Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > The main advantage of CMOS is itsa)High power...
Start Learning for Free
The main advantage of CMOS is its
- a)High power rating
- b)Small signal operation
- c)Switching capability
- d)Low power consumption
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
The main advantage of CMOS is itsa)High power ratingb)Small signal ope...
Introduction to CMOS Technology
CMOS, which stands for Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor, is widely used in digital circuits due to its unique characteristics. One of the most significant advantages of CMOS technology is its low power consumption.
Key Advantages of Low Power Consumption
- Energy Efficiency: CMOS circuits consume very little power when in a static state (not switching), which is crucial for battery-operated devices. This efficiency extends battery life significantly.
- Reduced Heat Generation: Low power consumption results in minimal heat generation. This is particularly important in high-density circuits where excessive heat can lead to reliability issues and damage.
- Scalability: As technology advances, CMOS technology can be scaled down to smaller geometries. This results in higher integration levels without a corresponding increase in power consumption, facilitating the development of compact and efficient devices.
- High Noise Margin: CMOS circuits operate with a high noise margin, which enhances the reliability of digital signals. This reduces the likelihood of errors, contributing to overall system efficiency.
Comparison with Other Technologies
- Bipolar Transistors: In contrast to CMOS, bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) consume more power in active states, making them less suitable for low-power applications.
- Static vs. Dynamic Power: While static power in CMOS is minimal, dynamic power can occur during switching. However, this power is still lower compared to other technologies, reinforcing the advantage of using CMOS.
Conclusion
In summary, the primary advantage of CMOS technology lies in its low power consumption, making it ideal for modern electronic devices that require energy efficiency, portability, and reliability. This characteristic has driven its widespread adoption in various applications, from microprocessors to mobile phones.
CMOS, which stands for Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor, is widely used in digital circuits due to its unique characteristics. One of the most significant advantages of CMOS technology is its low power consumption.
Key Advantages of Low Power Consumption
- Energy Efficiency: CMOS circuits consume very little power when in a static state (not switching), which is crucial for battery-operated devices. This efficiency extends battery life significantly.
- Reduced Heat Generation: Low power consumption results in minimal heat generation. This is particularly important in high-density circuits where excessive heat can lead to reliability issues and damage.
- Scalability: As technology advances, CMOS technology can be scaled down to smaller geometries. This results in higher integration levels without a corresponding increase in power consumption, facilitating the development of compact and efficient devices.
- High Noise Margin: CMOS circuits operate with a high noise margin, which enhances the reliability of digital signals. This reduces the likelihood of errors, contributing to overall system efficiency.
Comparison with Other Technologies
- Bipolar Transistors: In contrast to CMOS, bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) consume more power in active states, making them less suitable for low-power applications.
- Static vs. Dynamic Power: While static power in CMOS is minimal, dynamic power can occur during switching. However, this power is still lower compared to other technologies, reinforcing the advantage of using CMOS.
Conclusion
In summary, the primary advantage of CMOS technology lies in its low power consumption, making it ideal for modern electronic devices that require energy efficiency, portability, and reliability. This characteristic has driven its widespread adoption in various applications, from microprocessors to mobile phones.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The main advantage of CMOS is itsa)High power ratingb)Small signal ope...
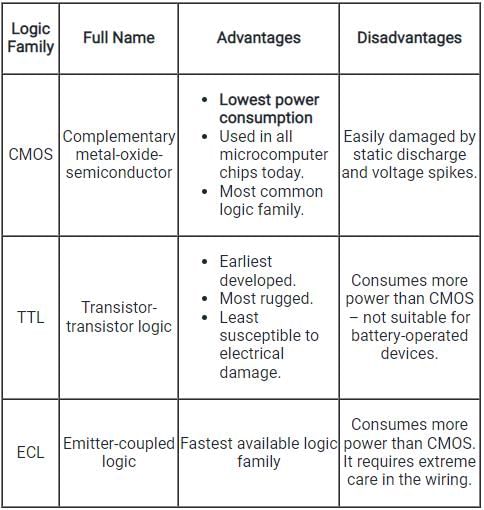
General comparison of three commonly available logic families is explained in the following table:


|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Question Description
The main advantage of CMOS is itsa)High power ratingb)Small signal operationc)Switching capabilityd)Low power consumptionCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about The main advantage of CMOS is itsa)High power ratingb)Small signal operationc)Switching capabilityd)Low power consumptionCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The main advantage of CMOS is itsa)High power ratingb)Small signal operationc)Switching capabilityd)Low power consumptionCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
The main advantage of CMOS is itsa)High power ratingb)Small signal operationc)Switching capabilityd)Low power consumptionCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about The main advantage of CMOS is itsa)High power ratingb)Small signal operationc)Switching capabilityd)Low power consumptionCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The main advantage of CMOS is itsa)High power ratingb)Small signal operationc)Switching capabilityd)Low power consumptionCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The main advantage of CMOS is itsa)High power ratingb)Small signal operationc)Switching capabilityd)Low power consumptionCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The main advantage of CMOS is itsa)High power ratingb)Small signal operationc)Switching capabilityd)Low power consumptionCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The main advantage of CMOS is itsa)High power ratingb)Small signal operationc)Switching capabilityd)Low power consumptionCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The main advantage of CMOS is itsa)High power ratingb)Small signal operationc)Switching capabilityd)Low power consumptionCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The main advantage of CMOS is itsa)High power ratingb)Small signal operationc)Switching capabilityd)Low power consumptionCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The main advantage of CMOS is itsa)High power ratingb)Small signal operationc)Switching capabilityd)Low power consumptionCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















