Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam > Electrical Engineering (EE) Questions > For a fully transposed transmission linea)pos...
Start Learning for Free
For a fully transposed transmission line
- a)positive, negative and zero sequence impedances are equal.
- b)positive and negative sequence impedances are equal.
- c)zero and positive sequence impedances are equal.
- d)negative and zero sequence impedances are equal
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
For a fully transposed transmission linea)positive, negative and zero ...
Explanation:
A fully transposed transmission line is a line where the positive, negative, and zero-sequence impedances are equal. Let's understand this concept in detail.
1. Positive Sequence Impedance:
The positive sequence impedance represents the impedance of the transmission line when all three phases have the same magnitude and rotate in the same direction. It is denoted by Z1.
2. Negative Sequence Impedance:
The negative sequence impedance represents the impedance of the transmission line when the three phases have the same magnitude but rotate in the opposite direction. It is denoted by Z2.
3. Zero Sequence Impedance:
The zero sequence impedance represents the impedance of the transmission line when all three phases have zero magnitude. It is denoted by Z0.
Equality of Positive and Negative Sequence Impedances (Option B):
In a fully transposed transmission line, the positive and negative sequence impedances are equal. This is because the line is designed to have symmetrical characteristics, and the impedance seen by the positive and negative sequence currents is the same. Therefore, option B is correct.
Equality of Zero and Positive Sequence Impedances (Option C):
In a fully transposed transmission line, the zero and positive sequence impedances are not necessarily equal. The zero sequence impedance depends on the arrangement of conductors and ground, while the positive sequence impedance represents the impedance of the line under normal operating conditions. Therefore, option C is incorrect.
Equality of Negative and Zero Sequence Impedances (Option D):
In a fully transposed transmission line, the negative and zero sequence impedances are not necessarily equal. The negative sequence impedance represents the impedance of the line when the three phases rotate in the opposite direction, while the zero sequence impedance represents the impedance when all three phases have zero magnitude. Therefore, option D is incorrect.
To summarize, in a fully transposed transmission line, the positive and negative sequence impedances are equal, while the zero sequence impedance can be different.
A fully transposed transmission line is a line where the positive, negative, and zero-sequence impedances are equal. Let's understand this concept in detail.
1. Positive Sequence Impedance:
The positive sequence impedance represents the impedance of the transmission line when all three phases have the same magnitude and rotate in the same direction. It is denoted by Z1.
2. Negative Sequence Impedance:
The negative sequence impedance represents the impedance of the transmission line when the three phases have the same magnitude but rotate in the opposite direction. It is denoted by Z2.
3. Zero Sequence Impedance:
The zero sequence impedance represents the impedance of the transmission line when all three phases have zero magnitude. It is denoted by Z0.
Equality of Positive and Negative Sequence Impedances (Option B):
In a fully transposed transmission line, the positive and negative sequence impedances are equal. This is because the line is designed to have symmetrical characteristics, and the impedance seen by the positive and negative sequence currents is the same. Therefore, option B is correct.
Equality of Zero and Positive Sequence Impedances (Option C):
In a fully transposed transmission line, the zero and positive sequence impedances are not necessarily equal. The zero sequence impedance depends on the arrangement of conductors and ground, while the positive sequence impedance represents the impedance of the line under normal operating conditions. Therefore, option C is incorrect.
Equality of Negative and Zero Sequence Impedances (Option D):
In a fully transposed transmission line, the negative and zero sequence impedances are not necessarily equal. The negative sequence impedance represents the impedance of the line when the three phases rotate in the opposite direction, while the zero sequence impedance represents the impedance when all three phases have zero magnitude. Therefore, option D is incorrect.
To summarize, in a fully transposed transmission line, the positive and negative sequence impedances are equal, while the zero sequence impedance can be different.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
For a fully transposed transmission linea)positive, negative and zero ...
Purpose of Transposition:
- Transmission lines are transposed to prevent interference with neighbouring telephone lines.
- The transposition arrangement of high voltage lines helps to reduce the system power loss.
