GMAT Exam > GMAT Questions > Directions: Each GMAT Data Sufficiency proble...
Start Learning for Free
Directions: Each GMAT Data Sufficiency problem consists of a question and two statements labeled (1) and (2), that provide data. Based on the data given plus your knowledge of mathematics and everyday facts, you must decide whether the data are sufficient for answering the question. The five answer choices are the same for every data sufficiency question.
What is the area of a triangle (with vertices at FCE) that is inscribed in a hexagon with vertices at ABCDE?
(1) The hexagon is regular and BE = 14.
(2) EC = 7√3.
(1) The hexagon is regular and BE = 14.
(2) EC = 7√3.
- a)Statement (1) ALONE is sufficient, but statement (2) alone is not sufficient to answer thequestion asked;
- b)Statement (2) ALONE is sufficient, but statement (1) alone is not sufficient to answer thequestion asked;
- c)BOTH statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER are sufficient to answer the question asked,but NEITHER statement ALONE is sufficient;
- d)EACH statement ALONE is sufficient to answer the question asked;
- e)Statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER are NOT sufficient to answer the question asked,and additional data are needed.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Directions: Each GMAT Data Sufficiency problem consists of a question ...
Statement 1:
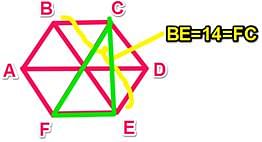

A regular hexagon can be divided into six equilateral triangles, each with a central angle measure of 60 degrees. Remember that we can inscribe a regular hexagon in a circle such that each vertex is a point on the circumference of the circle. Central Angle Theorem states that the central angle in a circle is always twice an inscribed angle when the point of the inscribed angle (in this case point C) is on the major arc. For this figure, this means angle FCE = 30. Since angle CFE = 60, we have a 30-60-90 triangle. If BE = 14, then FC = 14 as well. We’d now be able to solve for the height (CE) and base (FE) using the 30-60-90 side ratios. Since this is a data sufficiency question, we can stop here and conclude that statement 1 is sufficient.
However, if you actually had to calculate the area of triangle FCE, here is how you might proceed: The sides of a 30-60-90 are in the ratio 1 : √3 : 2 , so the sides of triangle FCE will have the following lengths: FE = 7, CE= 7√3 , FC=14.
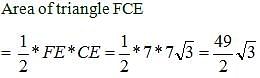
Statement 2:
If the hexagon is regular, we can calculate the area of triangle FCE using a process similar to the one illustrated above. However, statement 2 does not tell us that the hexagon is regular. If the hexagon is not regular, we can come up with different areas for triangle FCE, depending on what we assume. Statement 2 alone is not sufficient.
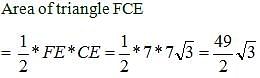
Statement 2:
If the hexagon is regular, we can calculate the area of triangle FCE using a process similar to the one illustrated above. However, statement 2 does not tell us that the hexagon is regular. If the hexagon is not regular, we can come up with different areas for triangle FCE, depending on what we assume. Statement 2 alone is not sufficient.
Most Upvoted Answer
Directions: Each GMAT Data Sufficiency problem consists of a question ...
Statement 1:


A regular hexagon can be divided into six equilateral triangles, each with a central angle measure of 60 degrees. Remember that we can inscribe a regular hexagon in a circle such that each vertex is a point on the circumference of the circle. Central Angle Theorem states that the central angle in a circle is always twice an inscribed angle when the point of the inscribed angle (in this case point C) is on the major arc. For this figure, this means angle FCE = 30. Since angle CFE = 60, we have a 30-60-90 triangle. If BE = 14, then FC = 14 as well. We’d now be able to solve for the height (CE) and base (FE) using the 30-60-90 side ratios. Since this is a data sufficiency question, we can stop here and conclude that statement 1 is sufficient.
However, if you actually had to calculate the area of triangle FCE, here is how you might proceed: The sides of a 30-60-90 are in the ratio 1 : √3 : 2 , so the sides of triangle FCE will have the following lengths: FE = 7, CE= 7√3 , FC=14.
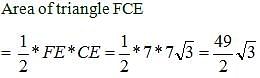
Statement 2:
If the hexagon is regular, we can calculate the area of triangle FCE using a process similar to the one illustrated above. However, statement 2 does not tell us that the hexagon is regular. If the hexagon is not regular, we can come up with different areas for triangle FCE, depending on what we assume. Statement 2 alone is not sufficient.
