Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > What is the phase angle between the capacitor...
Start Learning for Free
What is the phase angle between the capacitor current and the applied voltage in a parallel RC circuit?
- a)90°
- b)0°
- c)45°
- d)180°
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
What is the phase angle between the capacitor current and the applied ...
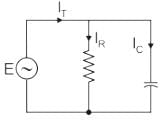
The phasor diagram is drawn as:
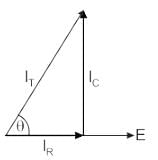
1) There is no phase difference between the applied voltage and the voltage across R and C in parallel.
2) The current through the resistive branch is in phase with the applied signal.
3) But the current through the capacitive branch leads its voltage Vc by 90 degrees.
.
Most Upvoted Answer
What is the phase angle between the capacitor current and the applied ...

The phasor diagram is drawn as:

1) There is no phase difference between the applied voltage and the voltage across R and C in parallel.
2) The current through the resistive branch is in phase with the applied signal.
3) But the current through the capacitive branch leads its voltage Vc by 90 degrees.
.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
What is the phase angle between the capacitor current and the applied ...
Understanding Phase Angle in Parallel RC Circuits
In a parallel RC circuit, the relationship between the voltage across the components and the current flowing through them is defined by the characteristics of the resistor (R) and capacitor (C).
Phase Angle Definition
- The phase angle indicates the phase difference between the voltage and the current in an AC circuit.
- In a purely resistive circuit, the current and voltage are in phase (0°).
- In a purely capacitive circuit, the current leads the voltage by 90°.
Current in a Parallel RC Circuit
- In a parallel RC circuit, the capacitor current (Ic) leads the voltage by 90° due to the nature of capacitors.
- The resistor current (Ir) is in phase with the applied voltage (0°).
Resultant Current and Phase Angle
- The total current (It) in the circuit is the vector sum of the resistor current and the capacitor current.
- Since Ic leads the voltage by 90° and Ir is in phase with the voltage, the resultant current will have a phase angle that is between 0° and 90°.
- However, when specifically assessing the capacitor current (Ic) in relation to the applied voltage, it is essential to note that it leads by 90°.
Conclusion
- Therefore, in the context of the phase relationship between the capacitor current and the applied voltage in a parallel RC circuit, the correct answer is 90° (option A).
This leads to the conclusion that the capacitor current always leads the applied voltage by 90°, confirming the correctness of option A.
In a parallel RC circuit, the relationship between the voltage across the components and the current flowing through them is defined by the characteristics of the resistor (R) and capacitor (C).
Phase Angle Definition
- The phase angle indicates the phase difference between the voltage and the current in an AC circuit.
- In a purely resistive circuit, the current and voltage are in phase (0°).
- In a purely capacitive circuit, the current leads the voltage by 90°.
Current in a Parallel RC Circuit
- In a parallel RC circuit, the capacitor current (Ic) leads the voltage by 90° due to the nature of capacitors.
- The resistor current (Ir) is in phase with the applied voltage (0°).
Resultant Current and Phase Angle
- The total current (It) in the circuit is the vector sum of the resistor current and the capacitor current.
- Since Ic leads the voltage by 90° and Ir is in phase with the voltage, the resultant current will have a phase angle that is between 0° and 90°.
- However, when specifically assessing the capacitor current (Ic) in relation to the applied voltage, it is essential to note that it leads by 90°.
Conclusion
- Therefore, in the context of the phase relationship between the capacitor current and the applied voltage in a parallel RC circuit, the correct answer is 90° (option A).
This leads to the conclusion that the capacitor current always leads the applied voltage by 90°, confirming the correctness of option A.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Question Description
What is the phase angle between the capacitor current and the applied voltage in a parallel RC circuit?a)90°b)0°c)45°d)180°Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about What is the phase angle between the capacitor current and the applied voltage in a parallel RC circuit?a)90°b)0°c)45°d)180°Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is the phase angle between the capacitor current and the applied voltage in a parallel RC circuit?a)90°b)0°c)45°d)180°Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
What is the phase angle between the capacitor current and the applied voltage in a parallel RC circuit?a)90°b)0°c)45°d)180°Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about What is the phase angle between the capacitor current and the applied voltage in a parallel RC circuit?a)90°b)0°c)45°d)180°Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is the phase angle between the capacitor current and the applied voltage in a parallel RC circuit?a)90°b)0°c)45°d)180°Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for What is the phase angle between the capacitor current and the applied voltage in a parallel RC circuit?a)90°b)0°c)45°d)180°Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of What is the phase angle between the capacitor current and the applied voltage in a parallel RC circuit?a)90°b)0°c)45°d)180°Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
What is the phase angle between the capacitor current and the applied voltage in a parallel RC circuit?a)90°b)0°c)45°d)180°Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for What is the phase angle between the capacitor current and the applied voltage in a parallel RC circuit?a)90°b)0°c)45°d)180°Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of What is the phase angle between the capacitor current and the applied voltage in a parallel RC circuit?a)90°b)0°c)45°d)180°Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice What is the phase angle between the capacitor current and the applied voltage in a parallel RC circuit?a)90°b)0°c)45°d)180°Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























