Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > Which of the following statement(s) is/are TR...
Start Learning for Free
Which of the following statement(s) is/are TRUE regarding the magnetic shielding in an electrodynamometer wattmeter?
A. To avoid stray magnetic field errors
B. instrument is enclosed in a casing of high permeability alloy
C. A soft iron core is placed to direct the flux
A. To avoid stray magnetic field errors
B. instrument is enclosed in a casing of high permeability alloy
C. A soft iron core is placed to direct the flux
- a)A and B
- b)B and C
- c)C and A
- d)A, B, and C
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Which of the following statement(s) is/are TRUE regarding the magnetic...
Electrodynamometer Instruments:
- The electrodynamometer is a transfer-type instrument.
- A transfer-type instrument is one that may be calibrated with a dc source and then used without modification to measure AC.
- This requires the transfer type instruments to have the same accuracy for both DC and AC.
- These instruments are also called Electrodynamic or Dynamometer Type Instruments.
- A schematic diagram of Electrodynamic or Dynamometer Type Instruments is shown below:
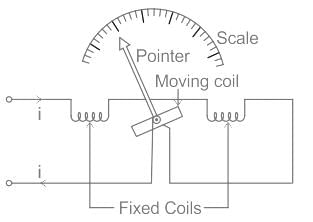
- An electrodynamic instrument is a moving-coil instrument in which the operating field is produced, not by a permanent magnet but by another fixed coil.
- This instrument can be used either as an ammeter or a voltmeter but is generally used as a wattmeter.
- The electrodynamic or dynamometer-type instrument is a moving-coil instrument but the magnetic field, in which the coil moves, is provided by two fixed coils rather than by permanent magnets (eg: PMMC instruments).
Construction:
Different parts of an Electrodynamometer instrument are briefly explained below
Fixed Coils:
Different parts of an Electrodynamometer instrument are briefly explained below
Fixed Coils:
- The field is produced by a fixed coil.
- This coil is divided into two sections to give a more uniform field near the center and to allow passage of the instrument shaft.
- The instrument as shown in the figure by a milliammeter, or may become a voltmeter by the addition of series resistance.
- The fixed coils are wound with fine wire for such applications.
- Field (fixed) coils are usually wound with a heavy wire carrying the main current in ammeters and watt meters.
- The wire is stranded where necessary to reduce eddy current losses in conductors.
- The coils are usually varnished and baked to form a solid assembly.
- These are then clamped in place against the coil supports, This makes the construction rigid so that there is no shifting or change in dimensions that might affect the calibration.
- The mounting supports are preferably made out of ceramic, as metal parts would weaken the field of the fixed coil on account of eddy currents.
Moving Coil:
- A single-element instrument has one moving coil.
- The moving coil is wound either as a self-sustaining coil or else on a non-metallic former.
- A metallic former cannot be used as eddy currents would be induced in it by the alternating field.
- Light but rigid construction is used for the moving coil.
- It should be noted that both fixed and moving coils are air-cored.
Control:
- The controlling torque is provided by two control springs.
- These springs act as leads to the moving coil.
Moving System:
- The moving coil is mounted on an aluminum spindle.
- The moving system also carries the counterweights and truss-type pointer.
- Sometimes a suspension may be used in case high sensitivity is desired.
Damping:
- Air friction damping is employed for these instruments and is provided by a pair of aluminum vanes, attached to the spindle at the bottom.
- These vanes move in sector-shaped chambers.
Shielding:
- The field produced by the fixed coils is somewhat weaker than in other types of instruments.
- It is nearly 0.005 to 0.006 Wb/m2.
- In DC measurements, even the earth’s magnetic field may affect the readings.
- Thus it is necessary to shield an electrodynamometer-type instrument from the effect of stray magnetic fields (0.0005 - 0.00075 Wb/m2).
- Air-cored electrodynamometer-type instruments are protected against external magnetic fields by enclosing them in a casing of high permeability alloy.
Cases and Scales:
- Laboratory standard instruments are usually contained in highly polished wooden cases.
- These cases are so constructed as to remain dimensionally stable over long periods.
- The glass is coated with some conducting material to completely remove the electrostatic effects.
- The case is supported by arable leveling screws.
- A spirit level is also provided to ensure proper leveling.
Most Upvoted Answer
Which of the following statement(s) is/are TRUE regarding the magnetic...
Explanation:
Magnetic Shielding in an Electrodynamometer Wattmeter:
- To avoid stray magnetic field errors: Magnetic shielding is necessary in an electrodynamometer wattmeter to prevent stray magnetic fields from affecting the accuracy of the measurements. Stray magnetic fields can cause interference and inaccuracies in the readings.