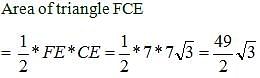
Statement 2:
If the hexagon is regular, we can calculate the area of triangle FCE using a process similar to the one illustrated above. However, statement 2 does not tell us that the hexagon is regular. If the hexagon is not regular, we can come up with different areas for triangle FCE, depending on what we assume. Statement 2 alone is not sufficient.
Attention GMAT Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed GMAT study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in GMAT.

|
Explore Courses for GMAT exam
|

|
Similar GMAT Doubts
Directions: Each GMAT Data Sufficiency problem consists of a question and two statements labeled (1) and (2), that provide data. Based on the data given plus your knowledge of mathematics and everyday facts, you must decide whether the data are sufficient for answering the question. The five answer choices are the same for every data sufficiency question.What is the area of a triangle (with vertices at FCE) that is inscribed in a hexagon with vertices at ABCDE?(1) The hexagon is regular and BE = 14.(2) EC = 7√3.a)Statement (1) ALONE is sufficient, but statement (2) alone is not sufficient to answer thequestion asked;b)Statement (2) ALONE is sufficient, but statement (1) alone is not sufficient to answer thequestion asked;c)BOTH statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER are sufficient to answer the question asked,but NEITHER statement ALONE is sufficient;d)EACH statement ALONE is sufficient to answer the question asked;e)Statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER are NOT sufficient to answer the question asked,and additional data are needed.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Directions: Each GMAT Data Sufficiency problem consists of a question and two statements labeled (1) and (2), that provide data. Based on the data given plus your knowledge of mathematics and everyday facts, you must decide whether the data are sufficient for answering the question. The five answer choices are the same for every data sufficiency question.What is the area of a triangle (with vertices at FCE) that is inscribed in a hexagon with vertices at ABCDE?(1) The hexagon is regular and BE = 14.(2) EC = 7√3.a)Statement (1) ALONE is sufficient, but statement (2) alone is not sufficient to answer thequestion asked;b)Statement (2) ALONE is sufficient, but statement (1) alone is not sufficient to answer thequestion asked;c)BOTH statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER are sufficient to answer the question asked,but NEITHER statement ALONE is sufficient;d)EACH statement ALONE is sufficient to answer the question asked;e)Statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER are NOT sufficient to answer the question asked,and additional data are needed.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for GMAT 2024 is part of GMAT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the GMAT exam syllabus. Information about Directions: Each GMAT Data Sufficiency problem consists of a question and two statements labeled (1) and (2), that provide data. Based on the data given plus your knowledge of mathematics and everyday facts, you must decide whether the data are sufficient for answering the question. The five answer choices are the same for every data sufficiency question.What is the area of a triangle (with vertices at FCE) that is inscribed in a hexagon with vertices at ABCDE?(1) The hexagon is regular and BE = 14.(2) EC = 7√3.a)Statement (1) ALONE is sufficient, but statement (2) alone is not sufficient to answer thequestion asked;b)Statement (2) ALONE is sufficient, but statement (1) alone is not sufficient to answer thequestion asked;c)BOTH statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER are sufficient to answer the question asked,but NEITHER statement ALONE is sufficient;d)EACH statement ALONE is sufficient to answer the question asked;e)Statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER are NOT sufficient to answer the question asked,and additional data are needed.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for GMAT 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Directions: Each GMAT Data Sufficiency problem consists of a question and two statements labeled (1) and (2), that provide data. Based on the data given plus your knowledge of mathematics and everyday facts, you must decide whether the data are sufficient for answering the question. The five answer choices are the same for every data sufficiency question.What is the area of a triangle (with vertices at FCE) that is inscribed in a hexagon with vertices at ABCDE?(1) The hexagon is regular and BE = 14.(2) EC = 7√3.a)Statement (1) ALONE is sufficient, but statement (2) alone is not sufficient to answer thequestion asked;b)Statement (2) ALONE is sufficient, but statement (1) alone is not sufficient to answer thequestion asked;c)BOTH statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER are sufficient to answer the question asked,but NEITHER statement ALONE is sufficient;d)EACH statement ALONE is sufficient to answer the question asked;e)Statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER are NOT sufficient to answer the question asked,and additional data are needed.