Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > A diode rectifier cannot perform rectificatio...
Start Learning for Free
A diode rectifier cannot perform rectification in both directions' is a perfect example of:
- a)Unilateral circuit
- b)Bilateral circuit
- c)Quadrilateral circuit
- d)Trilateral circuit
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
A diode rectifier cannot perform rectification in both directions is a...
Unilateral Circuit
A unilateral circuit is a circuit that allows the flow of current in only one direction. In other words, it can rectify AC (alternating current) into DC (direct current) but cannot perform rectification in both directions. A diode rectifier is a perfect example of a unilateral circuit.
Diode Rectifier
A diode rectifier is a device that converts alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) by allowing the flow of current in only one direction. It consists of a diode, which is a two-terminal semiconductor device that conducts current in one direction and blocks it in the opposite direction. When an AC signal is applied to a diode rectifier, it allows the positive half-cycle of the signal to pass through while blocking the negative half-cycle.
Function of a Diode
A diode has two terminals, an anode and a cathode. The anode is the positive terminal, and the cathode is the negative terminal. When a positive voltage is applied to the anode and a negative voltage is applied to the cathode, the diode is said to be forward-biased. In this condition, the diode acts like a closed switch and allows current to flow through it. On the other hand, when a negative voltage is applied to the anode and a positive voltage is applied to the cathode, the diode is said to be reverse-biased. In this condition, the diode acts like an open switch and blocks the flow of current.
Rectification
Rectification is the process of converting an AC signal into a DC signal. In a diode rectifier, the positive half-cycle of the AC signal is rectified and converted into a positive DC signal, while the negative half-cycle is blocked. This results in a pulsating DC waveform, where the voltage is positive for a certain duration and zero for the remaining duration of the AC signal.
Limitations of a Diode Rectifier
The main limitation of a diode rectifier is its inability to perform rectification in both directions. It can only rectify the positive half-cycle of an AC signal while blocking the negative half-cycle. Therefore, it can only produce a unidirectional DC output. If a bidirectional rectification is required, such as in a full-wave rectifier circuit, additional diodes or a different rectification technique, such as a bridge rectifier, is used.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a diode rectifier is a perfect example of a unilateral circuit because it can only perform rectification in one direction, allowing the flow of current in the forward-biased direction and blocking it in the reverse-biased direction. This limitation makes it unsuitable for applications that require bidirectional rectification.
A unilateral circuit is a circuit that allows the flow of current in only one direction. In other words, it can rectify AC (alternating current) into DC (direct current) but cannot perform rectification in both directions. A diode rectifier is a perfect example of a unilateral circuit.
Diode Rectifier
A diode rectifier is a device that converts alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) by allowing the flow of current in only one direction. It consists of a diode, which is a two-terminal semiconductor device that conducts current in one direction and blocks it in the opposite direction. When an AC signal is applied to a diode rectifier, it allows the positive half-cycle of the signal to pass through while blocking the negative half-cycle.
Function of a Diode
A diode has two terminals, an anode and a cathode. The anode is the positive terminal, and the cathode is the negative terminal. When a positive voltage is applied to the anode and a negative voltage is applied to the cathode, the diode is said to be forward-biased. In this condition, the diode acts like a closed switch and allows current to flow through it. On the other hand, when a negative voltage is applied to the anode and a positive voltage is applied to the cathode, the diode is said to be reverse-biased. In this condition, the diode acts like an open switch and blocks the flow of current.
Rectification
Rectification is the process of converting an AC signal into a DC signal. In a diode rectifier, the positive half-cycle of the AC signal is rectified and converted into a positive DC signal, while the negative half-cycle is blocked. This results in a pulsating DC waveform, where the voltage is positive for a certain duration and zero for the remaining duration of the AC signal.
Limitations of a Diode Rectifier
The main limitation of a diode rectifier is its inability to perform rectification in both directions. It can only rectify the positive half-cycle of an AC signal while blocking the negative half-cycle. Therefore, it can only produce a unidirectional DC output. If a bidirectional rectification is required, such as in a full-wave rectifier circuit, additional diodes or a different rectification technique, such as a bridge rectifier, is used.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a diode rectifier is a perfect example of a unilateral circuit because it can only perform rectification in one direction, allowing the flow of current in the forward-biased direction and blocking it in the reverse-biased direction. This limitation makes it unsuitable for applications that require bidirectional rectification.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
A diode rectifier cannot perform rectification in both directions is a...
Unilateral Circuit:
- In unilateral circuits, the property of the circuit changes with the change of direction of supply voltage or current.
- In other words, a unilateral circuit allows the current to flow only in one direction.
- A diode rectifier is the best example of a unilateral circuit because it does not perform the rectification in both directions of supply.
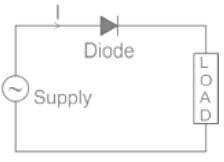
- The circuit consisting of Diodes like the rectifier circuit is an example of a Unilateral Circuit.
- In this circuit, the current can flow in one direction only because the diode allows the flow of current in one direction only.
Attention Electrical Engineering (EE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Electrical Engineering (EE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Electrical Engineering (EE).

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Similar Electrical Engineering (EE) Doubts
A diode rectifier cannot perform rectification in both directions is a perfect example of:a)Unilateral circuitb)Bilateral circuitc)Quadrilateral circuitd)Trilateral circuitCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A diode rectifier cannot perform rectification in both directions is a perfect example of:a)Unilateral circuitb)Bilateral circuitc)Quadrilateral circuitd)Trilateral circuitCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about A diode rectifier cannot perform rectification in both directions is a perfect example of:a)Unilateral circuitb)Bilateral circuitc)Quadrilateral circuitd)Trilateral circuitCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A diode rectifier cannot perform rectification in both directions is a perfect example of:a)Unilateral circuitb)Bilateral circuitc)Quadrilateral circuitd)Trilateral circuitCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
A diode rectifier cannot perform rectification in both directions is a perfect example of:a)Unilateral circuitb)Bilateral circuitc)Quadrilateral circuitd)Trilateral circuitCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about A diode rectifier cannot perform rectification in both directions is a perfect example of:a)Unilateral circuitb)Bilateral circuitc)Quadrilateral circuitd)Trilateral circuitCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A diode rectifier cannot perform rectification in both directions is a perfect example of:a)Unilateral circuitb)Bilateral circuitc)Quadrilateral circuitd)Trilateral circuitCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A diode rectifier cannot perform rectification in both directions is a perfect example of:a)Unilateral circuitb)Bilateral circuitc)Quadrilateral circuitd)Trilateral circuitCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A diode rectifier cannot perform rectification in both directions is a perfect example of:a)Unilateral circuitb)Bilateral circuitc)Quadrilateral circuitd)Trilateral circuitCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A diode rectifier cannot perform rectification in both directions is a perfect example of:a)Unilateral circuitb)Bilateral circuitc)Quadrilateral circuitd)Trilateral circuitCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A diode rectifier cannot perform rectification in both directions is a perfect example of:a)Unilateral circuitb)Bilateral circuitc)Quadrilateral circuitd)Trilateral circuitCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A diode rectifier cannot perform rectification in both directions is a perfect example of:a)Unilateral circuitb)Bilateral circuitc)Quadrilateral circuitd)Trilateral circuitCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A diode rectifier cannot perform rectification in both directions is a perfect example of:a)Unilateral circuitb)Bilateral circuitc)Quadrilateral circuitd)Trilateral circuitCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