- Instrument is enclosed in a casing of high permeability alloy: The instrument is typically enclosed in a casing made of a high permeability alloy such as mu-metal. This material helps in redirecting and confining the magnetic flux within the instrument, minimizing the influence of external magnetic fields.
- Soft iron core is placed to direct the flux: A soft iron core is often placed strategically within the instrument to help direct the magnetic flux and improve the overall efficiency of the wattmeter. The soft iron core enhances the magnetic shielding properties of the instrument.
Therefore, the true statement regarding the magnetic shielding in an electrodynamometer wattmeter is option A: To avoid stray magnetic field errors. This process helps in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the wattmeter readings by minimizing external magnetic field influences.
Magnetic Shielding in an Electrodynamometer Wattmeter:
- To avoid stray magnetic field errors: Magnetic shielding is necessary in an electrodynamometer wattmeter to prevent stray magnetic fields from affecting the accuracy of the measurements. Stray magnetic fields can cause interference and inaccuracies in the readings.
- Instrument is enclosed in a casing of high permeability alloy: The instrument is typically enclosed in a casing made of a high permeability alloy such as mu-metal. This material helps in redirecting and confining the magnetic flux within the instrument, minimizing the influence of external magnetic fields.
- Soft iron core is placed to direct the flux: A soft iron core is often placed strategically within the instrument to help direct the magnetic flux and improve the overall efficiency of the wattmeter. The soft iron core enhances the magnetic shielding properties of the instrument.
Therefore, the true statement regarding the magnetic shielding in an electrodynamometer wattmeter is option A: To avoid stray magnetic field errors. This process helps in ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the wattmeter readings by minimizing external magnetic field influences.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Which of the following statement(s) is/are TRUE regarding the magnetic...
Electrodynamometer Instruments:
- The electrodynamometer is a transfer-type instrument.
- A transfer-type instrument is one that may be calibrated with a dc source and then used without modification to measure AC.
- This requires the transfer type instruments to have the same accuracy for both DC and AC.
- These instruments are also called Electrodynamic or Dynamometer Type Instruments.
- A schematic diagram of Electrodynamic or Dynamometer Type Instruments is shown below:

- An electrodynamic instrument is a moving-coil instrument in which the operating field is produced, not by a permanent magnet but by another fixed coil.
- This instrument can be used either as an ammeter or a voltmeter but is generally used as a wattmeter.
- The electrodynamic or dynamometer-type instrument is a moving-coil instrument but the magnetic field, in which the coil moves, is provided by two fixed coils rather than by permanent magnets (eg: PMMC instruments).
Construction:
Different parts of an Electrodynamometer instrument are briefly explained below
Fixed Coils:
Different parts of an Electrodynamometer instrument are briefly explained below
Fixed Coils:
- The field is produced by a fixed coil.
- This coil is divided into two sections to give a more uniform field near the center and to allow passage of the instrument shaft.
- The instrument as shown in the figure by a milliammeter, or may become a voltmeter by the addition of series resistance.
- The fixed coils are wound with fine wire for such applications.
- Field (fixed) coils are usually wound with a heavy wire carrying the main current in ammeters and watt meters.
- The wire is stranded where necessary to reduce eddy current losses in conductors.
- The coils are usually varnished and baked to form a solid assembly.
- These are then clamped in place against the coil supports, This makes the construction rigid so that there is no shifting or change in dimensions that might affect the calibration.
- The mounting supports are preferably made out of ceramic, as metal parts would weaken the field of the fixed coil on account of eddy currents.
Moving Coil:
- A single-element instrument has one moving coil.
- The moving coil is wound either as a self-sustaining coil or else on a non-metallic former.
- A metallic former cannot be used as eddy currents would be induced in it by the alternating field.
- Light but rigid construction is used for the moving coil.
- It should be noted that both fixed and moving coils are air-cored.
Control:
- The controlling torque is provided by two control springs.
- These springs act as leads to the moving coil.
Moving System:
- The moving coil is mounted on an aluminum spindle.
- The moving system also carries the counterweights and truss-type pointer.
- Sometimes a suspension may be used in case high sensitivity is desired.
Damping:
- Air friction damping is employed for these instruments and is provided by a pair of aluminum vanes, attached to the spindle at the bottom.
- These vanes move in sector-shaped chambers.
Shielding:
- The field produced by the fixed coils is somewhat weaker than in other types of instruments.
- It is nearly 0.005 to 0.006 Wb/m2.
- In DC measurements, even the earth’s magnetic field may affect the readings.
- Thus it is necessary to shield an electrodynamometer-type instrument from the effect of stray magnetic fields (0.0005 - 0.00075 Wb/m2).