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Directions: Each GMAT Data Sufficiency problem consists of a question and two statements labeled (1) and (2), that provide data. Based on the data given plus your knowledge of mathematics and everyday facts, you must decide whether the data are sufficient for answering the question. The five answer choices are the same for every data sufficiency question.What is the area of a triangle (with vertices at FCE) that is inscribed in a hexagon with vertices at ABCDE?(1) The hexagon is regular and BE = 14.(2) EC = 7√3.a)Statement (1) ALONE is sufficient, but statement (2) alone is not sufficient to answer thequestion asked;b)Statement (2) ALONE is sufficient, but statement (1) alone is not sufficient to answer thequestion asked;c)BOTH statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER are sufficient to answer the question asked,but NEITHER statement ALONE is sufficient;d)EACH statement ALONE is sufficient to answer the question asked;e)Statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER are NOT sufficient to answer the question asked,and additional data are needed.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for GMAT 2024 is part of GMAT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the GMAT exam syllabus. Information about Directions: Each GMAT Data Sufficiency problem consists of a question and two statements labeled (1) and (2), that provide data. Based on the data given plus your knowledge of mathematics and everyday facts, you must decide whether the data are sufficient for answering the question. The five answer choices are the same for every data sufficiency question.What is the area of a triangle (with vertices at FCE) that is inscribed in a hexagon with vertices at ABCDE?(1) The hexagon is regular and BE = 14.(2) EC = 7√3.a)Statement (1) ALONE is sufficient, but statement (2) alone is not sufficient to answer thequestion asked;b)Statement (2) ALONE is sufficient, but statement (1) alone is not sufficient to answer thequestion asked;c)BOTH statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER are sufficient to answer the question asked,but NEITHER statement ALONE is sufficient;d)EACH statement ALONE is sufficient to answer the question asked;e)Statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER are NOT sufficient to answer the question asked,and additional data are needed.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for GMAT 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Directions: Each GMAT Data Sufficiency problem consists of a question and two statements labeled (1) and (2), that provide data. Based on the data given plus your knowledge of mathematics and everyday facts, you must decide whether the data are sufficient for answering the question. The five answer choices are the same for every data sufficiency question.What is the area of a triangle (with vertices at FCE) that is inscribed in a hexagon with vertices at ABCDE?(1) The hexagon is regular and BE = 14.(2) EC = 7√3.a)Statement (1) ALONE is sufficient, but statement (2) alone is not sufficient to answer thequestion asked;b)Statement (2) ALONE is sufficient, but statement (1) alone is not sufficient to answer thequestion asked;c)BOTH statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER are sufficient to answer the question asked,but NEITHER statement ALONE is sufficient;d)EACH statement ALONE is sufficient to answer the question asked;e)Statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER are NOT sufficient to answer the question asked,and additional data are needed.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Directions: Each GMAT Data Sufficiency problem consists of a question and two statements labeled (1) and (2), that provide data. Based on the data given plus your knowledge of mathematics and everyday facts, you must decide whether the data are sufficient for answering the question. The five answer choices are the same for every data sufficiency question.What is the area of a triangle (with vertices at FCE) that is inscribed in a hexagon with vertices at ABCDE?(1) The hexagon is regular and BE = 14.(2) EC = 7√3.a)Statement (1) ALONE is sufficient, but statement (2) alone is not sufficient to answer thequestion asked;b)Statement (2) ALONE is sufficient, but statement (1) alone is not sufficient to answer thequestion asked;c)BOTH statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER are sufficient to answer the question asked,but NEITHER statement ALONE is sufficient;d)EACH statement ALONE is sufficient to answer the question asked;e)Statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER are NOT sufficient to answer the question asked,and additional data are needed.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for GMAT.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for GMAT Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Directions: Each GMAT Data Sufficiency problem consists of a question and two statements labeled (1) and (2), that provide data. Based on the data given plus your knowledge of mathematics and everyday facts, you must decide whether the data are sufficient for answering the question. The five answer choices are the same for every data sufficiency question.What is the area of a triangle (with vertices at FCE) that is inscribed in a hexagon with vertices at ABCDE?