- We have developed transposition system for Single circuit tower using same tension tower with reduced deviation angle.
- Transposition arrangement of power line helps to reduce the effect of inductive coupling.
- It is proved more economical Solution, in comparison of the conventional transposition system.
Important:
Transposition arrangement
The transposition arrangement of the conductor can simply show in the following the figure. The conductor in Position 1, Position 2 and Position 3 changes in a specific arrangement to reduce the effect of capacitance and the electrostatic unbalanced voltages.
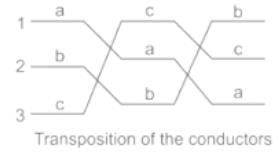

Z1 = Z2 = ZS - Zm
Zo = ZS + 2Zm
Where,
Z1 = positive sequence impedance
Z2 = positive sequence impedance
Zm = mutual impedance
ZS = self impedance
Positive and negative sequence impedances are equal.
Zo = ZS + 2Zm
Where,
Z1 = positive sequence impedance
Z2 = positive sequence impedance
Zm = mutual impedance
ZS = self impedance
Positive and negative sequence impedances are equal.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Similar Electrical Engineering (EE) Doubts
Question Description
For a fully transposed transmission linea)positive, negative and zero sequence impedances are equal.b)positive and negative sequence impedances are equal.c)zero and positive sequence impedances are equal.d)negative and zero sequence impedances are equalCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about For a fully transposed transmission linea)positive, negative and zero sequence impedances are equal.b)positive and negative sequence impedances are equal.c)zero and positive sequence impedances are equal.d)negative and zero sequence impedances are equalCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for For a fully transposed transmission linea)positive, negative and zero sequence impedances are equal.b)positive and negative sequence impedances are equal.c)zero and positive sequence impedances are equal.d)negative and zero sequence impedances are equalCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
For a fully transposed transmission linea)positive, negative and zero sequence impedances are equal.b)positive and negative sequence impedances are equal.c)zero and positive sequence impedances are equal.d)negative and zero sequence impedances are equalCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 is part of Electrical Engineering (EE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Electrical Engineering (EE) exam syllabus. Information about For a fully transposed transmission linea)positive, negative and zero sequence impedances are equal.b)positive and negative sequence impedances are equal.c)zero and positive sequence impedances are equal.d)negative and zero sequence impedances are equalCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Electrical Engineering (EE) 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for For a fully transposed transmission linea)positive, negative and zero sequence impedances are equal.b)positive and negative sequence impedances are equal.c)zero and positive sequence impedances are equal.d)negative and zero sequence impedances are equalCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for For a fully transposed transmission linea)positive, negative and zero sequence impedances are equal.b)positive and negative sequence impedances are equal.c)zero and positive sequence impedances are equal.d)negative and zero sequence impedances are equalCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Electrical Engineering (EE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Electrical Engineering (EE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of For a fully transposed transmission linea)positive, negative and zero sequence impedances are equal.b)positive and negative sequence impedances are equal.c)zero and positive sequence impedances are equal.d)negative and zero sequence impedances are equalCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
For a fully transposed transmission linea)positive, negative and zero sequence impedances are equal.b)positive and negative sequence impedances are equal.c)zero and positive sequence impedances are equal.d)negative and zero sequence impedances are equalCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for For a fully transposed transmission linea)positive, negative and zero sequence impedances are equal.b)positive and negative sequence impedances are equal.c)zero and positive sequence impedances are equal.d)negative and zero sequence impedances are equalCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of For a fully transposed transmission linea)positive, negative and zero sequence impedances are equal.b)positive and negative sequence impedances are equal.c)zero and positive sequence impedances are equal.d)negative and zero sequence impedances are equalCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice For a fully transposed transmission linea)positive, negative and zero sequence impedances are equal.b)positive and negative sequence impedances are equal.c)zero and positive sequence impedances are equal.d)negative and zero sequence impedances are equalCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Electrical Engineering (EE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Electrical Engineering (EE) exam
|

|
Signup to solve all Doubts
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.





