- Air-cored electrodynamometer-type instruments are protected against external magnetic fields by enclosing them in a casing of high permeability alloy.
Cases and Scales:
- Laboratory standard instruments are usually contained in highly polished wooden cases.
- These cases are so constructed as to remain dimensionally stable over long periods.
- The glass is coated with some conducting material to completely remove the electrostatic effects.
- The case is supported by arable leveling screws.
- A spirit level is also provided to ensure proper leveling.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Similar Electrical Engineering (EE) Doubts
Which of the following statement(s) is/are TRUE regarding the magnetic shielding in an electrodynamometer wattmeter?A. To avoid stray magnetic field errorsB. instrument is enclosed in a casing of high permeability alloyC. A soft iron core is placed to direct the fluxa)A and Bb)B and Cc)C and Ad)A, B, and CCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Which of the following statement(s) is/are TRUE regarding the magnetic shielding in an electrodynamometer wattmeter?A. To avoid stray magnetic field errorsB. instrument is enclosed in a casing of high permeability alloyC. A soft iron core is placed to direct the fluxa)A and Bb)B and Cc)C and Ad)A, B, and CCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following statement(s) is/are TRUE regarding the magnetic shielding in an electrodynamometer wattmeter?A. To avoid stray magnetic field errorsB. instrument is enclosed in a casing of high permeability alloyC. A soft iron core is placed to direct the fluxa)A and Bb)B and Cc)C and Ad)A, B, and CCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following statement(s) is/are TRUE regarding the magnetic shielding in an electrodynamometer wattmeter?A. To avoid stray magnetic field errorsB. instrument is enclosed in a casing of high permeability alloyC. A soft iron core is placed to direct the fluxa)A and Bb)B and Cc)C and Ad)A, B, and CCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Which of the following statement(s) is/are TRUE regarding the magnetic shielding in an electrodynamometer wattmeter?A. To avoid stray magnetic field errorsB. instrument is enclosed in a casing of high permeability alloyC. A soft iron core is placed to direct the fluxa)A and Bb)B and Cc)C and Ad)A, B, and CCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about Which of the following statement(s) is/are TRUE regarding the magnetic shielding in an electrodynamometer wattmeter?A. To avoid stray magnetic field errorsB. instrument is enclosed in a casing of high permeability alloyC. A soft iron core is placed to direct the fluxa)A and Bb)B and Cc)C and Ad)A, B, and CCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Which of the following statement(s) is/are TRUE regarding the magnetic shielding in an electrodynamometer wattmeter?A. To avoid stray magnetic field errorsB. instrument is enclosed in a casing of high permeability alloyC. A soft iron core is placed to direct the fluxa)A and Bb)B and Cc)C and Ad)A, B, and CCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Which of the following statement(s) is/are TRUE regarding the magnetic shielding in an electrodynamometer wattmeter?A. To avoid stray magnetic field errorsB. instrument is enclosed in a casing of high permeability alloyC. A soft iron core is placed to direct the fluxa)A and Bb)B and Cc)C and Ad)A, B, and CCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Which of the following statement(s) is/are TRUE regarding the magnetic shielding in an electrodynamometer wattmeter?A. To avoid stray magnetic field errorsB. instrument is enclosed in a casing of high permeability alloyC. A soft iron core is placed to direct the fluxa)A and Bb)B and Cc)C and Ad)A, B, and CCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Which of the following statement(s) is/are TRUE regarding the magnetic shielding in an electrodynamometer wattmeter?A. To avoid stray magnetic field errorsB. instrument is enclosed in a casing of high permeability alloyC. A soft iron core is placed to direct the fluxa)A and Bb)B and Cc)C and Ad)A, B, and CCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Which of the following statement(s) is/are TRUE regarding the magnetic shielding in an electrodynamometer wattmeter?A. To avoid stray magnetic field errorsB. instrument is enclosed in a casing of high permeability alloyC. A soft iron core is placed to direct the fluxa)A and Bb)B and Cc)C and Ad)A, B, and CCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Which of the following statement(s) is/are TRUE regarding the magnetic shielding in an electrodynamometer wattmeter?A. To avoid stray magnetic field errorsB. instrument is enclosed in a casing of high permeability alloyC. A soft iron core is placed to direct the fluxa)A and Bb)B and Cc)C and Ad)A, B, and CCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Which of the following statement(s) is/are TRUE regarding the magnetic shielding in an electrodynamometer wattmeter?A. To avoid stray magnetic field errorsB. instrument is enclosed in a casing of high permeability alloyC. A soft iron core is placed to direct the fluxa)A and Bb)B and Cc)C and Ad)A, B, and CCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


























