.
To understand why option C is the correct answer, let's break down the given information:
- The frequency range of the radio is from 2.5 MHz to 15 MHz.
- The corresponding wavelength band is being asked.
Understanding the Relationship between Frequency and Wavelength:
There is an inverse relationship between frequency and wavelength. As the frequency of a wave increases, its wavelength decreases, and vice versa. This relationship is defined by the equation:
Speed of light = Frequency x Wavelength
Since the speed of light is constant, any change in frequency will result in a corresponding change in wavelength.
Calculating the Wavelength Range:
1. The given frequency range is from 2.5 MHz to 15 MHz.
2. We can convert these frequencies to wavelengths using the equation:
Wavelength = Speed of light / Frequency
The speed of light is approximately 3 x 10^8 meters per second.
3. For the lower frequency of 2.5 MHz:
Wavelength = (3 x 10^8 m/s) / (2.5 x 10^6 Hz)
= 120 m
Therefore, the lower wavelength limit is 120 m.
4. For the higher frequency of 15 MHz:
Wavelength = (3 x 10^8 m/s) / (15 x 10^6 Hz)
= 20 m
Therefore, the higher wavelength limit is 20 m.
Conclusion:
The corresponding wavelength band for the given frequency range of 2.5 MHz to 15 MHz is from 20 m to 120 m. This matches with option C, making it the correct answer.
To understand why option C is the correct answer, let's break down the given information:
- The frequency range of the radio is from 2.5 MHz to 15 MHz.
- The corresponding wavelength band is being asked.
Understanding the Relationship between Frequency and Wavelength:
There is an inverse relationship between frequency and wavelength. As the frequency of a wave increases, its wavelength decreases, and vice versa. This relationship is defined by the equation:
Speed of light = Frequency x Wavelength
Since the speed of light is constant, any change in frequency will result in a corresponding change in wavelength.
Calculating the Wavelength Range:
1. The given frequency range is from 2.5 MHz to 15 MHz.
2. We can convert these frequencies to wavelengths using the equation:
Wavelength = Speed of light / Frequency
The speed of light is approximately 3 x 10^8 meters per second.
3. For the lower frequency of 2.5 MHz:
Wavelength = (3 x 10^8 m/s) / (2.5 x 10^6 Hz)
= 120 m
Therefore, the lower wavelength limit is 120 m.
4. For the higher frequency of 15 MHz:
Wavelength = (3 x 10^8 m/s) / (15 x 10^6 Hz)
= 20 m
Therefore, the higher wavelength limit is 20 m.
Conclusion:
The corresponding wavelength band for the given frequency range of 2.5 MHz to 15 MHz is from 20 m to 120 m. This matches with option C, making it the correct answer.
Community Answer
A radio can tune to any station in the frequency range from 2.5 MHz to...
Maximum wavelength in the band will correspond to the lowest frequency:
c = fminλmax
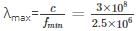
= 120 m
Minimum wavelength in the band will correspond to the highest frequency:
c = fmaxλmin
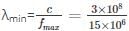
= 20 m
Therefore, the corresponding wavelength band is 20 m to 120 m.
c = fminλmax
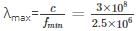
= 120 m
Minimum wavelength in the band will correspond to the highest frequency:
c = fmaxλmin
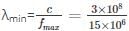
= 20 m
Therefore, the corresponding wavelength band is 20 m to 120 m.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Question Description
A radio can tune to any station in the frequency range from 2.5 MHz to 15 MHz bands. What is the corresponding wavelength band?a)30 m to 130 mb)40 m to 140 mc)20 m to 120 md)10 m to 110 mCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about A radio can tune to any station in the frequency range from 2.5 MHz to 15 MHz bands. What is the corresponding wavelength band?a)30 m to 130 mb)40 m to 140 mc)20 m to 120 md)10 m to 110 mCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A radio can tune to any station in the frequency range from 2.5 MHz to 15 MHz bands. What is the corresponding wavelength band?a)30 m to 130 mb)40 m to 140 mc)20 m to 120 md)10 m to 110 mCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
A radio can tune to any station in the frequency range from 2.5 MHz to 15 MHz bands. What is the corresponding wavelength band?a)30 m to 130 mb)40 m to 140 mc)20 m to 120 md)10 m to 110 mCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about A radio can tune to any station in the frequency range from 2.5 MHz to 15 MHz bands. What is the corresponding wavelength band?a)30 m to 130 mb)40 m to 140 mc)20 m to 120 md)10 m to 110 mCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A radio can tune to any station in the frequency range from 2.5 MHz to 15 MHz bands. What is the corresponding wavelength band?a)30 m to 130 mb)40 m to 140 mc)20 m to 120 md)10 m to 110 mCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A radio can tune to any station in the frequency range from 2.5 MHz to 15 MHz bands. What is the corresponding wavelength band?a)30 m to 130 mb)40 m to 140 mc)20 m to 120 md)10 m to 110 mCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A radio can tune to any station in the frequency range from 2.5 MHz to 15 MHz bands. What is the corresponding wavelength band?a)30 m to 130 mb)40 m to 140 mc)20 m to 120 md)10 m to 110 mCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A radio can tune to any station in the frequency range from 2.5 MHz to 15 MHz bands. What is the corresponding wavelength band?a)30 m to 130 mb)40 m to 140 mc)20 m to 120 md)10 m to 110 mCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A radio can tune to any station in the frequency range from 2.5 MHz to 15 MHz bands. What is the corresponding wavelength band?a)30 m to 130 mb)40 m to 140 mc)20 m to 120 md)10 m to 110 mCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A radio can tune to any station in the frequency range from 2.5 MHz to 15 MHz bands. What is the corresponding wavelength band?a)30 m to 130 mb)40 m to 140 mc)20 m to 120 md)10 m to 110 mCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A radio can tune to any station in the frequency range from 2.5 MHz to 15 MHz bands. What is the corresponding wavelength band?a)30 m to 130 mb)40 m to 140 mc)20 m to 120 md)10 m to 110 mCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