(1) The hexagon is regular and BE = 14.(2) EC = 7√3.a)Statement (1) ALONE is sufficient, but statement (2) alone is not sufficient to answer thequestion asked;b)Statement (2) ALONE is sufficient, but statement (1) alone is not sufficient to answer thequestion asked;c)BOTH statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER are sufficient to answer the question asked,but NEITHER statement ALONE is sufficient;d)EACH statement ALONE is sufficient to answer the question asked;e)Statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER are NOT sufficient to answer the question asked,and additional data are needed.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Directions: Each GMAT Data Sufficiency problem consists of a question and two statements labeled (1) and (2), that provide data. Based on the data given plus your knowledge of mathematics and everyday facts, you must decide whether the data are sufficient for answering the question. The five answer choices are the same for every data sufficiency question.What is the area of a triangle (with vertices at FCE) that is inscribed in a hexagon with vertices at ABCDE?(1) The hexagon is regular and BE = 14.(2) EC = 7√3.a)Statement (1) ALONE is sufficient, but statement (2) alone is not sufficient to answer thequestion asked;b)Statement (2) ALONE is sufficient, but statement (1) alone is not sufficient to answer thequestion asked;c)BOTH statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER are sufficient to answer the question asked,but NEITHER statement ALONE is sufficient;d)EACH statement ALONE is sufficient to answer the question asked;e)Statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER are NOT sufficient to answer the question asked,and additional data are needed.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Directions: Each GMAT Data Sufficiency problem consists of a question and two statements labeled (1) and (2), that provide data. Based on the data given plus your knowledge of mathematics and everyday facts, you must decide whether the data are sufficient for answering the question. The five answer choices are the same for every data sufficiency question.What is the area of a triangle (with vertices at FCE) that is inscribed in a hexagon with vertices at ABCDE?(1) The hexagon is regular and BE = 14.(2) EC = 7√3.a)Statement (1) ALONE is sufficient, but statement (2) alone is not sufficient to answer thequestion asked;b)Statement (2) ALONE is sufficient, but statement (1) alone is not sufficient to answer thequestion asked;c)BOTH statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER are sufficient to answer the question asked,but NEITHER statement ALONE is sufficient;d)EACH statement ALONE is sufficient to answer the question asked;e)Statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER are NOT sufficient to answer the question asked,and additional data are needed.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Directions: Each GMAT Data Sufficiency problem consists of a question and two statements labeled (1) and (2), that provide data. Based on the data given plus your knowledge of mathematics and everyday facts, you must decide whether the data are sufficient for answering the question. The five answer choices are the same for every data sufficiency question.What is the area of a triangle (with vertices at FCE) that is inscribed in a hexagon with vertices at ABCDE?(1) The hexagon is regular and BE = 14.(2) EC = 7√3.a)Statement (1) ALONE is sufficient, but statement (2) alone is not sufficient to answer thequestion asked;b)Statement (2) ALONE is sufficient, but statement (1) alone is not sufficient to answer thequestion asked;c)BOTH statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER are sufficient to answer the question asked,but NEITHER statement ALONE is sufficient;d)EACH statement ALONE is sufficient to answer the question asked;e)Statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER are NOT sufficient to answer the question asked,and additional data are needed.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Directions: Each GMAT Data Sufficiency problem consists of a question and two statements labeled (1) and (2), that provide data. Based on the data given plus your knowledge of mathematics and everyday facts, you must decide whether the data are sufficient for answering the question. The five answer choices are the same for every data sufficiency question.What is the area of a triangle (with vertices at FCE) that is inscribed in a hexagon with vertices at ABCDE?(1) The hexagon is regular and BE = 14.(2) EC = 7√3.a)Statement (1) ALONE is sufficient, but statement (2) alone is not sufficient to answer thequestion asked;b)Statement (2) ALONE is sufficient, but statement (1) alone is not sufficient to answer thequestion asked;c)BOTH statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER are sufficient to answer the question asked,but NEITHER statement ALONE is sufficient;d)EACH statement ALONE is sufficient to answer the question asked;e)Statements (1) and (2) TOGETHER are NOT sufficient to answer the question asked,and additional data are needed.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice GMAT tests.

|
Explore Courses for GMAT exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























