Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > The typical quiescent power dissipation of lo...
Start Learning for Free
The typical quiescent power dissipation of low-power CMOS units is
- a)1 mW
- b)0.5 mW
- c)2 nW
- d)50 nW
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
The typical quiescent power dissipation of low-power CMOS units isa)1 ...
- Complementary Metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) uses complementary & symmetrical pair of P-type & n-type MOSFETS.
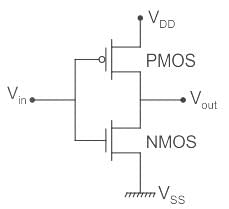
- The two important characteristics of CMOS devices are high noise immunity and low power dissipation.
- CMOS devices dissipate less power than NMOS devices because the CMOS dissipates power only when switching (“dynamic power), whereas N channel MOSFET dissipates power whenever the transistor is on because there is a current path from Vdd to Vss.
- In a CMOS, only one MOSFET is switched on at a time. Thus, there is no path from voltage source to ground so that a current can flow. Current flows in a MOSFET only during switching.
- Thus, compared to N-channel MOSFET has the advantage of lower drain current from the power supply, thereby causing less power dissipation.
- The typical quiescent power dissipation of low-power CMOS units is 2 nW
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The typical quiescent power dissipation of low-power CMOS units isa)1 ...
The typical quiescent power dissipation of low-power CMOS units is 2 nW.
Explanation:
CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) technology is widely used in low-power digital circuits due to its ability to minimize power consumption while providing high performance. The power dissipation of a CMOS unit refers to the amount of power it consumes when it is in a quiescent state, i.e., when there is no significant input activity or output load.
The quiescent power dissipation of a CMOS unit primarily depends on two factors: leakage currents and subthreshold leakage. Leakage currents occur due to the imperfect insulation between the different components of the CMOS device, causing a small amount of current to flow even when the device is not actively switching. Subthreshold leakage, on the other hand, refers to the small amount of current that flows through the channel of a transistor when it is in the off state.
Since low-power CMOS units are designed to minimize power consumption, they are optimized to reduce both leakage currents and subthreshold leakage. This optimization is achieved by using various techniques such as transistor sizing, threshold voltage scaling, and optimizing the device architecture.
The typical quiescent power dissipation of low-power CMOS units is 2 nW. This value is achieved by carefully balancing the trade-offs between power consumption and performance. By keeping the power dissipation at such a low level, low-power CMOS units are able to operate efficiently in battery-powered devices and other applications where power efficiency is crucial.
In summary, the typical quiescent power dissipation of low-power CMOS units is 2 nW. This low power consumption is achieved by minimizing leakage currents and subthreshold leakage through careful design and optimization techniques.
Explanation:
CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) technology is widely used in low-power digital circuits due to its ability to minimize power consumption while providing high performance. The power dissipation of a CMOS unit refers to the amount of power it consumes when it is in a quiescent state, i.e., when there is no significant input activity or output load.
The quiescent power dissipation of a CMOS unit primarily depends on two factors: leakage currents and subthreshold leakage. Leakage currents occur due to the imperfect insulation between the different components of the CMOS device, causing a small amount of current to flow even when the device is not actively switching. Subthreshold leakage, on the other hand, refers to the small amount of current that flows through the channel of a transistor when it is in the off state.
Since low-power CMOS units are designed to minimize power consumption, they are optimized to reduce both leakage currents and subthreshold leakage. This optimization is achieved by using various techniques such as transistor sizing, threshold voltage scaling, and optimizing the device architecture.
The typical quiescent power dissipation of low-power CMOS units is 2 nW. This value is achieved by carefully balancing the trade-offs between power consumption and performance. By keeping the power dissipation at such a low level, low-power CMOS units are able to operate efficiently in battery-powered devices and other applications where power efficiency is crucial.
In summary, the typical quiescent power dissipation of low-power CMOS units is 2 nW. This low power consumption is achieved by minimizing leakage currents and subthreshold leakage through careful design and optimization techniques.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Question Description
The typical quiescent power dissipation of low-power CMOS units isa)1 mWb)0.5 mWc)2 nWd)50 nWCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about The typical quiescent power dissipation of low-power CMOS units isa)1 mWb)0.5 mWc)2 nWd)50 nWCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The typical quiescent power dissipation of low-power CMOS units isa)1 mWb)0.5 mWc)2 nWd)50 nWCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
The typical quiescent power dissipation of low-power CMOS units isa)1 mWb)0.5 mWc)2 nWd)50 nWCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about The typical quiescent power dissipation of low-power CMOS units isa)1 mWb)0.5 mWc)2 nWd)50 nWCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The typical quiescent power dissipation of low-power CMOS units isa)1 mWb)0.5 mWc)2 nWd)50 nWCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The typical quiescent power dissipation of low-power CMOS units isa)1 mWb)0.5 mWc)2 nWd)50 nWCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The typical quiescent power dissipation of low-power CMOS units isa)1 mWb)0.5 mWc)2 nWd)50 nWCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The typical quiescent power dissipation of low-power CMOS units isa)1 mWb)0.5 mWc)2 nWd)50 nWCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The typical quiescent power dissipation of low-power CMOS units isa)1 mWb)0.5 mWc)2 nWd)50 nWCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The typical quiescent power dissipation of low-power CMOS units isa)1 mWb)0.5 mWc)2 nWd)50 nWCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The typical quiescent power dissipation of low-power CMOS units isa)1 mWb)0.5 mWc)2 nWd)50 nWCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















